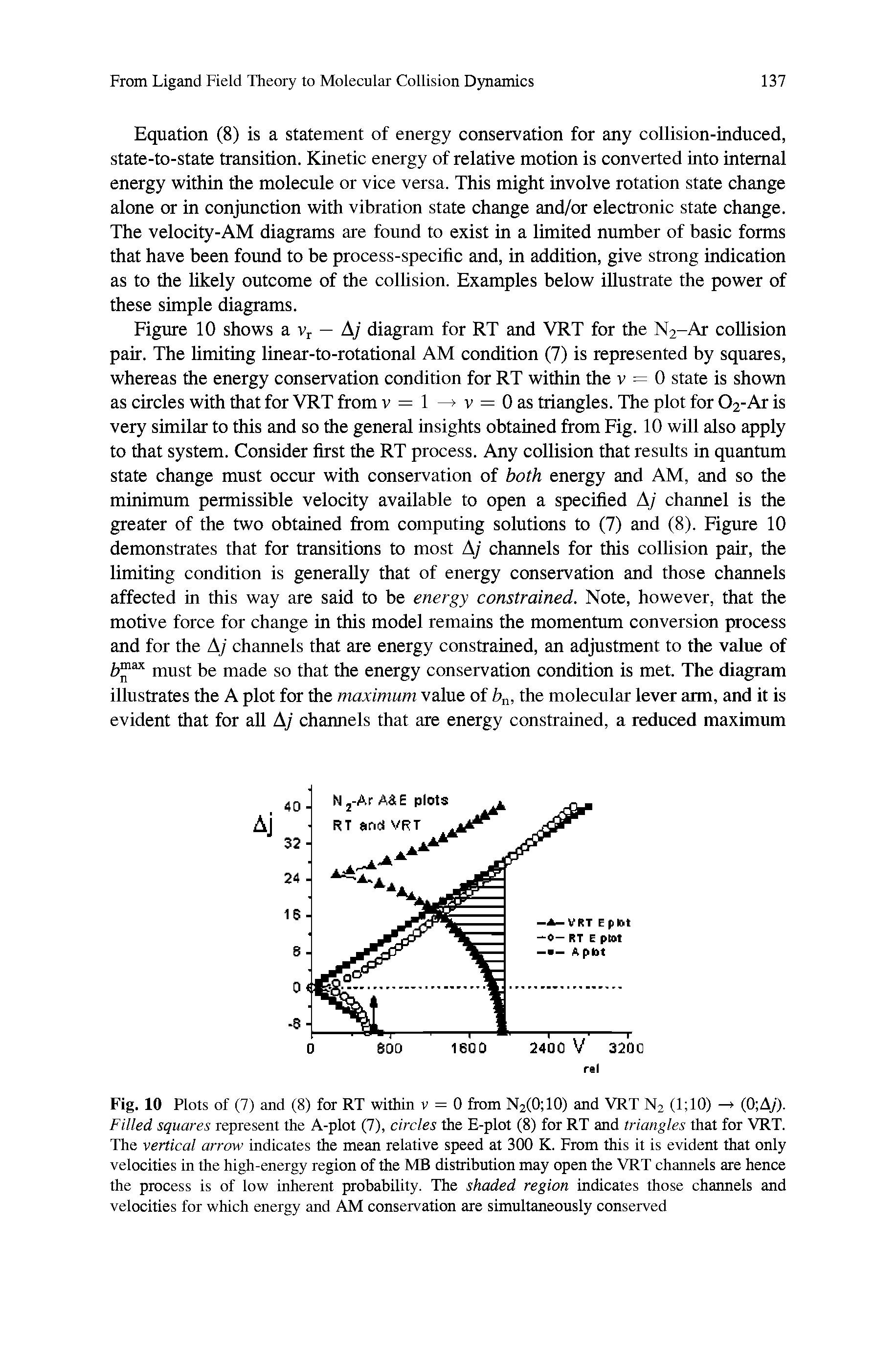
Relative speed is a fascinating concept in the world of physics and mathematics, essential for understanding movement and interactions between objects. It's a critical component in fields like transportation, astronomy, and even sports. This guide aims to delve deep into the nuances of relative speed, offering insights into its principles, calculations, and real-world applications. By grasping the fundamental ideas behind relative speed, you can enhance your comprehension of motion and its relative nature, which is crucial for both academic pursuits and practical scenarios.
The notion of relative speed is often encountered when examining how two or more objects move in relation to each other. It involves the calculation of velocity with respect to a reference point, which can sometimes be challenging to visualize. However, understanding this concept allows us to appreciate how different frames of reference can yield varying observations of speed and motion. This article will explore the intricacies of relative speed, from basic definitions to advanced applications, ensuring a thorough understanding of the topic.
In our everyday lives, we come across numerous instances where relative speed plays a significant role. Whether it's two cars traveling on a highway or celestial bodies moving through space, the concept is pervasive and vital for accurate measurements and predictions. As we unravel the complexities of relative speed, this guide will provide you with the knowledge and skills needed to analyze and interpret motion effectively, equipping you for a wide range of scientific and practical endeavors.
Read also:Prophet Brian Carns Wife Unveiling The Life And Journey
Table of Contents
- What is Relative Speed?
- Importance of Relative Speed in Physics
- How is Relative Speed Calculated?
- Real-World Applications of Relative Speed
- Relative Speed in Transportation
- Role of Relative Speed in Astronomy
- Relative Speed and Racing Sports
- How Does Relative Speed Affect Perception?
- Relative Speed in Technology and Innovation
- Educational Perspectives on Relative Speed
- Challenges in Understanding Relative Speed
- Relative Speed vs. Absolute Speed
- Can Relative Speed Be Measured Directly?
- Future Trends in Relative Speed Research
- FAQs on Relative Speed
- Conclusion
What is Relative Speed?
Relative speed is defined as the rate at which the distance between two objects changes as they move towards or away from each other. It is essentially the difference in speed between two moving bodies. In simpler terms, if two objects are moving in the same direction, their relative speed is the difference between their speeds. Conversely, if they are moving in opposite directions, their relative speed is the sum of their speeds.
To comprehend relative speed, one must appreciate the concept of reference frames. A reference frame is an abstract coordinate system that specifies the position of objects in space and time. Relative speed is always measured concerning a chosen reference frame, which can significantly alter the observed speed of an object. For instance, a passenger on a moving train may perceive the train as stationary while observing the scenery outside moving, illustrating the importance of relative frames in speed perception.
Importance of Relative Speed in Physics
Relative speed is a cornerstone in the field of physics, underpinning many fundamental theories and laws. It plays a crucial role in the study of kinematics—the branch of mechanics concerned with the motion of objects without considering the forces that cause the motion. By analyzing relative speed, physicists can predict and model the behavior of moving objects in various contexts.
Moreover, relative speed is integral to the theory of relativity, proposed by Albert Einstein. According to this theory, the laws of physics remain constant in all inertial frames of reference, and the speed of light is constant regardless of the observer's frame. This has profound implications for our understanding of time and space, emphasizing the significance of relative speed in theoretical physics.
How is Relative Speed Calculated?
Calculating relative speed involves determining the velocity difference between two objects. The formula for relative speed depends on the direction of motion:
- If two objects move in the same direction, relative speed = |v1 - v2|
- If two objects move in opposite directions, relative speed = |v1 + v2|
Here, v1 and v2 represent the speeds of the two objects. It's important to note that these calculations assume the speeds are measured relative to the same reference frame, ensuring consistency in the results.
Read also:Things To Do In Big Bear Adventure Awaits In The Mountain Oasis
Real-World Applications of Relative Speed
Relative speed is not just a theoretical concept but has numerous practical applications across various fields. It is especially crucial in transportation systems, where understanding the relative speed between vehicles is essential for safety and efficiency. For example, traffic management systems rely on relative speed calculations to prevent collisions and optimize vehicle flow.
The concept is also vital in astronomy, where it helps astronomers measure the movement of celestial bodies. By calculating relative speeds, scientists can determine the velocity and trajectory of stars, planets, and galaxies, providing insights into the universe's dynamics and evolution.
Relative Speed in Transportation
In the realm of transportation, relative speed is a key factor in ensuring the safety and efficiency of travel. It aids in the design of advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) and autonomous vehicles, which rely on sensors to detect the relative speed of surrounding vehicles. By accurately calculating relative speeds, these systems can make informed decisions to avoid accidents and maintain optimal distances between vehicles.
Additionally, relative speed calculations are essential for air traffic control, where the safe coordination of aircraft in shared airspace depends on precise measurements of their relative speeds and positions. This ensures safe takeoffs, landings, and in-flight navigation, reducing the risk of air collisions.
Role of Relative Speed in Astronomy
Astronomy heavily relies on the concept of relative speed to understand the motion of celestial bodies in the universe. By measuring the relative speed of stars and galaxies, astronomers can infer their velocities and distances, which are critical for mapping the cosmos and studying its expansion.
Relative speed also plays a significant role in the Doppler effect, where the frequency of light or sound waves changes due to the relative motion of the source and observer. This phenomenon allows astronomers to determine the speed at which celestial objects are moving towards or away from Earth, providing valuable data about their behavior and characteristics.
Relative Speed and Racing Sports
In the world of racing sports, relative speed is a fundamental concept that determines the outcome of races and competitions. Athletes and teams must have a keen understanding of relative speed to strategize and gain a competitive edge over their opponents.
For instance, in motorsports, drivers constantly assess their relative speed compared to other racers to make tactical decisions, such as when to overtake or conserve fuel. Similarly, in track and field events, runners must gauge their relative speed to maintain optimal pacing and timing throughout the race.
How Does Relative Speed Affect Perception?
Relative speed significantly influences our perception of motion and distance, altering how we experience movement in various contexts. This effect is evident in everyday scenarios, such as when driving a car or observing objects from a moving vehicle.
Our brains interpret relative speed based on reference frames, which can lead to intriguing optical illusions. For example, when two trains move alongside each other at similar speeds, passengers may perceive the trains as stationary relative to one another, despite their high velocities. This demonstrates how relative speed shapes our perception of movement and reality.
Relative Speed in Technology and Innovation
Relative speed is at the forefront of technological advancements and innovation, driving progress in various fields. In telecommunications, it enables the development of high-speed data transmission systems, ensuring efficient communication across vast distances.
In robotics, relative speed calculations are crucial for coordinating the movement of robotic arms and drones, enhancing precision and accuracy in industrial applications. By leveraging relative speed, engineers can design systems that adapt to changing environments and perform complex tasks with ease.
Educational Perspectives on Relative Speed
Understanding relative speed is a fundamental aspect of science education, providing students with valuable insights into motion and dynamics. It serves as a building block for more advanced concepts in physics and mathematics, fostering critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
Educators often use real-world examples and interactive simulations to teach relative speed, helping students visualize and grasp its principles. By exploring hands-on activities and experiments, learners can develop a deeper appreciation for the concept and its applications in everyday life.
Challenges in Understanding Relative Speed
While relative speed is a crucial concept, it can be challenging to comprehend due to its abstract nature and reliance on reference frames. Students and learners may struggle with visualizing relative motion and calculating velocities accurately.
To overcome these challenges, educators can employ a variety of teaching strategies, such as using visual aids, interactive simulations, and real-life examples. By creating an engaging and supportive learning environment, students can build a solid foundation in relative speed and its applications.
Relative Speed vs. Absolute Speed
Relative speed and absolute speed are two distinct concepts that describe motion in different contexts. Absolute speed refers to an object's velocity measured concerning a fixed reference point, such as the ground or a stationary observer.
In contrast, relative speed considers the motion of one object concerning another, often involving moving reference frames. Understanding the difference between these two concepts is essential for analyzing and interpreting motion accurately.
Can Relative Speed Be Measured Directly?
Measuring relative speed directly can be challenging, as it often involves complex calculations and multiple reference frames. However, modern technologies and instruments, such as radar and GPS, enable accurate measurement of relative speeds in various contexts.
For example, radar systems in vehicles and aircraft use electromagnetic waves to detect and calculate the relative speed of nearby objects, ensuring safety and efficiency in transportation. These technologies demonstrate the feasibility of measuring relative speed in practical applications.
Future Trends in Relative Speed Research
The field of relative speed research is continually evolving, with new advancements and discoveries on the horizon. Emerging technologies, such as artificial intelligence and machine learning, have the potential to revolutionize the way we understand and analyze relative speed.
As researchers continue to explore the intricacies of relative speed, we can expect to see innovations in areas like autonomous vehicles, space exploration, and telecommunications. These advancements will further enhance our understanding of motion and its relative nature, driving progress across numerous fields.
FAQs on Relative Speed
What is the difference between relative speed and velocity?
Relative speed refers to the rate at which two objects approach or recede from each other, while velocity is a vector quantity that describes an object's speed and direction. Relative speed focuses on the difference in speeds between objects, whereas velocity considers both speed and direction.
How is relative speed used in navigation?
In navigation, relative speed is essential for determining the position and movement of vessels, aircraft, and vehicles. By calculating relative speeds, navigators can make informed decisions to avoid collisions, optimize routes, and ensure safe travel in shared spaces.
Why is relative speed important in space exploration?
Relative speed is critical in space exploration for understanding the motion of celestial bodies and spacecraft. By measuring relative speeds, scientists can calculate trajectories, plan missions, and study the dynamics of the universe, enhancing our knowledge of space.
Can relative speed be negative?
Yes, relative speed can be negative when two objects move towards each other, indicating a decrease in the distance between them. In such cases, the relative speed is the negative of the rate at which the distance between the objects is decreasing.
How does relative speed affect time perception?
Relative speed can influence time perception by altering how we experience motion and events. According to the theory of relativity, time dilation occurs when objects move at high relative speeds, causing time to pass differently for observers in different frames of reference.
What tools are used to measure relative speed?
Various tools and technologies, such as radar, GPS, and LIDAR, are used to measure relative speed. These instruments detect and calculate the relative speed of objects by analyzing their positions, velocities, and distances, ensuring accurate measurements in diverse applications.
Conclusion
Relative speed is a fundamental concept that permeates numerous fields, from physics and astronomy to transportation and technology. By understanding its principles and applications, we can enhance our comprehension of motion and its relative nature, equipping ourselves for a wide range of scientific and practical endeavors. As research and innovation continue to advance, the study of relative speed will remain at the forefront of scientific exploration, driving progress and discovery across diverse domains.