When we think of Britain, many of us conjure up images of iconic landmarks like Big Ben, the rolling green hills of the countryside, and the bustling streets of London. However, understanding what countries make up Britain can be somewhat confusing due to the overlapping terms often used interchangeably. The term "Britain" is frequently confused with the United Kingdom, leading to misconceptions about the geographical and political boundaries it encompasses. With its rich history and unique cultural identities, Britain is a fascinating region that comprises several distinct countries, each with its own heritage and traditions.
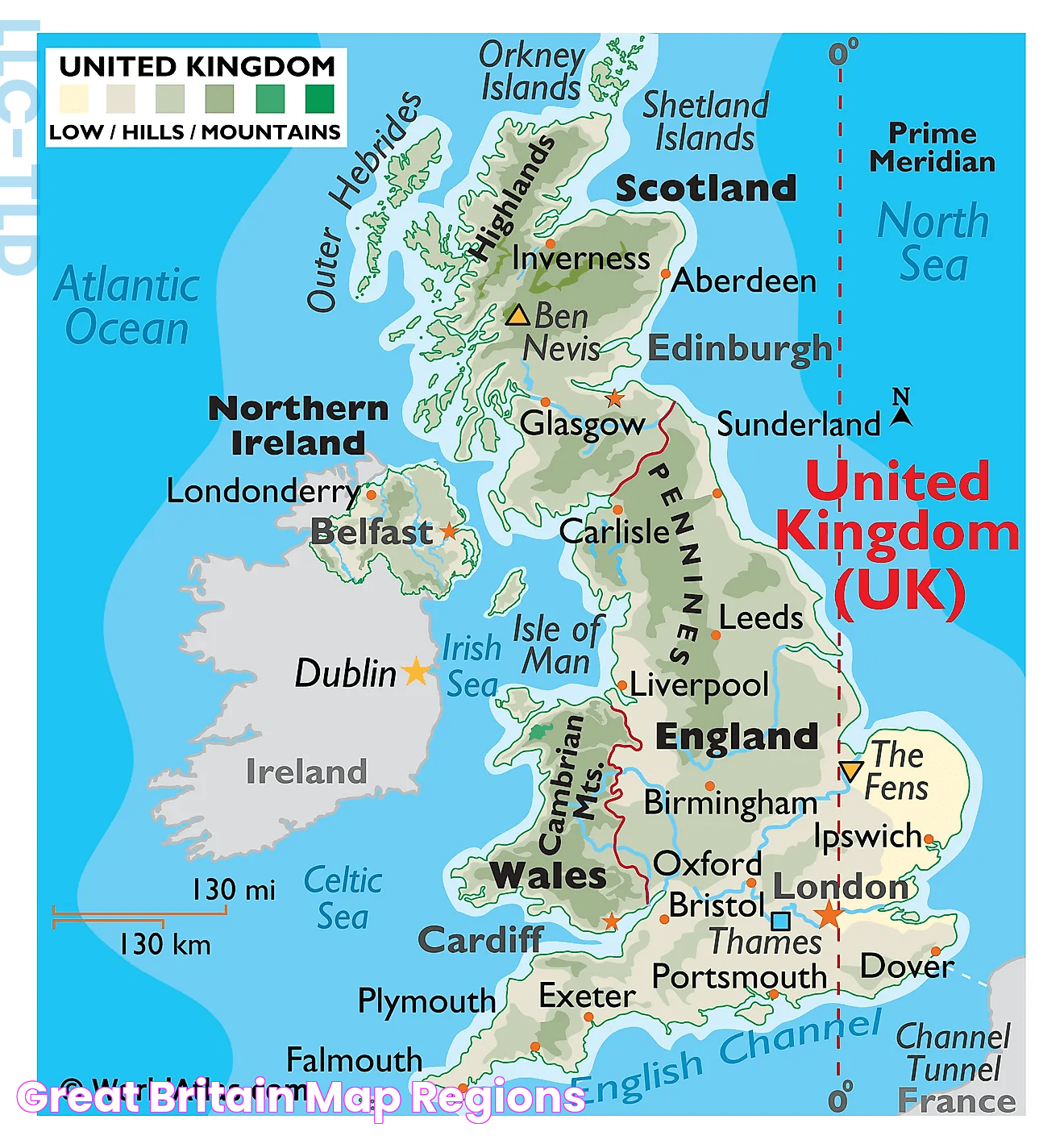
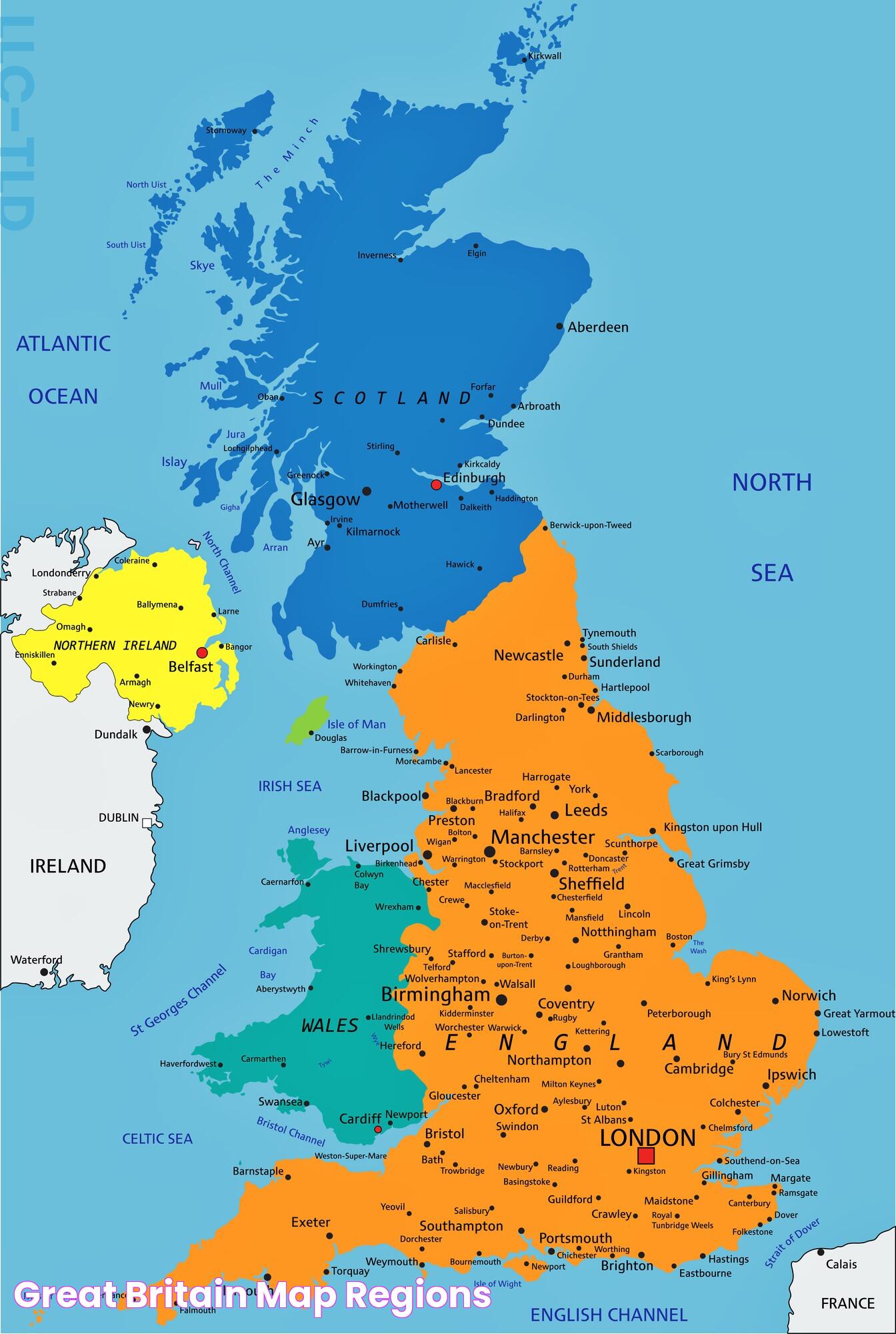
Britain, in its simplest form, is a part of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland. When we refer to Britain, we're typically speaking about the island of Great Britain, which includes three countries: England, Scotland, and Wales. These countries, while united under one sovereign state, maintain a level of autonomy and have their own legal systems and educational frameworks. The diversity within Britain is vast, with each country offering its own unique contributions to the collective identity of the region.
Understanding what countries make up Britain requires us to delve into the historical and political nuances that have shaped the region. The United Kingdom itself is a sovereign state that includes Northern Ireland in addition to Great Britain. While Northern Ireland is part of the UK, it is not geographically part of Britain. This distinction is crucial in understanding the complexity of the relationships between these countries, as well as the cultural and political dynamics at play. As we explore the individual characteristics of each country within Britain, we'll uncover the rich tapestry of history, culture, and identity that makes this region so unique.
Read also:Ultimate Guide To Replacement Screens For Windows Enhance Your Homes Comfort And Aesthetics
Table of Contents
- What is Britain?
- England: The Heart of Britain
- Scotland: Land of Legends
- Wales: The Land of Castles
- How Do England, Scotland, and Wales Differ?
- The United Kingdom vs. Britain
- What Role Does Northern Ireland Play?
- Cultural Diversity Within Britain
- Political Structures and Governance
- Historical Evolution of Britain
- Britain in the Modern World
- Impact of British Culture Globally
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
What is Britain?
Understanding what countries make up Britain begins with defining the term "Britain" itself. Geographically, Britain refers to the island known as Great Britain, which forms the largest part of the United Kingdom. This island is home to three countries: England, Scotland, and Wales. The term "Britain" is often used colloquially to refer to the United Kingdom, but this is technically incorrect as the UK includes Northern Ireland, which is not part of the island of Great Britain.
The distinction is important for both geographical and political reasons. Geographically, Great Britain is the largest of the British Isles, situated to the northwest of mainland Europe. Politically, the countries that make up Britain—England, Scotland, and Wales—are part of a larger sovereign state known as the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland.
Despite being part of a single political entity, each country within Britain has a distinct identity, with its own cultural traditions, languages, and historical backgrounds. This diversity is a defining feature of the region, contributing to its rich and varied cultural landscape.
England: The Heart of Britain
England, as the largest and most populous country within Britain, plays a central role in the region's cultural and political life. It occupies over half of the island of Great Britain and is bordered by Scotland to the north and Wales to the west. England is home to the capital city, London, which is not only the largest city in the UK but also a global hub of finance, culture, and politics.
As the birthplace of Shakespeare and the Industrial Revolution, England's contributions to global culture and history are significant. The English language, originating from England, is one of the most widely spoken languages in the world. England's rich history is evident in its numerous historic landmarks, including Stonehenge, the Tower of London, and Buckingham Palace.
England: Society and Culture
England's society is a melting pot of cultures, influenced by waves of immigration from former British colonies and beyond. This has enriched the cultural fabric of the country, evident in its diverse culinary scene, music, and art. England is known for its cultural exports, including literature, music, and film, which have shaped global entertainment and arts.
Read also:A Guide To Crisp And Juicy Perfecting The Art Of Flavorful Delights
England: Political Structure
Politically, England does not have its own devolved government like Scotland and Wales. Instead, it is governed directly by the UK Parliament located in London. However, proposals for regional devolution within England have been a topic of political debate, reflecting the ongoing discussions about governance and representation in the UK.
Scotland: Land of Legends
Scotland, occupying the northern third of the island of Great Britain, is renowned for its stunning landscapes, rich history, and vibrant cultural traditions. Characterized by its rugged highlands, ancient castles, and historic cities like Edinburgh and Glasgow, Scotland offers a unique blend of natural beauty and cultural heritage.
Scotland has a distinct legal system, education system, and cultural identity, which have been preserved over centuries despite political union with England. The Scottish Gaelic language, tartan patterns, and traditional music are integral to its cultural identity, while festivals like the Edinburgh Festival Fringe attract global attention.
Scotland: Political Autonomy
Scotland has a devolved government, the Scottish Parliament, which has powers over areas such as education, health, and justice. The question of Scottish independence has been a recurring theme in contemporary politics, with a significant independence referendum held in 2014. While the majority voted to remain in the UK, calls for a second referendum continue to be a topic of political discourse.
Scotland: Economy and Industry
Scotland's economy is diverse, with key sectors including oil and gas, renewable energy, finance, and tourism. The North Sea oil reserves have been a significant economic asset, while Scotland's whisky industry is world-renowned. The push towards renewable energy, particularly wind power, reflects Scotland's commitment to sustainable development.
Wales: The Land of Castles
Wales, located to the west of England, is a country known for its rugged coastline, mountainous national parks, and Celtic culture. Its history is marked by the construction of numerous castles, many of which are UNESCO World Heritage Sites, underscoring Wales's historical significance in the medieval period.
The Welsh language, spoken by a significant portion of the population, is a core part of Welsh identity and is taught in schools throughout the country. Wales boasts a vibrant cultural scene, with national events such as the Eisteddfod celebrating Welsh music, poetry, and art.
Wales: Political Landscape
Wales has a devolved government, the Senedd (Welsh Parliament), which has powers over areas such as health, education, and local government. Devolution has allowed Wales to tailor policies to better meet the needs of its population, while maintaining its place within the UK.
Wales: Economy and Tourism
The Welsh economy is characterized by a mix of traditional industries such as agriculture and newer sectors like technology and renewable energy. Tourism is a major driver of the economy, with visitors attracted by Wales's natural beauty and rich cultural heritage. The promotion of sustainable tourism practices is a priority for the Welsh government, ensuring the preservation of its unique landscapes and communities.
How Do England, Scotland, and Wales Differ?
While England, Scotland, and Wales are all part of Britain, they each have distinct identities and differences that set them apart. These differences are evident in their cultural traditions, languages, and governance structures.
- Cultural Traditions: England is known for its literary heritage and global cultural influence, Scotland for its Gaelic traditions and festivals, and Wales for its Celtic culture and music.
- Languages: English is the predominant language across Britain, but Welsh and Scottish Gaelic are also spoken, reflecting the linguistic diversity within the region.
- Governance: Both Scotland and Wales have devolved governments with powers over certain domestic policies, whereas England is governed directly by the UK Parliament.
These differences contribute to the rich tapestry of identities within Britain, offering a diverse and dynamic cultural landscape that attracts people from around the world.
The United Kingdom vs. Britain
It's important to clarify the distinction between the United Kingdom and Britain. The United Kingdom, officially known as the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, is a sovereign state comprising four countries: England, Scotland, Wales, and Northern Ireland. Britain, on the other hand, specifically refers to the island of Great Britain, which includes England, Scotland, and Wales.
This distinction is crucial for understanding the geographical and political boundaries of the region. While Britain is part of the UK, it does not encompass Northern Ireland. The term "British" is often used to describe citizens of the UK, reflecting the union of these countries under one sovereign state.
What Role Does Northern Ireland Play?
Northern Ireland, while part of the United Kingdom, is not part of the island of Great Britain. Located on the island of Ireland, Northern Ireland shares a border with the Republic of Ireland, an independent country. This unique position has influenced its cultural and political landscape significantly.
Historically, Northern Ireland has been marked by sectarian conflict, known as "The Troubles," which was largely resolved by the Good Friday Agreement in 1998. The agreement established a devolved government, the Northern Ireland Assembly, which shares power between unionists and nationalists.
Northern Ireland: Culture and Identity
Northern Ireland's culture is characterized by a blend of Irish and British influences, reflected in its music, literature, and festivals. The region's identity is complex, shaped by its historical ties to both the UK and Ireland.
Northern Ireland: Economy and Challenges
Northern Ireland's economy has diversified in recent years, with growth in sectors such as technology, manufacturing, and tourism. However, political uncertainty, particularly concerning Brexit and its impact on the Irish border, poses ongoing challenges for the region.
Cultural Diversity Within Britain
The cultural diversity within Britain is one of its defining features, contributing to its vibrant and dynamic society. This diversity is the result of historical migrations, colonial ties, and globalization, which have brought people from different backgrounds together.
Britain is home to numerous ethnic communities, each contributing to the cultural mosaic of the region. This diversity is celebrated through various festivals, cuisines, and cultural events, making Britain a truly multicultural society.
Political Structures and Governance
The political structure of Britain is characterized by a complex system of governance, with power divided between the UK Parliament and devolved governments in Scotland, Wales, and Northern Ireland. This system allows for a balance of centralized and regional authority, ensuring that regional needs and priorities are addressed.
The UK Parliament, located in Westminster, London, is responsible for areas such as defense, foreign affairs, and economic policy. Devolved governments have powers over areas such as health, education, and local government, allowing for tailored policies that reflect regional priorities.
Historical Evolution of Britain
The history of Britain is one of evolution and adaptation, marked by significant events that have shaped its current identity. From the Roman conquest to the Norman invasion, the Industrial Revolution to the establishment of the British Empire, Britain's history is rich and varied.
The Act of Union in 1707 unified England and Scotland, while the subsequent Act of Union in 1801 included Ireland, forming the United Kingdom. The partition of Ireland in 1921 led to the establishment of Northern Ireland as part of the UK, while the rest of Ireland became independent.
Britain in the Modern World
In the modern world, Britain stands as a global player with significant influence in international politics, economics, and culture. Its role in international organizations, such as the United Nations and NATO, underscores its commitment to global cooperation and security.
Brexit, the UK's exit from the European Union, has been a defining moment in recent history, impacting Britain's relationships with its European neighbors and the world. The implications of Brexit continue to shape Britain's economic and political landscape.
Impact of British Culture Globally
British culture has had a profound impact globally, influencing areas such as literature, music, fashion, and entertainment. The English language, spoken worldwide, is a testament to Britain's cultural reach and legacy.
British music, from The Beatles to contemporary artists, has shaped global music trends, while British literature, from Shakespeare to modern authors, continues to be celebrated worldwide. The British fashion industry, known for its innovation and creativity, has a significant presence on the global stage.
Frequently Asked Questions
What countries are part of Britain?
Britain, or Great Britain, includes England, Scotland, and Wales. These countries make up the island of Great Britain, which is part of the United Kingdom.
Is Northern Ireland part of Britain?
No, Northern Ireland is not part of Britain. It is part of the United Kingdom but is located on the island of Ireland, separate from Great Britain.
What is the difference between the United Kingdom and Britain?
The United Kingdom (UK) is a sovereign state that includes England, Scotland, Wales, and Northern Ireland. Britain, or Great Britain, refers specifically to the island comprising England, Scotland, and Wales.
Why is the British Isles a complex region?
The British Isles is a complex region due to its overlapping geographical and political entities, including the UK, Great Britain, and the Republic of Ireland. This complexity is rooted in historical events and political agreements.
How is governance structured in Britain?
Governance in Britain involves the UK Parliament and devolved governments in Scotland, Wales, and Northern Ireland. The UK Parliament handles national matters, while devolved governments manage regional affairs like health and education.
What is the cultural significance of the British Isles?
The British Isles have a rich cultural heritage, with contributions to literature, music, art, and philosophy. The region's history and cultural diversity make it an important center of global cultural influence.
Conclusion
Understanding what countries make up Britain involves exploring the geographical, political, and cultural complexities of the region. Britain, composed of England, Scotland, and Wales, is part of the United Kingdom, which also includes Northern Ireland. Each country within Britain has its own unique identity and cultural heritage, contributing to the rich tapestry of the region. As a global cultural and political force, Britain's impact is felt worldwide, underscoring its ongoing significance in the modern era.
Britain's history of evolution and adaptation has shaped its current identity, with the interplay of tradition and modernity evident in its cultural exports, political structures, and societal dynamics. As we navigate the complexities of the British Isles, we gain a deeper appreciation for the diversity and richness that define this remarkable region.
For further information on the UK's political structure and historical context, you can visit the UK Government's official website.