When it comes to nutrition, protein is an essential macronutrient that plays a vital role in building and repairing tissues, as well as producing enzymes and hormones. The calorie content in protein is a key factor for those looking to manage their weight, enhance muscle growth, or maintain overall health. Understanding the calories in each gram of protein can help individuals make informed dietary choices, balancing their needs for protein with their caloric intake.
Protein provides energy, much like carbohydrates and fats, but with a different caloric density. Each gram of protein contains approximately 4 calories, making it a relatively moderate source of energy compared to fats, which have 9 calories per gram. This caloric value is crucial for both athletes who need to fuel their workouts and individuals on weight loss plans who aim to reduce their caloric intake while maintaining muscle mass. By integrating the right amount of protein into your diet, you can effectively support your body's needs without exceeding your daily calorie goals.
Incorporating adequate protein into your diet doesn't just support physical performance; it also plays a significant role in satiety and weight management. Proteins are known to be more satiating than carbohydrates or fats, helping to curb hunger and reduce overall calorie consumption. Whether you're an active individual, a bodybuilder, or someone looking to improve their diet, understanding the calorie content in protein can help you optimize your meal plans. In this guide, we'll explore various aspects of protein intake, including types of protein, their role in nutrition, and how to effectively balance them within your dietary regimen.
Read also:Enhancing Meals With Medium Eggs Nutritional Benefits And Culinary Uses
Table of Contents
- What Are Calories?
- Understanding Protein: The Basics
- How Many Calories Are in Each Gram of Protein?
- Why Is Protein Important in Our Diet?
- Protein vs. Carbohydrates: Which Is Better?
- What Are the Different Types of Protein?
- How to Calculate Your Protein Needs?
- High Protein Foods and Their Caloric Values
- Is Protein Effective for Weight Loss?
- Role of Protein in Muscle Growth
- How to Balance Protein in Your Diet?
- Common Myths About Protein and Calories
- Are There Health Risks of High Protein Intake?
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
What Are Calories?
Calories are a unit of energy that measure how much energy food provides to the body. They are essential for fueling our daily activities, from basic functions like breathing to more complex tasks like running or lifting weights. When you consume food, your body breaks it down to release energy. This energy is then used for various bodily functions, or stored for later use.
In terms of nutrition, understanding calories is crucial for maintaining a balanced diet. Consuming more calories than your body needs can lead to weight gain, while consuming too few can result in weight loss. The key is to find the right balance that aligns with your health goals, whether it's losing weight, gaining muscle, or simply maintaining your current physique.
Understanding Protein: The Basics
Protein is one of the three primary macronutrients, alongside carbohydrates and fats. It is composed of amino acids, which are the building blocks of the body's tissues and organs. Proteins are essential for various bodily functions, including the growth and repair of cells, the production of enzymes and hormones, and the support of the immune system.
There are 20 different amino acids, nine of which are considered essential because the body cannot produce them on its own. These essential amino acids must be obtained through the diet. Protein can be found in a variety of foods, including meat, fish, eggs, dairy products, legumes, nuts, and seeds.
How Many Calories Are in Each Gram of Protein?
Each gram of protein contains approximately 4 calories. This makes protein a moderate source of energy compared to carbohydrates, which also provide 4 calories per gram, and fats, which provide 9 calories per gram. Understanding the calorie content of protein can help individuals manage their energy intake, whether they are looking to lose weight, gain muscle, or maintain their current weight.
While protein is not as calorie-dense as fat, it is more filling, which can help reduce overall calorie consumption by promoting feelings of fullness and satisfaction. This is particularly beneficial for those on a calorie-restricted diet, as consuming adequate protein can help preserve muscle mass while losing fat.
Read also:Master The Art Of Cooking Frozen Ears Of Corn Simple Steps And Tips
Why Is Protein Important in Our Diet?
Protein is crucial for maintaining good health and supporting various bodily functions. It plays a key role in:
- Muscle Repair and Growth: Protein provides the necessary amino acids for repairing and building muscles, which is especially important for athletes and those engaging in regular physical activity.
- Hormone Production: Proteins are involved in the production of hormones, which are essential for regulating bodily processes such as metabolism, growth, and mood.
- Immune Function: Antibodies, which are proteins, help protect the body from infections and diseases.
- Energy Supply: While not the body's primary energy source, protein can be used for energy when carbohydrates and fats are not available.
- Weight Management: Protein can help control appetite and reduce overall calorie intake by promoting feelings of fullness.
Protein vs. Carbohydrates: Which Is Better?
When comparing protein and carbohydrates, it's important to recognize that both nutrients have unique roles and benefits. Carbohydrates are the body's preferred energy source, providing quick and easily accessible energy for physical activities. They are particularly important for high-intensity workouts and endurance sports.
Protein, on the other hand, is essential for building and repairing tissues, supporting muscle growth, and maintaining overall health. While carbohydrates are important for energy, protein provides the necessary amino acids for bodily functions beyond just energy provision.
The choice between protein and carbohydrates depends on individual goals and dietary needs. For those looking to build muscle or lose weight, a higher protein intake may be beneficial. On the other hand, athletes and active individuals may require more carbohydrates to fuel their performance.
What Are the Different Types of Protein?
Proteins can be classified into two main categories: complete and incomplete proteins. Understanding these types can help individuals make informed dietary choices.
Complete Proteins
Complete proteins contain all nine essential amino acids in adequate amounts. They are typically found in animal-based foods, such as:
- Meat (beef, pork, lamb)
- Poultry (chicken, turkey)
- Fish and seafood
- Eggs
- Dairy products (milk, cheese, yogurt)
These sources provide a comprehensive amino acid profile, making them ideal for supporting muscle growth and overall health.
Incomplete Proteins
Incomplete proteins lack one or more essential amino acids. They are usually found in plant-based foods, such as:
- Legumes (beans, lentils, peas)
- Nuts and seeds
- Grains (quinoa, rice, oats)
- Vegetables
While incomplete proteins don't contain all essential amino acids, they can be combined with other protein sources to create a complete protein profile. For example, combining beans and rice provides all essential amino acids.
How to Calculate Your Protein Needs?
Calculating your protein needs involves considering several factors, including age, gender, weight, activity level, and health goals. The Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) for protein is 0.8 grams per kilogram of body weight for sedentary adults. However, individual protein requirements may vary based on specific needs.
Here's a step-by-step guide to calculate your protein needs:
- Determine your weight in kilograms by dividing your weight in pounds by 2.2.
- Multiply your weight in kilograms by the recommended protein intake based on your activity level:
- Sedentary (little to no exercise): 0.8 grams per kilogram
- Moderately active (exercise 3-4 times a week): 1.0-1.2 grams per kilogram
- Active (exercise 5-7 times a week): 1.2-1.5 grams per kilogram
- Athlete or bodybuilder: 1.5-2.0 grams per kilogram
It's essential to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian for personalized protein recommendations tailored to your individual needs and goals.
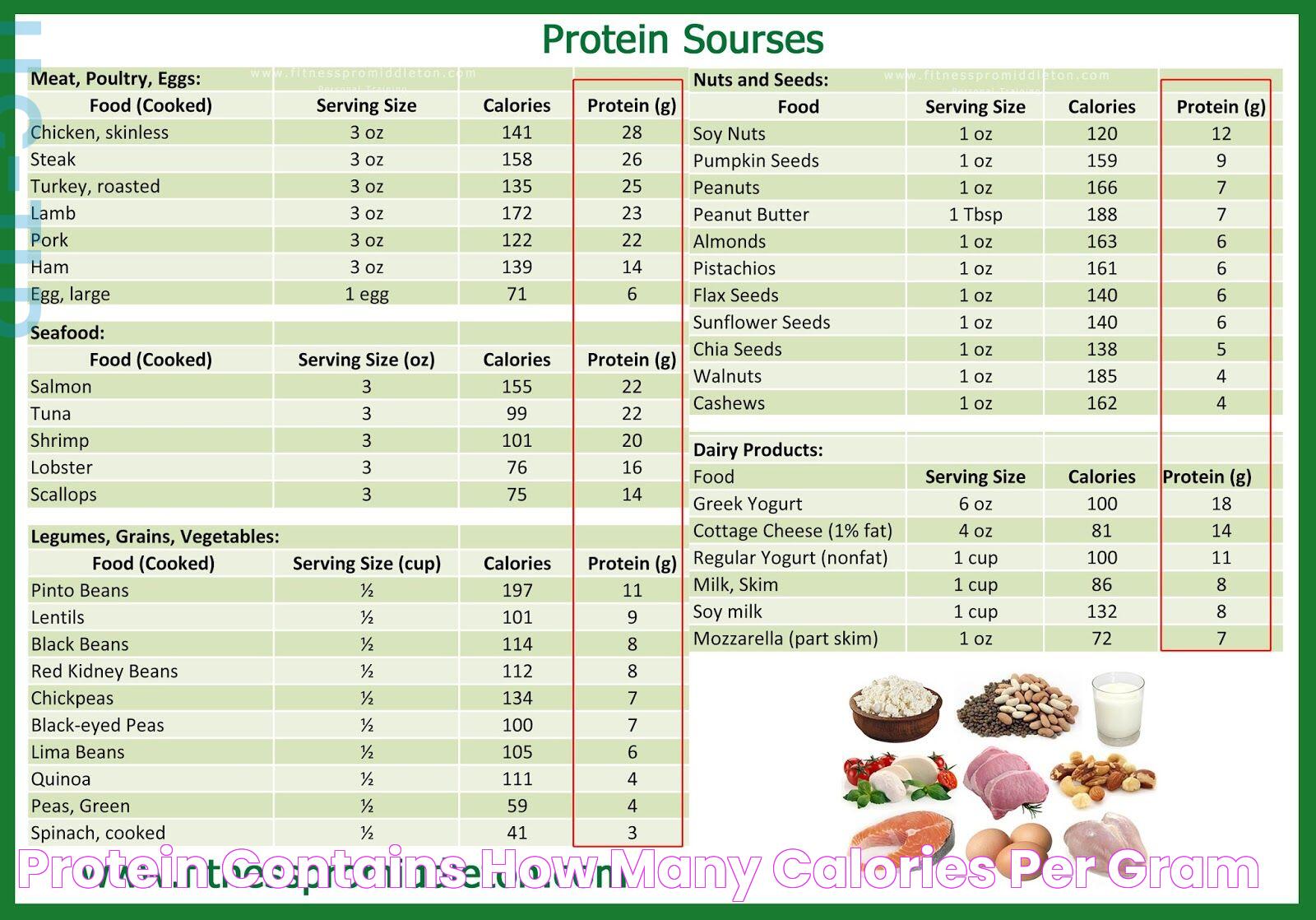
High Protein Foods and Their Caloric Values
Incorporating high-protein foods into your diet can help meet your protein needs while providing essential nutrients. Here are some examples of high-protein foods and their caloric values:
- Chicken Breast: 31 grams of protein per 100 grams, approximately 165 calories
- Salmon: 25 grams of protein per 100 grams, approximately 206 calories
- Eggs: 6 grams of protein per egg, approximately 68 calories
- Greek Yogurt: 10 grams of protein per 100 grams, approximately 59 calories
- Almonds: 21 grams of protein per 100 grams, approximately 579 calories
- Lentils: 9 grams of protein per 100 grams, approximately 116 calories
- Quinoa: 8 grams of protein per 100 grams, approximately 120 calories
Including a variety of high-protein foods in your diet can help meet your nutritional needs while supporting overall health and well-being.
Is Protein Effective for Weight Loss?
Protein can be highly effective for weight loss due to its ability to promote satiety, reduce appetite, and preserve muscle mass. Consuming adequate protein can help individuals feel fuller for longer, reducing the likelihood of overeating and snacking between meals.
Several studies have shown that higher protein intake can lead to greater weight loss and fat loss compared to lower protein diets. This is because protein has a higher thermic effect, meaning the body burns more calories digesting and metabolizing protein compared to carbohydrates and fats.
Incorporating protein-rich foods into a calorie-controlled diet can help individuals achieve their weight loss goals while maintaining lean body mass. It's important to choose high-quality protein sources and combine them with a balanced intake of carbohydrates and fats for optimal results.
Role of Protein in Muscle Growth
Protein plays a crucial role in muscle growth and repair, making it an essential nutrient for athletes, bodybuilders, and individuals engaging in resistance training. During exercise, muscle fibers experience micro-tears, which are repaired and rebuilt stronger with the help of protein.
Consuming adequate protein after exercise is critical for maximizing muscle protein synthesis, the process by which the body builds new muscle tissue. This is particularly important for those looking to increase muscle mass and strength.
Protein-rich foods and supplements, such as whey protein, casein, and plant-based protein powders, can help individuals meet their protein needs and support muscle growth. It's essential to consume protein in combination with carbohydrates to replenish glycogen stores and optimize recovery.
How to Balance Protein in Your Diet?
Balancing protein in your diet involves incorporating a variety of protein sources while maintaining a healthy intake of carbohydrates and fats. Here are some tips for achieving a balanced diet:
- Include a Source of Protein in Every Meal: Aim to include a protein-rich food in each meal, such as eggs, chicken, fish, or legumes.
- Combine Plant and Animal Proteins: Mix plant-based proteins, such as beans and nuts, with animal-based proteins for a complete amino acid profile.
- Monitor Portion Sizes: Be mindful of portion sizes to avoid consuming excessive calories while meeting protein needs.
- Opt for Lean Protein Sources: Choose lean cuts of meat and low-fat dairy products to reduce saturated fat intake.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water to support digestion and metabolism, especially when consuming high-protein diets.
It's important to listen to your body's needs and adjust your protein intake based on your activity level, health goals, and dietary preferences.
Common Myths About Protein and Calories
There are several myths and misconceptions about protein and calories that can lead to confusion. Here are some common myths and the facts behind them:
Myth 1: Eating More Protein Always Leads to More Muscle
While protein is essential for muscle growth, consuming excessive amounts won't necessarily result in more muscle. The body can only utilize a certain amount of protein for muscle synthesis, and any excess protein may be stored as fat.
Myth 2: High-Protein Diets Are Harmful to the Kidneys
For healthy individuals, high-protein diets are generally safe and do not harm kidney function. However, individuals with pre-existing kidney conditions should consult with a healthcare professional before increasing protein intake.
Myth 3: All Proteins Are Created Equal
Not all proteins are created equal. Complete proteins provide all essential amino acids, while incomplete proteins lack one or more. It's important to include a variety of protein sources for optimal nutrition.
Myth 4: Protein Supplements Are Necessary for Everyone
While protein supplements can be convenient for meeting protein needs, they are not necessary for everyone. Whole food sources of protein are sufficient for most individuals to meet their dietary requirements.
Are There Health Risks of High Protein Intake?
While protein is essential for health, excessive intake can pose potential risks, particularly for individuals with certain health conditions. Here are some considerations:
- Kidney Strain: High protein intake can put strain on the kidneys, especially in individuals with pre-existing kidney conditions. It's important to consult with a healthcare professional before significantly increasing protein intake.
- Bone Health: Some studies suggest that high protein intake may lead to increased calcium excretion and potential bone loss. However, adequate calcium intake and a balanced diet can mitigate this risk.
- Dehydration: High protein diets may increase the risk of dehydration as the body requires more water to metabolize protein. Staying hydrated is crucial when consuming high levels of protein.
Moderation and balance are key when it comes to protein intake. It's important to tailor protein consumption to individual needs and consult with healthcare professionals for personalized guidance.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How many calories are in each gram of protein?
Each gram of protein contains approximately 4 calories.
2. Can I consume too much protein?
Yes, excessive protein intake can lead to potential health risks, particularly for individuals with certain conditions. It's important to balance protein intake based on individual needs.
3. What are some high-protein foods?
High-protein foods include chicken, fish, eggs, Greek yogurt, almonds, lentils, and quinoa.
4. Is protein effective for weight loss?
Yes, protein can be effective for weight loss due to its ability to promote satiety, reduce appetite, and preserve muscle mass.
5. How can I calculate my protein needs?
Protein needs can be calculated based on factors such as age, gender, weight, activity level, and health goals. Consulting with a healthcare professional can provide personalized recommendations.
6. Are protein supplements necessary?
Protein supplements are not necessary for everyone. Whole food sources of protein are sufficient for most individuals to meet their dietary requirements.
Conclusion
Understanding the calories in each gram of protein is essential for making informed dietary choices and achieving health and fitness goals. Protein plays a crucial role in supporting muscle growth, weight management, and overall well-being. By incorporating a variety of high-protein foods into a balanced diet, individuals can optimize their nutrition and support their body's needs. Whether you're looking to lose weight, build muscle, or maintain your current physique, protein is a vital component of a healthy diet.