The Greek alphabet, a cornerstone of Western civilization, has a rich history dating back to ancient Greece. It has been the foundation for many modern alphabets, including the Latin alphabet, which is used in English today. The Greek alphabet consists of 24 letters, each with its own unique symbol and phonetic value. These letters have been used not only for writing the Greek language but also for mathematical, scientific, and religious purposes.
As we explore the Greek alphabet in the English language, we'll uncover the fascinating journey of these ancient symbols from their origins to their present-day applications. This guide will cover everything from the historical development of the Greek alphabet to its role in modern science and technology. Whether you're a language enthusiast, a student, or simply curious about the Greek alphabet's impact on the English language, this article will provide you with a wealth of information.
History of the Greek Alphabet
The Greek alphabet has a long and storied history, dating back to the 8th century BCE. It evolved from the Phoenician alphabet, a writing system used by the Phoenician civilization, which was one of the earliest known alphabets. The Greeks adapted the Phoenician alphabet to suit their language, adding vowels and creating a more versatile system.
Initially, the Greek alphabet was written in various local variants, but by the 4th century BCE, the Ionic alphabet from the region of Ionia became the standard form. This standardized version consisted of 24 letters, which are still used today. The introduction of vowels was a significant innovation, making the Greek alphabet one of the first true alphabets, where each symbol represented a single sound.
The Greek alphabet played a crucial role in the spread of Greek culture and ideas during the Hellenistic period. It was used to write the works of famous philosophers, historians, and playwrights, contributing to the preservation and dissemination of Greek literature and knowledge. Over time, the Greek alphabet influenced the development of other alphabets, including the Latin alphabet, which forms the basis of the English language.
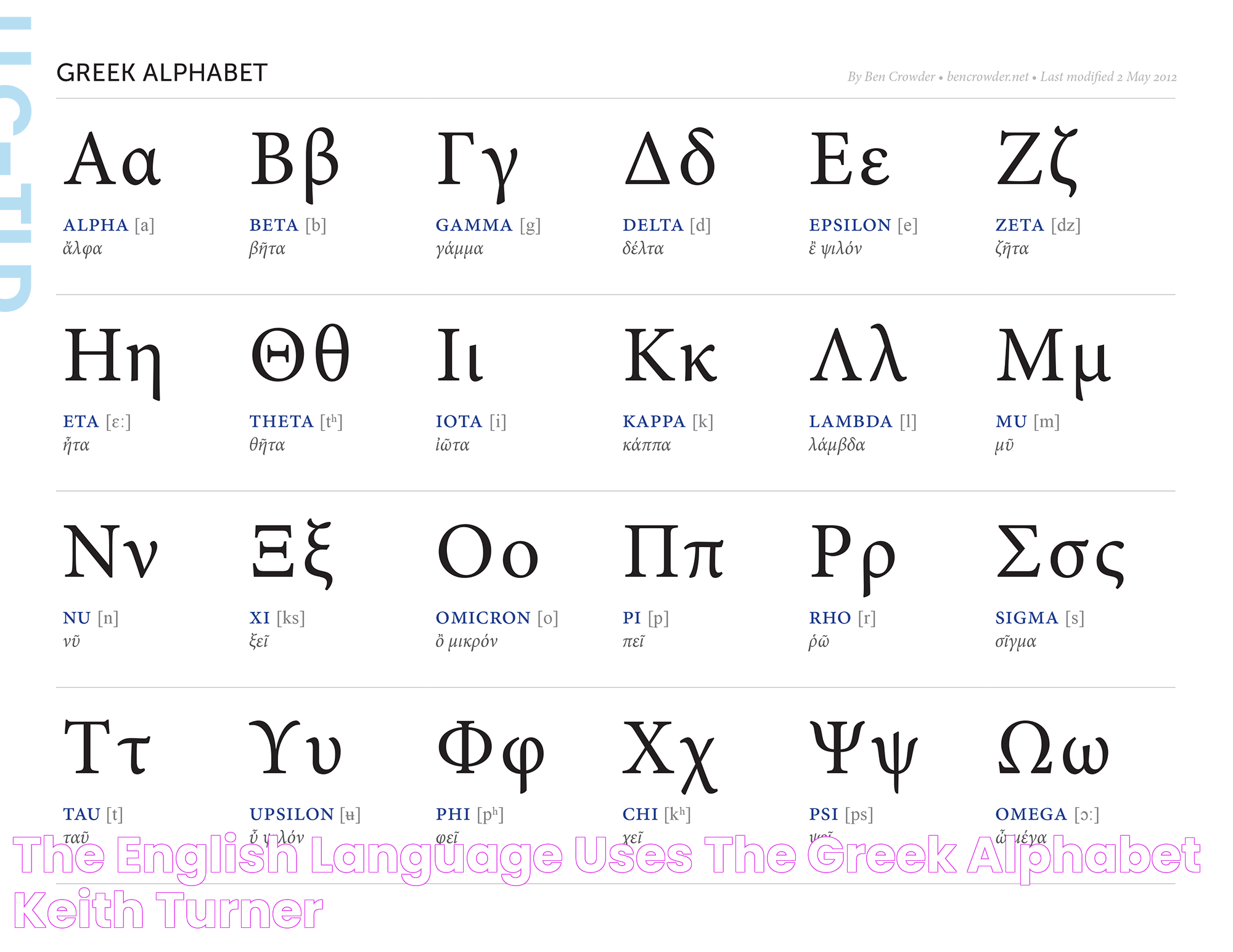
What are the Greek Alphabet Symbols?
The Greek alphabet consists of 24 letters, each with an uppercase and lowercase form. Here is a list of the Greek alphabet symbols along with their English equivalents:
- Α α - Alpha
- Β β - Beta
- Γ γ - Gamma
- Δ δ - Delta
- Ε ε - Epsilon
- Ζ ζ - Zeta
- Η η - Eta
- Θ θ - Theta
- Ι ι - Iota
- Κ κ - Kappa
- Λ λ - Lambda
- Μ μ - Mu
- Ν ν - Nu
- Ξ ξ - Xi
- Ο ο - Omicron
- Π π - Pi
- Ρ ρ - Rho
- Σ σ/ς - Sigma
- Τ τ - Tau
- Υ υ - Upsilon
- Φ φ - Phi
- Χ χ - Chi
- Ψ ψ - Psi
- Ω ω - Omega
Each letter has a distinct pronunciation and role within both the Greek language and various other fields such as mathematics and science. The Greek alphabet is not only a linguistic tool but also a symbol of cultural and historical significance.
How is the Greek Alphabet Used in Mathematics?
The Greek alphabet is extensively used in mathematics, serving as symbols for constants, variables, and functions. Here are some common uses of Greek letters in mathematics:
Read also: Direct Vs Indirect Hernia A Comprehensive Guide
- Alpha (α): Often used to represent angles in geometry.
- Beta (β): Used for angles and coefficients in equations.
- Gamma (γ): Represents the gamma function and angles.
- Delta (Δ, δ): Used to denote change or difference in calculus (Δ) and angles (δ).
- Epsilon (ε): Represents small quantities in calculus and limits.
- Pi (π): The most famous Greek letter, representing the mathematical constant approximately equal to 3.14159.
- Sigma (Σ, σ): Used for summation (Σ) and standard deviation (σ).
- Theta (θ): Commonly used to represent angles.
- Lambda (λ): Represents eigenvalues in linear algebra.
- Omega (Ω, ω): Used for ohms in physics (Ω) and angular velocity (ω).
The use of Greek letters in mathematics is a testament to the enduring influence of the Greek alphabet. These symbols provide a universal language for mathematicians and scientists around the world, facilitating communication and understanding across different fields and languages.
The Greek Alphabet in Science and Technology
The Greek alphabet is deeply ingrained in the lexicon of science and technology. Its symbols are ubiquitous in fields such as physics, chemistry, and engineering. Here are a few examples of how Greek letters are used in these disciplines:
Physics: Greek letters are used to denote various physical quantities and constants. For example, alpha (α) represents the fine-structure constant, beta (β) is used for beta particles, and theta (θ) denotes angles in rotational motion.
Chemistry: Greek letters are employed in chemical equations and formulas. For instance, delta (Δ) denotes a change in enthalpy or Gibbs free energy, while lambda (λ) is used for wavelength.
Engineering: Greek letters are used in various engineering disciplines to represent coefficients, angles, and other parameters. For example, phi (φ) is used in electrical engineering to represent magnetic flux, and tau (τ) is used in mechanical engineering for torque.
The adoption of Greek letters in science and technology underscores their versatility and universality. These symbols transcend language barriers, providing a common framework for researchers and practitioners worldwide.
Greek Alphabet in Modern English
The Greek alphabet has left an indelible mark on the English language, influencing both vocabulary and writing systems. Many English words have Greek roots, particularly in fields such as medicine, science, and philosophy. For example, the words biology, philosophy, and psychology all have Greek origins.
In addition to vocabulary, the Greek alphabet has also influenced the development of writing systems. The Latin alphabet, which is the basis for the English alphabet, was derived from the Greek alphabet. This connection highlights the historical and cultural ties between Greek and English.
The Greek alphabet continues to be relevant in modern English, serving as a source of inspiration for new words and concepts. Its influence can be seen in the naming of scientific phenomena, technological innovations, and even popular culture, where Greek letters are often used as symbols or motifs.
What is the Significance of the Greek Alphabet in Literature?
The Greek alphabet holds a special place in the world of literature. Many of the foundational texts of Western literature were written in Greek, including the works of Homer, Sophocles, and Euripides. These texts have been translated into numerous languages, including English, allowing their rich stories and themes to resonate with audiences worldwide.
Greek mythology, which is deeply intertwined with the Greek alphabet, has also had a significant impact on literature. Mythological figures and themes have inspired countless works of fiction, poetry, and drama. The stories of gods, heroes, and mythical creatures continue to captivate readers and writers alike.
The Greek alphabet's legacy in literature extends beyond ancient texts. Contemporary authors often draw upon Greek mythology and literature for inspiration, creating new works that pay homage to these timeless stories. The enduring appeal of the Greek alphabet in literature is a testament to its cultural and historical significance.
How to Write the Greek Alphabet in English?
Writing the Greek alphabet in English involves transliterating the Greek letters into their English equivalents. This process allows readers to pronounce Greek words using the English alphabet. Here is a transliteration guide for the Greek alphabet:
- Α α - A a
- Β β - B b
- Γ γ - G g
- Δ δ - D d
- Ε ε - E e
- Ζ ζ - Z z
- Η η - H h
- Θ θ - Th th
- Ι ι - I i
- Κ κ - K k
- Λ λ - L l
- Μ μ - M m
- Ν ν - N n
- Ξ ξ - X x
- Ο ο - O o
- Π π - P p
- Ρ ρ - R r
- Σ σ/ς - S s
- Τ τ - T t
- Υ υ - U u
- Φ φ - Ph ph
- Χ χ - Ch ch
- Ψ ψ - Ps ps
- Ω ω - O o
This transliteration guide can help English speakers read and pronounce Greek words with greater accuracy. Understanding the transliteration of the Greek alphabet is especially useful for students of the Greek language or those interested in Greek culture and history.
Greek Alphabet in Religious Texts
The Greek alphabet has played a pivotal role in the dissemination of religious texts, particularly in Christianity. The New Testament of the Christian Bible was originally written in Greek, known as Koine Greek, which was the common language of the Eastern Mediterranean during the early centuries of Christianity.
Many early Christian theologians and scholars used the Greek alphabet to write theological treatises, commentaries, and hymns. The Greek alphabet provided a means for preserving and sharing religious teachings, contributing to the spread of Christianity throughout the ancient world.
In addition to Christianity, the Greek alphabet has been used in the study and translation of other religious texts. Its role in religious scholarship highlights its significance as a tool for communication and cultural exchange.
The Role of the Greek Alphabet in Education
The Greek alphabet has long been a subject of study in educational institutions, particularly in the fields of classics and linguistics. Learning the Greek alphabet is often a foundational step for students studying ancient Greek language and literature.
In addition to language studies, the Greek alphabet is taught in mathematics and science courses due to its widespread use as symbols for various concepts and quantities. Familiarity with Greek letters is essential for students pursuing careers in these fields.
The study of the Greek alphabet in education extends beyond its practical applications. It provides students with a deeper understanding of the historical and cultural influences that have shaped modern languages and societies. By studying the Greek alphabet, students gain valuable insights into the interconnectedness of language, culture, and history.
What are the Differences Between Greek and English Alphabets?
The Greek and English alphabets differ in several key ways, reflecting their unique linguistic and cultural contexts. Here are some of the main differences:
- Number of Letters: The Greek alphabet consists of 24 letters, while the English alphabet has 26 letters.
- Vowels and Consonants: The Greek alphabet includes both vowels and consonants, similar to the English alphabet. However, the specific letters and their pronunciations differ between the two alphabets.
- Letter Forms: The Greek alphabet has distinct uppercase and lowercase forms, similar to the English alphabet. However, the shapes of the letters are different, reflecting the unique writing styles of each language.
- Pronunciation: The pronunciation of Greek letters differs from their English counterparts. For example, the Greek letter Beta (Β, β) is pronounced as "v" in modern Greek, while the English letter "B" is pronounced as "b."
- Historical Development: The Greek alphabet has a longer history, dating back to ancient Greece, while the English alphabet developed from the Latin alphabet, which was influenced by the Greek alphabet.
Despite these differences, the Greek and English alphabets share a common heritage, highlighting the interconnectedness of languages and cultures throughout history.
How Has the Greek Alphabet Evolved Over Time?
The evolution of the Greek alphabet is a testament to its adaptability and resilience. Since its inception, the Greek alphabet has undergone several transformations, influenced by historical, cultural, and linguistic changes.
In its early stages, the Greek alphabet borrowed heavily from the Phoenician alphabet. Over time, the Greeks introduced vowels and refined the letterforms, creating a more versatile and expressive writing system. This innovation set the stage for the development of other alphabets, including the Latin alphabet.
The Greek alphabet continued to evolve through the Hellenistic period, as the spread of Greek culture and language led to the adoption of Greek letters in various regions. The Byzantine Empire further influenced the Greek alphabet, standardizing certain letterforms and introducing new writing styles.
In modern times, the Greek alphabet has remained relatively stable, with minor changes to letterforms and pronunciation. Today, it continues to be used in Greece and Cyprus, as well as in academic and scientific contexts worldwide. The enduring legacy of the Greek alphabet reflects its historical significance and its ongoing relevance in contemporary society.
Greek Alphabet in Pop Culture
The Greek alphabet has permeated popular culture, appearing in various forms of media, entertainment, and branding. Its symbols are often used to convey a sense of mystery, sophistication, or historical depth.
In literature and film, the Greek alphabet is frequently employed in titles, character names, and plot elements. For example, the popular book and film series "Percy Jackson & the Olympians" draws heavily on Greek mythology and uses Greek symbols to enhance its storytelling.
In branding and advertising, Greek letters are often used to create memorable logos and product names. Companies may choose Greek letters to evoke qualities such as intelligence, innovation, or tradition. This use of Greek symbols in marketing highlights their cultural and aesthetic appeal.
The Greek alphabet's presence in pop culture reflects its enduring influence and versatility. Whether through literature, film, or branding, Greek symbols continue to captivate and inspire audiences around the world.
The Greek Alphabet in Linguistics
The Greek alphabet has played a significant role in the field of linguistics, providing valuable insights into the development and structure of languages. Linguists study the Greek alphabet to understand its phonetic, morphological, and syntactic properties.
The Greek alphabet serves as a key reference point for comparative studies of alphabets and writing systems. By examining the similarities and differences between Greek and other alphabets, linguists can trace the historical and cultural connections between languages.
In addition to its use in linguistic research, the Greek alphabet is also studied for its role in the transcription and translation of ancient texts. Linguists use the Greek alphabet to reconstruct and interpret historical languages, shedding light on the linguistic practices of past civilizations.
The study of the Greek alphabet in linguistics underscores its importance as a linguistic and cultural artifact. Its enduring legacy continues to inform our understanding of language and communication.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How many letters are in the Greek alphabet?
The Greek alphabet consists of 24 letters, each with an uppercase and lowercase form.
2. Why is the Greek alphabet important in mathematics?
The Greek alphabet is used in mathematics to represent constants, variables, and functions. Its symbols provide a universal language for mathematicians, facilitating communication and understanding across different fields and languages.
3. How is the Greek alphabet used in science and technology?
The Greek alphabet is used in science and technology as symbols for various physical quantities, constants, and parameters. Its widespread use reflects its versatility and universality in scientific and technological contexts.
4. What is the historical significance of the Greek alphabet?
The Greek alphabet has a rich history, dating back to ancient Greece. It played a crucial role in the spread of Greek culture and ideas, influencing the development of other alphabets, including the Latin alphabet, which forms the basis of the English language.
5. How has the Greek alphabet influenced the English language?
The Greek alphabet has influenced the English language through its impact on vocabulary, writing systems, and cultural expressions. Many English words have Greek roots, and the Latin alphabet, which is the basis for the English alphabet, was derived from the Greek alphabet.
6. How can I learn to write the Greek alphabet in English?
To write the Greek alphabet in English, you can use a transliteration guide that converts Greek letters into their English equivalents. This process allows you to pronounce Greek words using the English alphabet.
Conclusion
The Greek alphabet in the English language is a fascinating subject, offering insights into the historical, cultural, and linguistic connections between two of the world's most influential alphabets. From its origins in ancient Greece to its modern applications in science, mathematics, and popular culture, the Greek alphabet continues to captivate and inspire.
By understanding the Greek alphabet and its impact on the English language, we gain a deeper appreciation for the interconnectedness of languages and cultures throughout history. The Greek alphabet's legacy is a testament to its enduring relevance and significance in our world today.
As we continue to explore and study the Greek alphabet, we uncover new layers of meaning and significance, enriching our understanding of language, history, and human expression. Whether through literature, science, or everyday communication, the Greek alphabet remains a vital part of our global cultural heritage.