The metric system is an internationally recognized system of measurement that is used in most countries around the world. It is a decimal-based system, which makes it easy to convert between different units of measurement. One of the most basic conversions within the metric system is from meters to centimeters. But how many cm are in one meter? This question is often asked by students, travelers, and professionals who work with measurements on a daily basis.
Understanding the conversion between meters and centimeters is essential for anyone who deals with measurements. Whether you're a student learning about measurements in school, a traveler trying to understand distances in a foreign country, or a professional working in a field that requires precise measurements, knowing how many cm are in one meter is crucial. The answer is simple: there are 100 centimeters in one meter. This conversion is straightforward because the metric system is based on powers of ten.
In this article, we will explore the metric system in detail, focusing on the conversion between meters and centimeters. We will discuss the history of the metric system, its advantages, and how it is used in different fields. We will also answer some frequently asked questions about the metric system and provide tips for converting between different units of measurement. By the end of this article, you will have a thorough understanding of the metric system and how many cm are in one meter.
Read also:Taryn Hanes An Inspiring Tale Of Talent And Tenacity
Table of Contents
- Introduction to the Metric System
- History and Evolution of the Metric System
- Advantages of Using the Metric System
- How Many Cm Are in One Meter?
- Practical Applications of Meters and Centimeters
- Converting Meters to Other Units
- Common Misconceptions About the Metric System
- Metric System in Different Countries
- Metric System in Education
- Metric System in Science and Industry
- How to Master Metric Conversions?
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion and Final Thoughts
Introduction to the Metric System
The metric system is a comprehensive system of measurement that is used worldwide. It is based on units of ten, making it easy to learn and use. The basic units of the metric system include meters for length, kilograms for mass, and liters for volume. These units are universally recognized and are used in most countries for everyday measurements, scientific research, and industrial applications.
The metric system was developed in France during the late 18th century as a response to the chaotic and inconsistent measurement systems that existed at the time. The goal was to create a standardized system that could be used by everyone, regardless of their location or profession. Today, the metric system is used in almost every country in the world, with the exception of the United States, Myanmar, and Liberia, which still use the imperial system for some measurements.
The simplicity and consistency of the metric system make it an ideal choice for education, science, and industry. Its decimal-based structure allows for easy conversion between units, which is particularly useful in scientific research and engineering. For example, converting from meters to centimeters simply involves moving the decimal point two places to the right, as there are 100 centimeters in one meter. This ease of conversion is one of the key benefits of using the metric system.
History and Evolution of the Metric System
The metric system has a rich history that dates back to the Age of Enlightenment in the 18th century. During this time, there was a growing desire for a universal system of measurement that could be used across different regions and countries. The existing systems were often based on arbitrary units that varied from place to place, leading to confusion and inefficiency.
In 1790, the French National Assembly commissioned the creation of a new measurement system that would be based on natural constants. A team of scientists, including Jean-Charles de Borda and Pierre-Simon Laplace, was tasked with developing this system. They decided to base the unit of length, the meter, on one ten-millionth of the distance from the equator to the North Pole. This decision laid the foundation for the metric system as we know it today.
Over the years, the metric system has evolved and expanded to include additional units and subunits. The International System of Units (SI) was established in 1960 to provide a standardized framework for the metric system. The SI system includes seven base units: meter, kilogram, second, ampere, kelvin, mole, and candela. These units are used in conjunction with prefixes such as kilo-, centi-, and milli- to create a wide range of measurements.
Read also:Historical Significance And Future Prospects Of Third Temple Construction
Advantages of Using the Metric System
The metric system offers several advantages over other measurement systems, particularly the imperial system. Some of the key benefits include:
- Simplicity: The metric system is based on powers of ten, making it easy to learn and use. This simplicity is particularly beneficial in educational settings, where students can quickly grasp the concepts of measurement and conversion.
- Consistency: The metric system is used worldwide, providing a consistent framework for measurement in science, industry, and everyday life. This consistency is especially important in international trade and communication, where accurate and standardized measurements are essential.
- Precision: The metric system allows for precise measurements, which are crucial in scientific research and engineering. The use of decimal points and prefixes ensures that measurements can be as accurate as necessary for a given application.
- Ease of Conversion: Converting between units in the metric system is straightforward, as it involves simply moving the decimal point. This ease of conversion reduces the risk of errors and simplifies calculations in various fields.
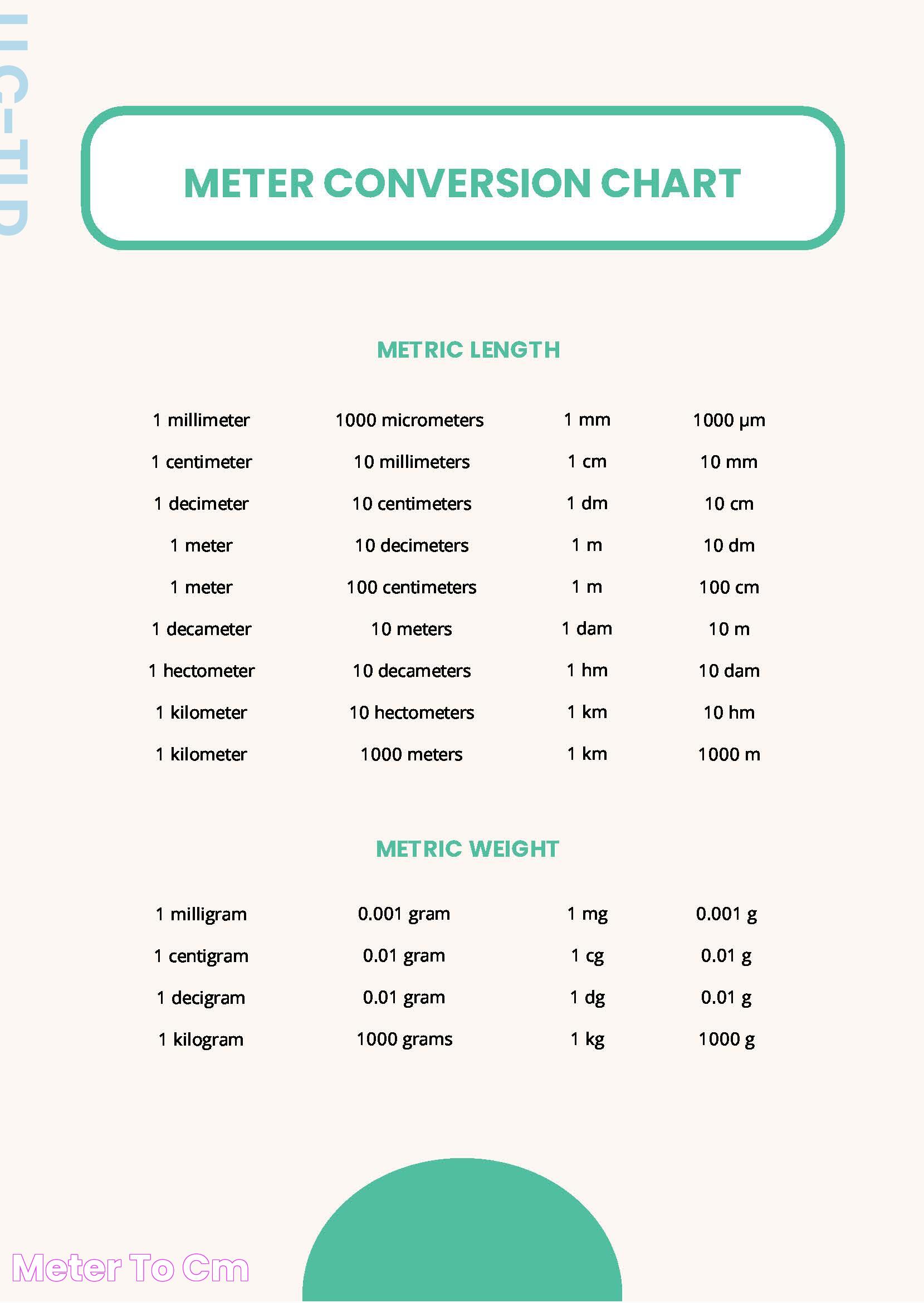
How Many Cm Are in One Meter?
The question of how many cm are in one meter is a common one, particularly for those who are new to the metric system. The answer is simple: there are 100 centimeters in one meter. This conversion is based on the metric system's use of powers of ten, which makes it easy to move between units of measurement.
To understand this conversion, it's helpful to think of the meter as the base unit of length in the metric system. A centimeter is one-hundredth of a meter, so there are 100 centimeters in one meter. This relationship can be expressed mathematically as:
1 meter = 100 centimeters
This conversion is particularly useful in fields such as construction, engineering, and science, where precise measurements are required. For example, a scientist measuring the length of a specimen might use centimeters for smaller measurements and meters for larger ones. Similarly, an engineer designing a building might use meters for the overall dimensions and centimeters for smaller details.
Practical Applications of Meters and Centimeters
Meters and centimeters are used in a wide range of practical applications, from everyday tasks to specialized fields. Some common uses include:
- Construction: In the construction industry, meters and centimeters are used to measure the dimensions of buildings, roads, and other structures. These units are essential for ensuring that projects are built to the correct specifications and are structurally sound.
- Interior Design: Interior designers use meters and centimeters to measure spaces and furniture, ensuring that everything fits together harmoniously. These measurements are crucial for creating functional and aesthetically pleasing interiors.
- Science and Research: Scientists use meters and centimeters to measure distances, lengths, and sizes of specimens and equipment. Accurate measurements are vital for conducting experiments and analyzing data.
- Everyday Life: In daily life, people use meters and centimeters for tasks such as measuring fabric for sewing, determining the size of a room, or assessing the length of a piece of wood for a DIY project.
Converting Meters to Other Units
While the conversion from meters to centimeters is straightforward, there are many other conversions within the metric system that can be useful in different contexts. Some common conversions include:
- Meters to Millimeters: To convert from meters to millimeters, multiply the number of meters by 1,000. For example, 2 meters is equal to 2,000 millimeters.
- Meters to Kilometers: To convert from meters to kilometers, divide the number of meters by 1,000. For example, 5,000 meters is equal to 5 kilometers.
- Meters to Inches: To convert from meters to inches, multiply the number of meters by 39.37. For example, 1 meter is approximately 39.37 inches.
- Meters to Feet: To convert from meters to feet, multiply the number of meters by 3.281. For example, 1 meter is approximately 3.281 feet.
These conversions can be useful in various fields, particularly when working with international measurements or translating between metric and imperial systems. It's important to use the correct conversion factors to ensure accuracy in calculations and measurements.
Common Misconceptions About the Metric System
Despite its widespread use, there are several misconceptions about the metric system that can lead to confusion or errors. Some of these misconceptions include:
- The Metric System Is Complicated: While some people may find the metric system unfamiliar, it is actually simpler than the imperial system due to its decimal-based structure. Once you understand the basic units and prefixes, conversions become straightforward.
- The Metric System Is Only Used in Science: While the metric system is essential in scientific research, it is also used in everyday life, industry, and education. Most countries use the metric system as their primary system of measurement.
- Metric Units Are Less Accurate: Metric units can be as precise as necessary, depending on the application. The use of decimal points allows for accurate measurements in fields ranging from engineering to cooking.
Metric System in Different Countries
The metric system is used in most countries around the world, with a few exceptions. Some countries, such as the United States, continue to use the imperial system for certain measurements, although the metric system is used in scientific and international contexts.
In countries that have adopted the metric system, it is used for all types of measurements, including length, weight, volume, and temperature. This standardization facilitates communication and trade between countries, as everyone uses the same units of measurement.
In recent years, there has been a push for countries that still use the imperial system to fully adopt the metric system. This transition would eliminate confusion and errors caused by having multiple systems in use and would further streamline international communication and commerce.
Metric System in Education
The metric system is an integral part of education in many countries, where it is taught from an early age. Students learn about the basic units of the metric system, such as meters, liters, and grams, as well as how to convert between different units.
Teaching the metric system in schools helps students develop a strong foundation in mathematics and science, as it promotes a clear understanding of measurements and conversions. This knowledge is essential for success in many fields, including engineering, medicine, and environmental science.
In countries that use the imperial system, there is often a focus on teaching both systems to ensure that students are prepared for international work and study. This dual approach provides students with the skills they need to navigate a world where the metric system is the standard.
Metric System in Science and Industry
The metric system is the standard system of measurement in science and industry, where precision and accuracy are crucial. In scientific research, measurements are often taken to several decimal places, and the use of the metric system ensures that these measurements are consistent and easily understood.
In industry, the metric system is used for manufacturing, construction, and engineering. Companies around the world rely on the metric system to ensure that products are made to exact specifications and that measurements are consistent across different countries and markets.
The use of the metric system in science and industry highlights its importance as a tool for innovation and development. By providing a clear and consistent framework for measurement, the metric system enables scientists and engineers to work together and share their findings with the global community.
How to Master Metric Conversions?
Mastering metric conversions is a valuable skill that can be useful in many different contexts. Here are some tips for becoming proficient in metric conversions:
- Understand the Basics: Start by learning the basic units of the metric system, such as meters, liters, and grams, and their corresponding prefixes, such as kilo-, centi-, and milli-.
- Practice Converting: Practice converting between different units, starting with simple conversions like meters to centimeters and progressing to more complex ones like millimeters to kilometers.
- Use a Conversion Chart: Keep a conversion chart handy for quick reference. This can be especially helpful when working with unfamiliar units or when you need to make multiple conversions.
- Use Online Tools: Take advantage of online conversion tools and apps that can quickly and accurately convert between different units. These tools can be useful for checking your work and ensuring accuracy.
- Stay Consistent: When working with measurements, be consistent in your use of units. Make sure to label your answers with the correct units and double-check your conversions for accuracy.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the metric system based on?
The metric system is based on powers of ten, making it a decimal-based system. This structure allows for easy conversion between different units of measurement.
Why is the metric system better than the imperial system?
The metric system is considered better than the imperial system because it is simpler, more consistent, and allows for precise measurements. Its decimal-based structure makes conversions straightforward and reduces the risk of errors.
How is the metric system used in everyday life?
The metric system is used in everyday life for tasks such as measuring distances, cooking, and weighing items. It is also used in education, science, and industry for more specialized applications.
What countries do not use the metric system?
The United States, Myanmar, and Liberia are the only countries that have not fully adopted the metric system for all measurements. However, the metric system is used in scientific and international contexts in these countries.
How can I learn the metric system easily?
The best way to learn the metric system is to start with the basics, practice conversions, and use resources like conversion charts and online tools. Consistent practice and real-world application will also help reinforce your understanding.
Is the metric system used in scientific research?
Yes, the metric system is the standard system of measurement in scientific research. It provides a consistent and precise framework for taking measurements, conducting experiments, and sharing results with the global scientific community.
Conclusion and Final Thoughts
The metric system is a powerful and versatile system of measurement that is used worldwide. Understanding how many cm are in one meter is just the beginning of mastering this system. With its simplicity, consistency, and precision, the metric system is an essential tool for education, science, and industry.
By learning the metric system and becoming proficient in metric conversions, you can enhance your skills and improve your ability to work in a global context. Whether you're a student, a professional, or simply someone who wants to understand measurements better, the metric system offers a clear and reliable framework for measuring and understanding the world around us.
As you continue to explore the metric system, remember to practice regularly, use resources like conversion charts and online tools, and apply your knowledge in real-world situations. With dedication and practice, you can become confident in your ability to navigate the metric system and use it to your advantage.