Generational categorization has long been a fascinating aspect of human society, providing insights into the distinct characteristics and cultural nuances that define each cohort. "Generation years" refer to the specific time frames that demarcate different generational groups, each influenced by unique historical, social, and economic factors. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for businesses, educators, and policymakers as they adapt to the changing needs and values of diverse age groups. The concept of generation years is more than just a timeline; it is a window into the evolving human experience, revealing the ways in which each generation has contributed to shaping the world we live in today.
From the Silent Generation to Generation Alpha, each group carries its own set of values, expectations, and technological proficiencies. The differences in generation years help explain why certain innovations resonate more strongly with specific age groups, why particular social issues are prioritized, and how generational shifts influence everything from workplace dynamics to consumer behavior. As we delve into the details of generation years, we uncover a tapestry of human development, marked by the triumphs, challenges, and transformations that have defined our collective journey through time.
In an age where technology and global communication have blurred traditional boundaries, the significance of generation years remains undiminished. With each passing decade, the characteristics of each generation continue to evolve, reflecting the rapid pace of change in our world. As we explore the intricacies of generation years, it becomes clear that this framework provides invaluable insights not only into the past but also into the future, offering a roadmap for understanding the ongoing evolution of societal trends and human behavior. This article aims to shed light on the complexities and relevance of generation years, offering a comprehensive overview that is both informative and accessible to readers of all backgrounds.
Read also:Rita Tax Ohio Everything You Need To Know For Stressfree Tax Compliance
Table of Contents
- What Are Generation Years?
- The Silent Generation (1928-1945)
- Baby Boomers (1946-1964)
- Generation X (1965-1980)
- Millennials (1981-1996)
- Generation Z (1997-2012)
- Generation Alpha (2013-Present)
- How Do Generations Influence Culture?
- The Impact of Technology on Generation Years
- Generational Differences in the Workplace
- What Challenges Do Different Generations Face?
- How Generations Shape Consumer Behavior
- Understanding Generational Values and Beliefs
- How Does Education Vary Across Generations?
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
What Are Generation Years?
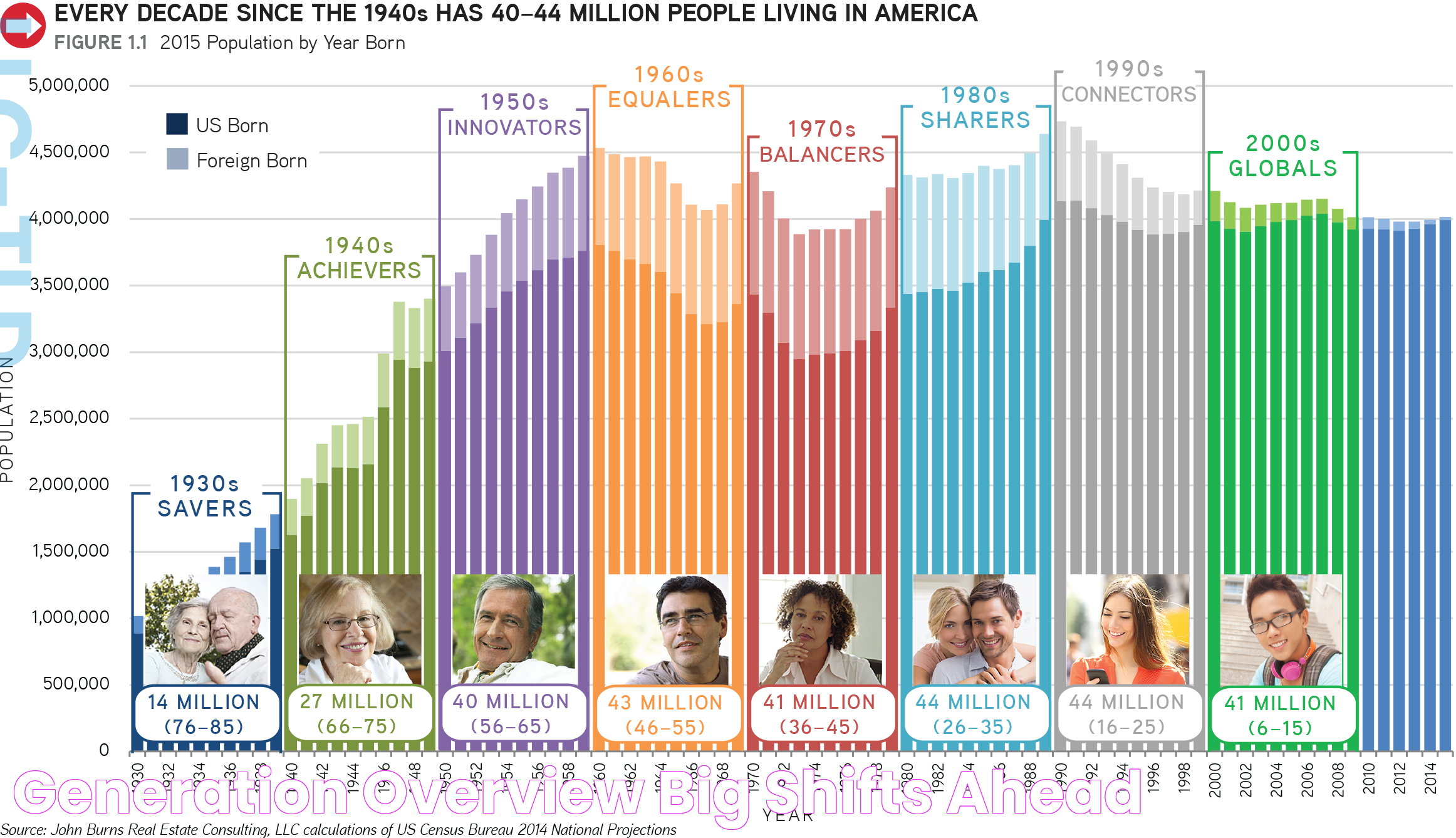
Generation years refer to the time frames that define the boundaries of different generational cohorts. These cohorts are typically categorized based on birth years, with each generation sharing common experiences that influence their perspectives and behaviors. Generational groupings are not arbitrary; they are shaped by significant historical events, technological advancements, and cultural shifts that occur during a particular period.
For instance, the Silent Generation was born during the Great Depression and World War II, which imbued them with a sense of resilience and frugality. Baby Boomers, on the other hand, were shaped by post-war prosperity and the rise of consumer culture. Generation X grew up during the transition to digital technology, while Millennials came of age during the internet revolution. Generation Z is defined by their digital nativity, having never known a world without instant access to information.
These generational labels are useful for understanding broad social trends, but it's important to remember that individual experiences within a generation can vary widely. The concept of generation years provides a framework for examining how different age groups respond to the world around them and how these responses can affect societal change.
The Silent Generation (1928-1945)
The Silent Generation, also known as the "Traditionalists," were born between 1928 and 1945. This generation grew up during some of the most challenging times in modern history, including the Great Depression and World War II. As a result, they are often characterized by their stoicism, work ethic, and value for stability and security.
This generation values hard work and loyalty, often staying with the same employer for decades. They are known for their frugality and conservative approach to finance, having been shaped by an era of economic scarcity. The Silent Generation also witnessed the civil rights movement and the beginnings of significant social change.
Members of the Silent Generation are often seen as the keepers of tradition, with strong ties to family and community. They tend to be more cautious and risk-averse compared to younger generations, which can be attributed to the hardships they experienced during their formative years.
Read also:The Ultimate Guide To The Kardashian Dating Tree Love Relationships And Connections
Baby Boomers (1946-1964)
Baby Boomers, born between 1946 and 1964, emerged in the post-war era during a time of economic expansion and optimism. This generation is characterized by a strong sense of identity, ambition, and a desire to make a difference in the world. They were the driving force behind numerous social movements, including civil rights, women's liberation, and environmental conservation.
As a large and influential cohort, Baby Boomers have had a significant impact on society. They are often associated with the rise of consumer culture, as well as a focus on personal fulfillment and self-expression. Many Boomers pursued higher education and professional careers, contributing to the growth of the middle class.
Today, Baby Boomers are navigating retirement and aging, with many seeking to redefine what it means to grow older. They remain active and engaged, challenging stereotypes about age and continuing to shape cultural and economic trends.
Generation X (1965-1980)
Generation X, born between 1965 and 1980, is often described as the "in-between" generation, bridging the gap between Baby Boomers and Millennials. This cohort grew up during a time of significant social and technological change, including the rise of personal computers and the internet.
Members of Generation X are known for their independence, adaptability, and entrepreneurial spirit. They were the first generation to experience widespread divorce and the decline of traditional family structures, which has influenced their perspectives on relationships and work-life balance.
Generation X has often been overshadowed by the larger Baby Boomer and Millennial generations, but they have made a lasting impact on the workforce and popular culture. This generation values authenticity, work-life balance, and flexibility, often leading the charge in advocating for remote work and alternative career paths.
Millennials (1981-1996)
Millennials, also known as Generation Y, were born between 1981 and 1996. They came of age during the digital revolution, with access to the internet, social media, and mobile technology shaping their lives in unprecedented ways. As a result, Millennials are often characterized by their tech-savviness and ability to navigate digital spaces.
This generation values diversity, inclusivity, and social justice, often driving conversations around these issues. Millennials are known for their commitment to work-life balance, seeking meaningful and purpose-driven careers. They are also the most educated generation, with many having pursued higher education despite the rising cost of tuition.
As Millennials enter their prime working and family-raising years, they continue to redefine traditional norms, challenging established practices in the workplace and beyond. Their influence is felt across industries, from technology and entertainment to politics and social change.
Generation Z (1997-2012)
Generation Z, born between 1997 and 2012, is the first generation to grow up in a fully digital world. This cohort is characterized by their comfort with technology and their ability to adapt quickly to new digital tools and platforms. They are often described as "digital natives," having never known a world without the internet.
Generation Z is marked by a strong sense of social and environmental responsibility. They are vocal advocates for issues such as climate change, equality, and mental health. This generation is also known for their entrepreneurial spirit, with many starting their own businesses or pursuing unconventional career paths.
As Generation Z enters the workforce, they bring a fresh perspective and a desire for change. They prioritize diversity and inclusivity and seek workplaces that align with their values. This generation's influence is expected to grow as they become more established in their careers and take on leadership roles.
Generation Alpha (2013-Present)
Generation Alpha, born from 2013 onwards, is the youngest and newest generation. This cohort is growing up in a world defined by rapid technological advancements and a globalized society. They are expected to be the most technologically adept generation yet, with access to cutting-edge innovations from an early age.
Members of Generation Alpha are being shaped by their parents' experiences, as well as the societal changes occurring around them. This generation is predicted to be highly educated, with a strong emphasis on STEM (science, technology, engineering, and mathematics) fields.
While it is still early to fully understand the characteristics and values of Generation Alpha, it is clear that they will play a crucial role in shaping the future. As they grow, they will navigate a world that is increasingly interconnected, diverse, and technology-driven.
How Do Generations Influence Culture?
Generations play a significant role in shaping culture by influencing societal norms, values, and behaviors. Each generation brings its own set of experiences, perspectives, and priorities, which collectively contribute to cultural evolution. As generational cohorts move through different life stages, they leave a lasting impact on various aspects of society, from fashion and music to politics and technology.
The cultural influence of generations is evident in the way they drive social change. For instance, Baby Boomers were instrumental in the civil rights movement and the feminist movement, challenging traditional norms and advocating for equality. Millennials have continued this legacy by championing issues such as LGBTQ+ rights, racial justice, and environmental sustainability.
Generational influence is also seen in consumer behavior, as each cohort has distinct preferences and expectations. Businesses must adapt to the changing demands of each generation, from product offerings to marketing strategies. Understanding generational differences is crucial for organizations seeking to engage and connect with diverse audiences.
The Impact of Technology on Generation Years
Technology has played a pivotal role in shaping the experiences and characteristics of different generations. Each generation has been influenced by the technological advancements of their time, from the introduction of television and radio for the Silent Generation to the rise of the internet and social media for Millennials and Generation Z.
For older generations, such as Baby Boomers and Generation X, technology has often been a tool for enhancing productivity and communication. They witnessed the transition from analog to digital and have adapted to new technologies over time. Millennials and Generation Z, on the other hand, are digital natives who have grown up with technology as an integral part of their lives.
The rapid pace of technological change has also contributed to the shortening of generation years, as new innovations continue to reshape the way we live, work, and interact. As technology evolves, so too do the characteristics and behaviors of each generation, highlighting the need for adaptability and lifelong learning.
Generational Differences in the Workplace
Generational differences in the workplace can significantly impact organizational culture, communication, and productivity. Each generation brings unique strengths, perspectives, and expectations to the table, which can either enhance or challenge workplace dynamics.
For instance, Baby Boomers often value loyalty and job stability, while Generation X seeks work-life balance and flexibility. Millennials prioritize collaboration and purpose-driven work, whereas Generation Z values diversity and inclusivity. Understanding these differences is essential for fostering a harmonious and productive work environment.
Effective communication is key to bridging generational gaps in the workplace. Organizations must adapt their communication styles and strategies to accommodate the preferences of different generations. This may involve leveraging technology, promoting intergenerational mentorship, and encouraging open dialogue.
What Challenges Do Different Generations Face?
Each generation faces unique challenges shaped by the socio-economic and cultural context of their time. Understanding these challenges is crucial for addressing the needs and concerns of diverse age groups.
- Silent Generation: As they age, members of the Silent Generation face challenges related to healthcare, retirement planning, and ageism. They may also grapple with adapting to new technologies and maintaining social connections.
- Baby Boomers: Baby Boomers are navigating retirement and financial security, as well as health and wellness concerns. They may also face challenges in adapting to rapidly changing technologies and societal norms.
- Generation X: Generation X often juggles multiple responsibilities, including work, family, and caregiving for aging parents. They may face challenges related to job security and career advancement, as well as managing work-life balance.
- Millennials: Millennials face economic challenges, including student debt, housing affordability, and job market instability. They may also encounter societal pressures related to achieving traditional milestones, such as marriage and homeownership.
- Generation Z: Generation Z faces mental health challenges, as well as issues related to social media and digital privacy. They may also grapple with navigating an uncertain job market and addressing pressing social and environmental concerns.
How Generations Shape Consumer Behavior
Generational cohorts have a significant impact on consumer behavior, influencing purchasing decisions, brand loyalty, and market trends. Each generation has distinct preferences and priorities that businesses must consider when developing products and marketing strategies.
For example, Baby Boomers have significant purchasing power and often prioritize quality and value in their buying decisions. They are more likely to be brand loyal and prefer traditional shopping methods. Generation X values convenience and efficiency, often seeking out products and services that offer flexibility and time-saving benefits.
Millennials are known for their preference for experiences over material goods, often seeking products that align with their values and social consciousness. They are also more likely to engage with brands through digital channels and social media. Generation Z, as digital natives, prioritize authenticity and transparency, often favoring brands that demonstrate social and environmental responsibility.
Understanding the consumer behavior of different generations is essential for businesses looking to connect with diverse audiences and drive growth in an ever-evolving marketplace.
Understanding Generational Values and Beliefs
Generational values and beliefs are shaped by the unique experiences and historical events that define each cohort. These values influence how individuals perceive the world, interact with others, and make decisions in their personal and professional lives.
The Silent Generation often values tradition, stability, and hard work, reflecting the challenges they faced during the Great Depression and World War II. Baby Boomers are known for their optimism, ambition, and desire for social change, having come of age during a period of post-war prosperity and cultural transformation.
Generation X values independence, adaptability, and authenticity, shaped by a rapidly changing world and the rise of digital technology. Millennials prioritize diversity, inclusivity, and work-life balance, influenced by the internet revolution and a growing awareness of social issues.
Generation Z is marked by their commitment to social and environmental responsibility, driven by their digital nativity and exposure to global challenges. Understanding these generational values is crucial for fostering empathy, collaboration, and mutual understanding across age groups.
How Does Education Vary Across Generations?
Education has evolved significantly across generations, reflecting changes in societal priorities, technological advancements, and access to information. Each generation has experienced education differently, influencing their learning styles, career aspirations, and perspectives on lifelong learning.
For the Silent Generation and Baby Boomers, education was often viewed as a means to secure stable employment and upward mobility. Traditional classroom settings and face-to-face instruction were the norm, with a focus on memorization and rote learning.
Generation X witnessed the integration of technology into education, with the introduction of personal computers and the internet. This generation values practical skills and experiential learning, often seeking out opportunities for professional development and career advancement.
Millennials have embraced online learning and digital resources, prioritizing flexibility and accessibility in their educational pursuits. They are more likely to pursue higher education, despite rising tuition costs, and value learning experiences that align with their personal and professional goals.
Generation Z is characterized by their preference for interactive and collaborative learning, often utilizing digital tools and platforms to enhance their educational experience. They value creativity, critical thinking, and problem-solving skills, recognizing the importance of adaptability in a rapidly changing world.
Frequently Asked Questions
What defines a generation year?
Generation years are defined by the specific time frames that distinguish different generational cohorts, influenced by unique historical, social, and economic factors.
Why is understanding generation years important?
Understanding generation years is important for businesses, educators, and policymakers as they adapt to the changing needs and values of diverse age groups.
How do generation years affect consumer behavior?
Generation years affect consumer behavior by influencing purchasing decisions, brand loyalty, and market trends, as each cohort has distinct preferences and priorities.
What challenges do Millennials face today?
Millennials face economic challenges, including student debt, housing affordability, and job market instability, as well as societal pressures related to achieving traditional milestones.
How do generational values influence workplace dynamics?
Generational values influence workplace dynamics by shaping organizational culture, communication, and productivity, as each generation brings unique strengths and expectations to the table.
What is the impact of technology on different generations?
Technology has shaped the experiences and characteristics of different generations, influencing everything from communication and productivity to social interactions and consumer behavior.
Conclusion
The concept of "generation years" offers a valuable framework for understanding the intricate tapestry of human development and societal change. By examining the distinct characteristics, values, and experiences of each generational cohort, we gain insights into the evolving dynamics of our world. From the Silent Generation to Generation Alpha, each group has played a unique role in shaping the cultural, economic, and technological landscape.
As we navigate the complexities of an ever-changing society, understanding generation years becomes increasingly important. It empowers us to bridge generational gaps, foster empathy and collaboration, and create inclusive environments that honor the diverse perspectives of all age groups. By embracing the lessons and contributions of each generation, we pave the way for a more connected, innovative, and equitable future.
For more information on generational trends and societal change, visit Pew Research Center.