In today's technology-driven world, maintaining an optimal CPU temperature is crucial for the efficiency and longevity of your computer. A CPU, or Central Processing Unit, acts as the brain of your computer, executing instructions that enable your device to function smoothly. However, just like any other piece of machinery, it generates heat as it operates. Managing this heat is essential to prevent overheating, which can lead to performance issues or even permanent damage to your device.
Keeping a close eye on your CPU temperature ensures that your device runs at its best. It not only helps in maintaining the performance but also extends the lifespan of your computer hardware. Understanding how to monitor, manage, and resolve CPU temperature issues can save you from unexpected crashes and costly repairs. Whether you're a casual user, a gamer, or someone who uses a computer for professional tasks, knowledge about CPU temperature management is invaluable.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the significance of CPU temperature, explore various factors affecting it, and provide practical solutions to maintain an optimal temperature. From understanding the ideal temperature range to discovering the latest cooling solutions, this article is designed to equip you with the knowledge needed to keep your computer in tip-top shape. Let's embark on this journey to ensure your CPU's performance is always at its peak.
Read also:Discover The Best Learning Platforms For Enhanced Education
Table of Contents
- Understanding CPU Temperature
- Importance of Maintaining Optimal CPU Temperature
- What Affects CPU Temperature?
- How Do You Monitor CPU Temperature?
- Ideal CPU Temperature Ranges
- Common Causes of High CPU Temperature
- How to Lower CPU Temperature?
- Types of Cooling Solutions
- Impact of High CPU Temperature on Performance
- When Should You Be Concerned About CPU Temperature?
- Future Technologies in CPU Cooling
- Role of Software in CPU Temperature Management
- How to Prevent CPU Overheating?
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
Understanding CPU Temperature
CPU temperature refers to the amount of heat generated by the central processing unit as it performs tasks. CPUs are made up of millions of transistors that constantly switch on and off to process data, which inherently produces heat. The efficiency of a CPU is partially determined by its ability to manage and dissipate this heat effectively.
A CPU temperature is typically measured in degrees Celsius (°C) or Fahrenheit (°F) and can vary depending on the workload and the cooling solutions in place. Modern CPUs are equipped with thermal sensors that provide real-time data on temperature, enabling users to monitor and manage it effectively.
Understanding CPU temperature is essential as it directly impacts the performance, stability, and lifespan of your computer. When the temperature rises beyond the manufacturer's recommended limits, it can lead to thermal throttling, where the CPU reduces its clock speed to prevent overheating, resulting in decreased performance.
Importance of Maintaining Optimal CPU Temperature
Keeping your CPU at an optimal temperature is crucial for several reasons. First and foremost, it ensures the stability and reliability of your computer. Overheating can cause your system to crash or behave erratically, which can be particularly frustrating during important tasks or gaming sessions.
Moreover, maintaining a lower CPU temperature can extend the lifespan of your device. Excessive heat can degrade the components of your computer over time, leading to hardware failures and costly repairs. By keeping the temperature in check, you can avoid these issues and ensure your system runs smoothly for years.
Lastly, an optimal CPU temperature can enhance the overall performance of your computer. A cooler CPU can operate at higher speeds without the risk of overheating, allowing you to enjoy faster processing and improved multitasking capabilities. This is especially important for power users and gamers who require maximum performance from their systems.
Read also:Peter Falks Life And How He Passed Away A Detailed Look
What Affects CPU Temperature?
Several factors can influence CPU temperature, ranging from the workload to the environment. Understanding these factors can help you take proactive steps to manage and reduce heat effectively.
Workload and Usage
The workload on your CPU significantly impacts its temperature. Higher workloads, such as gaming, video editing, or running complex software, generate more heat compared to lighter tasks like browsing the web or word processing. Monitoring your CPU usage and managing tasks can help in keeping the temperature down.
Cooling Solutions
The effectiveness of your cooling solution plays a crucial role in managing CPU temperature. Air and liquid cooling systems can dissipate heat efficiently, but their performance can degrade over time due to dust accumulation or component wear. Regular maintenance and upgrades can help ensure optimal cooling performance.
Ambient Temperature
The temperature of the environment where your computer is located also affects CPU temperature. Higher ambient temperatures can lead to increased CPU temperatures, so it's important to ensure proper ventilation and cooling in your workspace.
Hardware Configuration
Your computer's hardware configuration, including the type of CPU, its architecture, and the presence of additional components like graphics cards, can impact temperature. High-performance components often generate more heat, necessitating robust cooling solutions.
How Do You Monitor CPU Temperature?
Monitoring your CPU temperature is a straightforward process that can be done using various tools and software available on the market.
BIOS/UEFI
Most modern motherboards come equipped with BIOS or UEFI firmware that enables you to check the CPU temperature. You can access this information during the boot process by pressing a specific key (usually Del, F2, or Esc) and navigating to the hardware monitoring section.
Software Tools
There are numerous software tools available that provide real-time CPU temperature monitoring. Popular options include HWMonitor, Core Temp, and SpeedFan. These tools offer detailed information about your CPU's temperature, allowing you to keep track and make necessary adjustments.
Operating System Utilities
Some operating systems have built-in utilities that allow you to monitor CPU temperature. For example, Windows users can use the Task Manager to view CPU usage, while Mac users can rely on Activity Monitor for similar insights.
Ideal CPU Temperature Ranges
The ideal CPU temperature range varies depending on the manufacturer and model, but there are general guidelines that can help you determine if your CPU is operating within a safe range.
Idle Temperatures
When your computer is idle or performing light tasks, the CPU temperature should typically range between 30°C and 40°C (86°F and 104°F). This indicates that your cooling solution is effectively managing heat during low-intensity operations.
Load Temperatures
Under heavy workloads, such as gaming or video rendering, CPU temperatures can rise. Ideally, your CPU should remain below 80°C (176°F) during these tasks. Temperatures above this threshold can lead to thermal throttling and reduced performance.
Maximum Temperatures
Most CPUs have a maximum operating temperature, known as Tjunction Max, specified by the manufacturer. Exceeding this temperature can cause permanent damage to the CPU. It's crucial to monitor and ensure that your CPU stays well below this limit.
Common Causes of High CPU Temperature
Identifying the causes of high CPU temperature is the first step in addressing and resolving overheating issues.
Insufficient Cooling
Inadequate cooling solutions, such as failing fans or clogged heatsinks, can lead to increased CPU temperatures. Regular maintenance and cleaning can help ensure your cooling system is functioning efficiently.
Poor Ventilation
Proper airflow is vital for maintaining optimal CPU temperature. Dust accumulation and cluttered cables can obstruct airflow, leading to heat buildup. Ensuring a clean and organized workspace can help improve ventilation.
High Ambient Temperature
External factors, such as high room temperature or exposure to direct sunlight, can contribute to increased CPU temperatures. Keeping your computer in a cool, shaded area can help mitigate this issue.
Overclocking
Overclocking involves increasing your CPU's clock speed to achieve better performance. However, this can significantly raise the CPU temperature. Implementing robust cooling solutions is essential if you choose to overclock your CPU.
How to Lower CPU Temperature?
If your CPU temperature is consistently high, there are several steps you can take to lower it and prevent overheating.
Improve Airflow
Enhancing airflow within your computer case can help dissipate heat more effectively. This can be achieved by organizing cables, adding additional fans, or using a case with better ventilation.
Upgrade Cooling System
Investing in a more efficient cooling system, such as a high-performance air cooler or a liquid cooling system, can significantly reduce CPU temperatures. These solutions are especially beneficial for high-performance builds or overclocked systems.
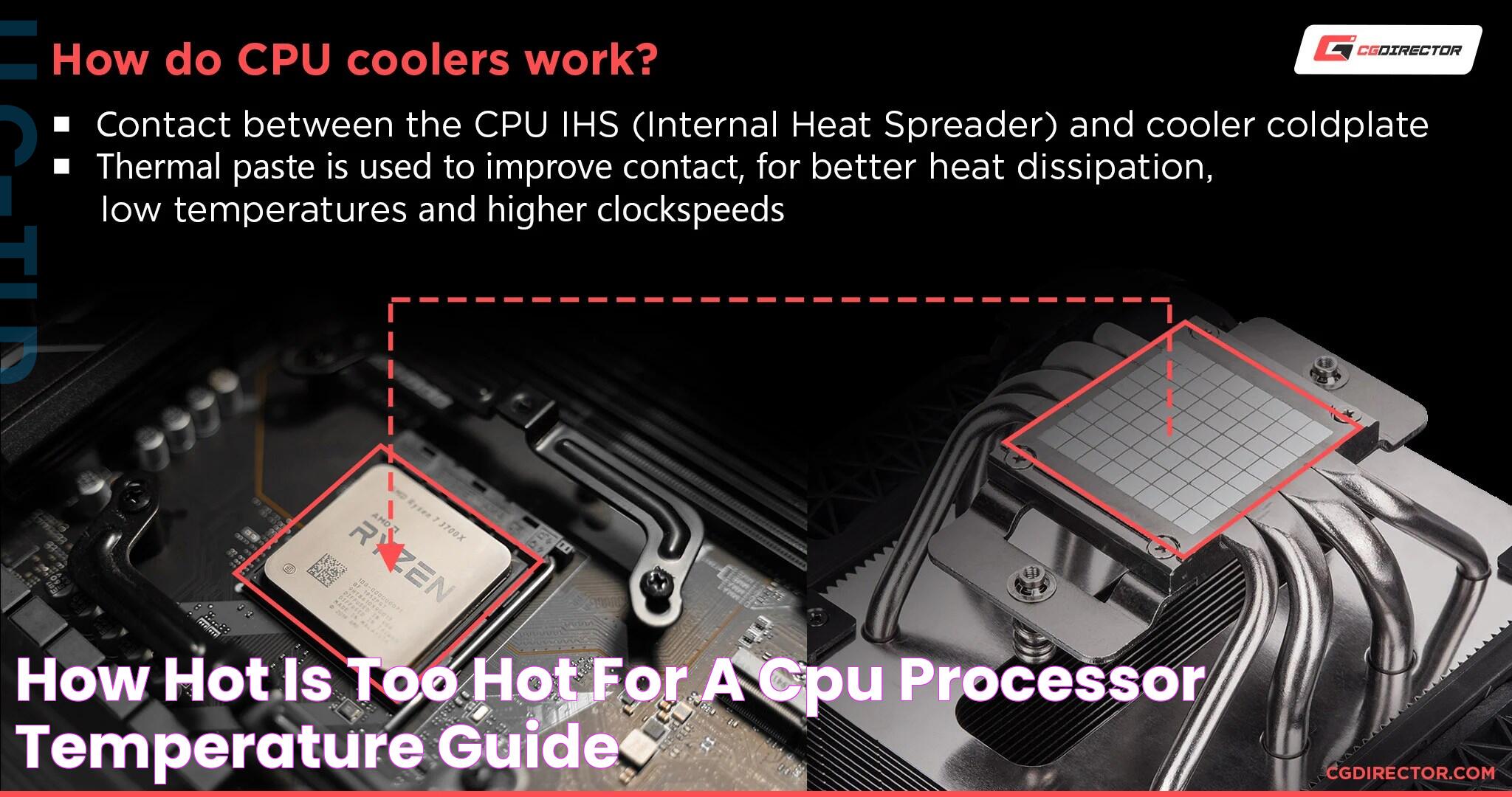
Apply Thermal Paste
Thermal paste facilitates heat transfer between the CPU and the heatsink. Over time, it can dry out and lose its effectiveness. Reapplying thermal paste can improve heat dissipation and lower CPU temperatures.
Reduce Workload
Limiting the number of running applications and background processes can reduce CPU usage and, consequently, temperature. Closing unnecessary programs and optimizing your system can help manage heat.
Types of Cooling Solutions
There are various cooling solutions available to help manage CPU temperature, each with its advantages and disadvantages.
Air Cooling
Air cooling is the most common method of cooling CPUs. It involves the use of fans and heatsinks to dissipate heat. Air coolers are affordable, easy to install, and effective for most users.
Liquid Cooling
Liquid cooling systems use a pump to circulate coolant through a series of tubes and a radiator, effectively removing heat from the CPU. These systems offer superior cooling performance but can be more expensive and complex to install.
Passive Cooling
Passive cooling relies on heat sinks without fans to absorb and dissipate heat. It is a silent and maintenance-free option, suitable for low-power systems.
Hybrid Cooling
Hybrid cooling solutions combine elements of both air and liquid cooling to provide efficient heat dissipation. These systems offer the benefits of both methods, making them ideal for high-performance builds.
Impact of High CPU Temperature on Performance
High CPU temperatures can have several adverse effects on the performance and stability of your computer.
Thermal Throttling
When a CPU reaches critical temperatures, it can initiate thermal throttling to reduce heat generation. This process involves lowering the CPU's clock speed, resulting in decreased performance and slower processing speeds.
System Instability
Consistently high CPU temperatures can lead to system instability, causing unexpected crashes, freezes, or shutdowns. This can disrupt your workflow and even result in data loss if not addressed promptly.
Hardware Damage
Prolonged exposure to high temperatures can cause permanent damage to your CPU and other components. This can lead to costly repairs or the need for component replacements.
When Should You Be Concerned About CPU Temperature?
Monitoring your CPU temperature regularly can help you identify when it becomes a cause for concern.
Consistently High Temperatures
If your CPU temperature consistently exceeds the recommended limits, it may indicate a cooling issue that requires immediate attention. Ignoring high temperatures can lead to long-term damage.
Performance Degradation
If you notice a decline in system performance, such as reduced processing speed or frequent crashes, it may be time to check your CPU temperature. Addressing high temperatures can restore performance.
Unusual Noises
Unusual noises from your cooling system, such as grinding or rattling sounds, can indicate a failing fan or cooling component. Investigating these noises can help prevent overheating.
Future Technologies in CPU Cooling
Advancements in technology continue to drive innovation in CPU cooling solutions, promising even more efficient heat management in the future.
Phase-Change Cooling
Phase-change cooling utilizes refrigerants to absorb and dissipate heat. This technology offers superior cooling performance and is being explored for high-performance computing systems.
Graphene-Based Solutions
Graphene's exceptional thermal conductivity makes it a promising material for future cooling solutions. Researchers are exploring graphene-based thermal interfaces for improved heat dissipation.
Nanotechnology
Nanotechnology is being leveraged to develop advanced cooling solutions, such as nano-coatings and microfluidic systems, which offer precise and efficient heat management.
Role of Software in CPU Temperature Management
Software plays a vital role in monitoring and managing CPU temperature, offering valuable insights and control over thermal management.
Temperature Monitoring Software
Software tools provide real-time data on CPU temperature, enabling users to monitor and make informed decisions about cooling solutions. These tools often include alerts and notifications for high temperatures.
Fan Control Utilities
Fan control software allows users to adjust fan speeds based on CPU temperature, optimizing airflow and cooling performance. This can help maintain optimal temperatures under varying workloads.
System Optimization Tools
System optimization software can identify and close unnecessary background processes, reducing CPU usage and temperature. These tools help maintain efficient performance and heat management.
How to Prevent CPU Overheating?
Preventing CPU overheating involves a combination of regular maintenance and proactive measures to manage heat effectively.
Regular Cleaning
Dust and debris can accumulate in your computer's cooling system, obstructing airflow and causing overheating. Regular cleaning of fans, heatsinks, and vents can help maintain optimal cooling performance.
Monitor Temperature
Consistently monitor your CPU temperature using software tools to identify potential issues early. Keeping track of temperature trends can help you take preventive action before overheating occurs.
Upgrade Cooling Solutions
If your current cooling solution is insufficient, consider upgrading to a more efficient system. High-performance air or liquid coolers can provide better heat management for demanding workloads.
Maintain Optimal Environment
Ensure your computer is located in a cool, well-ventilated area. Avoid exposing it to direct sunlight or placing it near heat sources, which can contribute to increased temperatures.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a safe CPU temperature range?
A safe CPU temperature range is typically between 30°C and 40°C when idle, and below 80°C under load. Exceeding these temperatures can lead to thermal throttling and potential damage.
How can I check my CPU temperature?
You can check your CPU temperature through BIOS/UEFI, or by using software tools like HWMonitor, Core Temp, or SpeedFan. These options provide real-time temperature data.
What happens if my CPU overheats?
If your CPU overheats, it can lead to thermal throttling, system instability, and hardware damage. Prolonged overheating can shorten the lifespan of your components.
Can high ambient temperature affect CPU temperature?
Yes, high ambient temperatures can increase CPU temperatures, as the cooling system may struggle to dissipate heat effectively. It's important to maintain a cool environment for your computer.
Is liquid cooling better than air cooling?
Liquid cooling generally offers superior cooling performance compared to air cooling, making it suitable for high-performance systems. However, it can be more expensive and complex to install.
What is thermal throttling?
Thermal throttling is a process where the CPU reduces its clock speed to lower heat generation when temperatures exceed safe limits. This results in decreased performance to prevent overheating.
Conclusion
Managing CPU temperature is vital for maintaining the performance, stability, and longevity of your computer. By understanding the factors that affect temperature, monitoring it regularly, and implementing effective cooling solutions, you can prevent overheating and ensure your system operates at its best. Whether you're a casual user or a power enthusiast, taking proactive steps to manage CPU temperature is an investment in the longevity and reliability of your device.
Remember, a cooler CPU not only enhances performance but also extends the lifespan of your hardware, saving you from unexpected repairs and replacements. Stay informed, stay proactive, and enjoy a seamless computing experience.