When discussing motion and forces in physics, two terms often come up: centripetal and centrifugal. While they sound similar and are frequently used interchangeably, they refer to different concepts. These forces play crucial roles in understanding the dynamics of objects moving in circular paths. In this article, we will explore the differences between centripetal and centrifugal forces, their applications, and how they impact our daily lives.
Our journey into the world of centripetal vs centrifugal forces will delve into the underlying principles governing these forces. We'll examine how they manifest in various scenarios, from amusement park rides to the rotation of celestial bodies. By understanding the distinctions and similarities between these forces, we can appreciate their significance in both theoretical and practical contexts.
Moreover, we will cover the scientific explanations and mathematical formulations that describe these forces. By the end of this article, you will have a comprehensive understanding of centripetal and centrifugal forces, their real-world applications, and how they are crucial in the broader field of physics. Let's start by outlining the major sections of our exploration into these fascinating forces.
Read also:Mastering The Art Of Spelling How To Spell Followed Correctly
Table of Contents
- Understanding Forces in Physics
- Defining Centripetal Force
- Defining Centrifugal Force
- Centripetal vs Centrifugal in Everyday Life
- Mathematical Representation of Forces
- Applications in Technology
- Astronomical Implications
- Impact on Motion and Stability
- Real-World Examples of Centripetal and Centrifugal Forces
- Centripetal vs Centrifugal: Which One Prevails?
- How Do Engineers Use These Forces?
- Challenges and Misconceptions
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
Understanding Forces in Physics
Forces are fundamental to understanding motion and interactions in the physical world. They are vector quantities, characterized by both magnitude and direction, and are responsible for changes in the state of motion of objects. In physics, a force is any interaction that, when unopposed, changes the motion of an object.
Two common forces discussed in the context of circular motion are centripetal and centrifugal forces. Both are essential in describing how objects move in a circular path, but they operate in different ways. To grasp the concepts of centripetal vs centrifugal, we must first understand the basics of forces and Newton's laws of motion, which provide a foundation for analyzing these phenomena.
Newton's first law, often called the law of inertia, states that an object will remain at rest or in uniform motion unless acted upon by an external force. Newton's second law introduces the concept of acceleration, indicating that the force acting on an object is equal to the mass of the object multiplied by its acceleration (F=ma). Finally, Newton's third law states that for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction.
Defining Centripetal Force
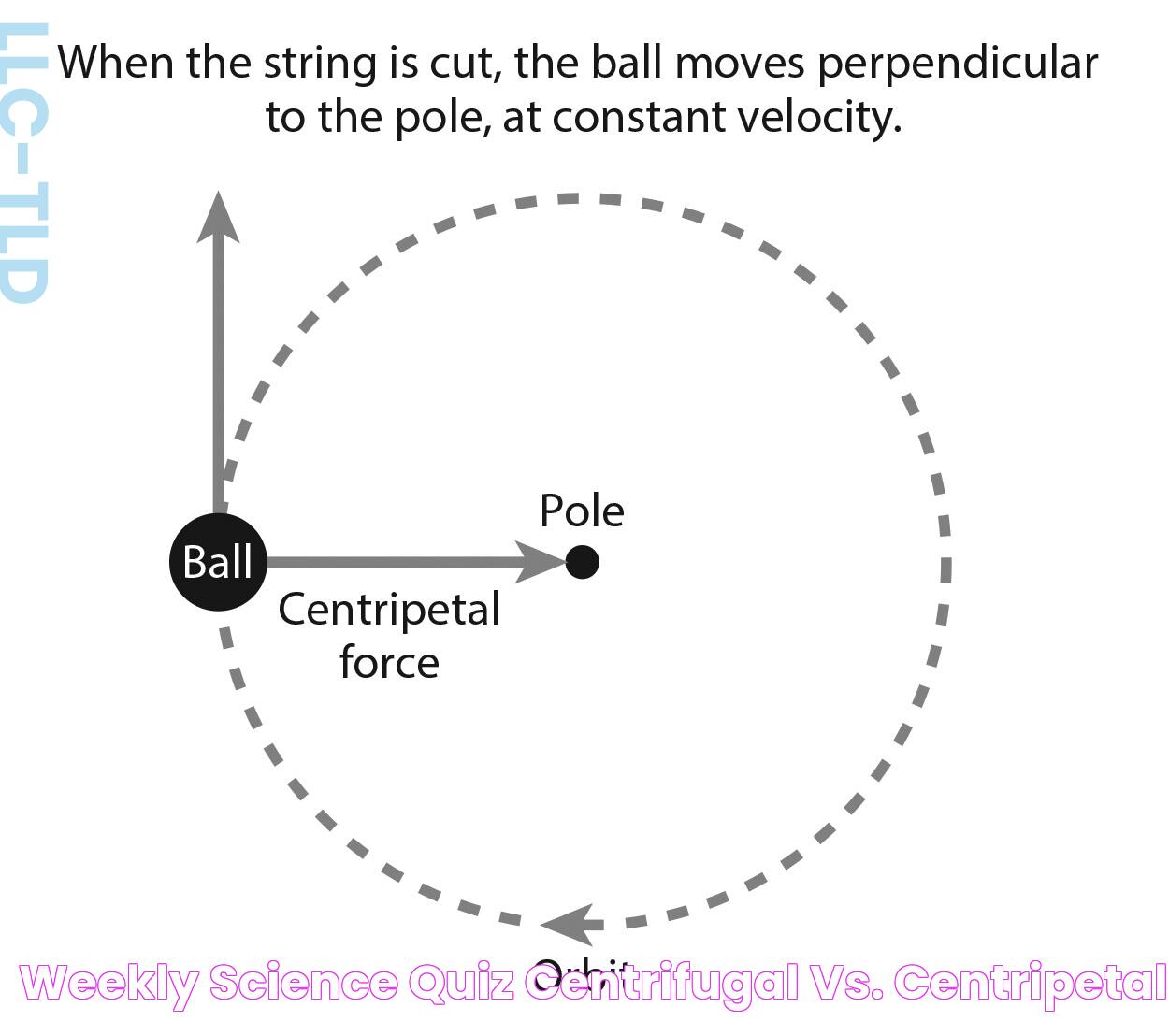
Centripetal force is a real force that acts on an object moving in a circular path, directed towards the center of the circle around which the object is moving. This force is necessary to keep the object in its circular path and is essential for understanding phenomena such as the orbits of planets and the operation of centrifuges.
The term "centripetal" comes from the Latin words "centrum," meaning "center," and "petere," meaning "to seek." Thus, centripetal force is a "center-seeking" force. It can be caused by various factors, including tension, gravity, or friction, depending on the context of the motion.
Mathematically, centripetal force (Fc) can be calculated using the equation: Fc = (mv2)/r, where "m" is the mass of the object, "v" is its velocity, and "r" is the radius of the circular path. This equation highlights that centripetal force is directly proportional to the mass of the object and the square of its velocity, and inversely proportional to the radius of the circular path.
Read also:Uncover The Wonders Of Skyes Avi A Detailed Exploration
Defining Centrifugal Force
Centrifugal force, on the other hand, is often described as a "fictitious" or "pseudo" force that appears when observing motion from a rotating reference frame. Unlike centripetal force, centrifugal force seems to push an object away from the center of rotation, but it is not a true force because it does not arise from a physical interaction.
The concept of centrifugal force becomes apparent when an observer is in a rotating system, such as a car turning a corner or a merry-go-round. To an observer within the system, it feels as though there is a force pushing them outward, away from the center, but this sensation is due to the inertia of their motion, not an actual force.
In non-inertial reference frames, like those rotating or accelerating, centrifugal force is used to explain the outward sensation. However, it's important to remember that in an inertial frame of reference, only centripetal force is acting on the object, keeping it in its circular path.
Centripetal vs Centrifugal in Everyday Life
Both centripetal and centrifugal forces play significant roles in our daily experiences, although we might not always be aware of them. Understanding these forces helps explain the physics behind various common occurrences.
For instance, when you take a sharp turn while driving, centripetal force is what keeps your car on the curve, while the sensation of being pushed outward is due to centrifugal force. Similarly, when you spin a bucket of water in a circular motion, centripetal force keeps the water inside the bucket, preventing it from spilling.
Amusement park rides, such as roller coasters and spinning rides, are excellent examples of centripetal and centrifugal forces in action. The thrilling sensations experienced are due to the interplay of these forces, as the ride's design manipulates motion to maximize excitement and safety.
Mathematical Representation of Forces
The mathematical representation of centripetal and centrifugal forces allows us to predict and analyze the behavior of objects in circular motion. Understanding the equations and variables involved is crucial for applications in engineering, physics, and other scientific disciplines.
Applications in Technology
Centripetal and centrifugal forces are pivotal in various technological applications. From the design of vehicles and amusement park rides to the functioning of centrifuges and washing machines, these forces are harnessed to achieve specific outcomes.
Astronomical Implications
In astronomy, the principles of centripetal and centrifugal forces are crucial in understanding the orbits of planets, moons, and other celestial bodies. These forces help explain the stability and dynamics of planetary systems.
Impact on Motion and Stability
The balance between centripetal and centrifugal forces affects the motion and stability of objects. In engineering, this understanding is vital for maintaining equilibrium and ensuring the safe operation of machinery and structures.
Real-World Examples of Centripetal and Centrifugal Forces
Examining real-world examples helps illustrate the practical significance of these forces. From satellites orbiting Earth to athletes using centrifugal force in sports, the applications are diverse and impactful.
Centripetal vs Centrifugal: Which One Prevails?
In debates about centripetal vs centrifugal forces, it's essential to recognize their roles and contexts. While centripetal force is a real force essential for circular motion, centrifugal force is perceived based on the observer's frame of reference.
How Do Engineers Use These Forces?
Engineers leverage centripetal and centrifugal forces in designing systems and structures. Understanding these forces enables the development of safer, more efficient technologies and solutions to complex challenges.
Challenges and Misconceptions
Misconceptions about centripetal and centrifugal forces can arise from a lack of understanding of their nature and application. Addressing these misconceptions is crucial for accurate comprehension and effective utilization of these forces.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is the difference between centripetal and centrifugal forces? Centripetal force is a real force directed towards the center of a circular path, while centrifugal force is a perceived force experienced in a rotating reference frame.
- Can centrifugal force be considered a real force? No, centrifugal force is not a real force; it is a perceived force experienced due to inertia in a rotating reference frame.
- How does centripetal force keep objects in circular motion? Centripetal force acts towards the center, providing the necessary force to maintain the object's circular path.
- What are some examples of centripetal force in everyday life? Examples include a car turning a corner, a satellite orbiting Earth, and a roller coaster loop.
- Why do we feel pushed outward in a rotating system? The sensation of being pushed outward is due to inertia, not a real force, and is perceived as centrifugal force.
- How do engineers use these forces in design? Engineers use these forces in designing vehicles, amusement park rides, and machinery to ensure stability and safety.
Conclusion
Understanding centripetal vs centrifugal forces is essential for grasping the dynamics of circular motion. While centripetal force is a real, center-seeking force, centrifugal force is a perceived effect experienced in rotating systems. These forces are integral to various fields, from engineering and technology to astronomy and everyday experiences. By appreciating the distinctions and applications of these forces, we can enhance our comprehension of motion and the physical world.