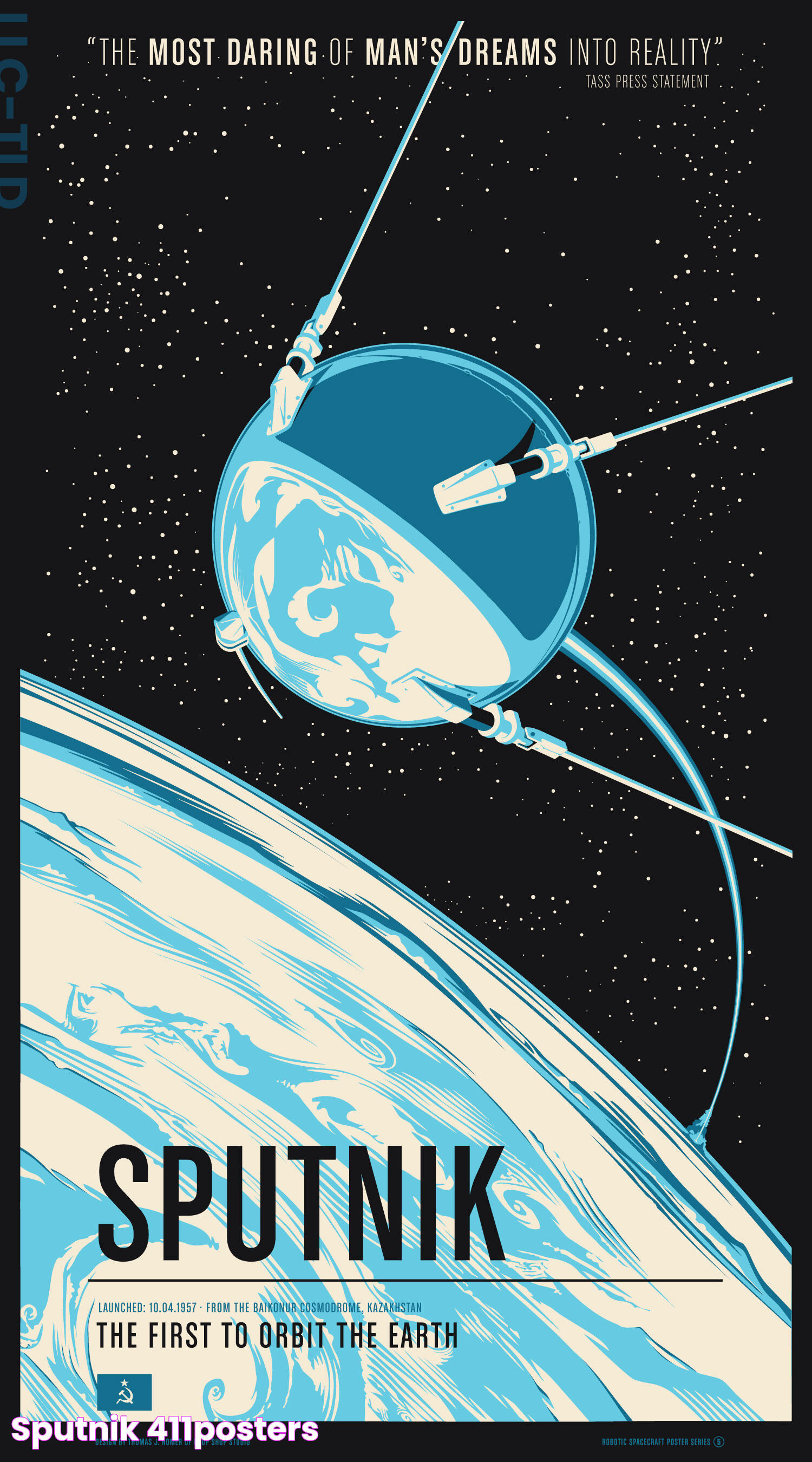
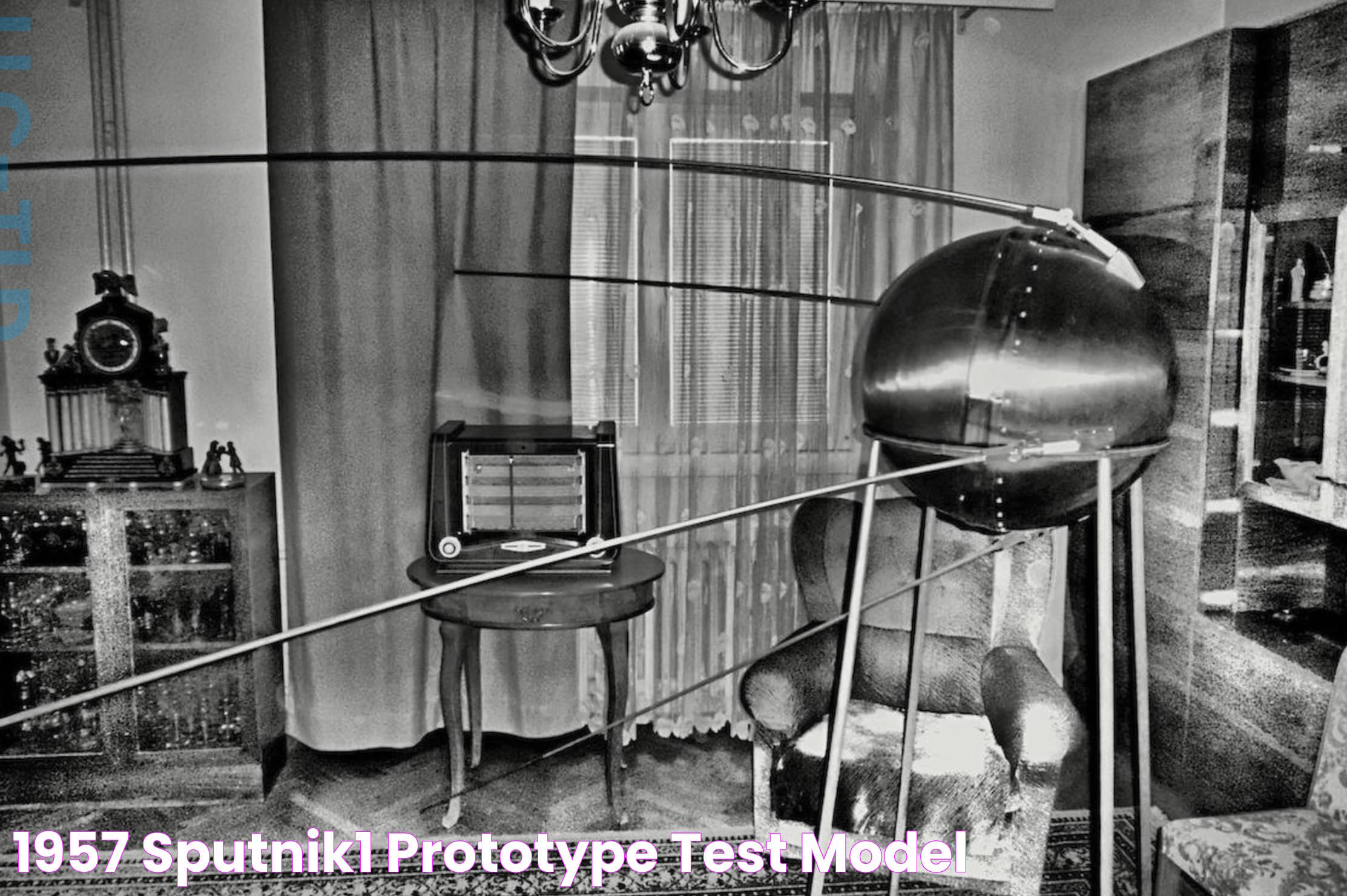
On October 4, 1957, the world witnessed a monumental leap in human achievement with the launch of Sputnik 1, the first artificial Earth satellite. This event marked the beginning of the space age and forever changed the course of history. The Soviet Union, under the leadership of Sergei Korolev, successfully launched the satellite, igniting a fierce space race with the United States. Sputnik 1's launch was not only a technological triumph but also a demonstration of political and military prowess during the Cold War era.
The satellite, a 58-centimeter-diameter metal sphere with four external radio antennas, emitted radio pulses that could be detected by radios around the globe. Sputnik 1's simple design masked its profound impact on science, technology, and international relations. The data gathered from its orbit provided invaluable insights into the density of the upper atmosphere and paved the way for future space exploration missions. The success of Sputnik 1 fueled a surge of interest in science and engineering, leading to advancements in technology that continue to shape our world today.
Sputnik 1's launch not only marked a significant milestone in space exploration but also underscored the importance of international cooperation and competition in pushing the boundaries of human knowledge. As we reflect on this historic achievement, we recognize the enduring legacy of Sputnik 1 and its role in inspiring generations of scientists, engineers, and dreamers to look beyond the confines of our planet and explore the mysteries of the cosmos.
Read also:Snapgod Izzy S A Deep Dive Into The Life And Legacy
Table of Contents
- The Birth of Sputnik 1
- Technical Specifications of Sputnik 1
- The Launch of Sputnik 1
- How Did Sputnik 1 Impact the World?
- Scientific Contributions of Sputnik 1
- Sputnik 1 and the Cold War
- Who Was Behind the Success of Sputnik 1?
- Challenges Faced During Sputnik 1 Development
- Sputnik 1 in Popular Culture
- The Legacy of Sputnik 1
- What Lessons Did We Learn from Sputnik 1?
- Frequently Asked Questions About Sputnik 1
- Conclusion
The Birth of Sputnik 1
The story of Sputnik 1 begins in the Soviet Union during the early 1950s, a time when the world was gripped by the tensions of the Cold War. The Soviet government, eager to establish its dominance in the field of space exploration, initiated a series of projects aimed at developing the capability to launch artificial satellites. Sergei Korolev, a visionary engineer and scientist, played a pivotal role in the development of Sputnik 1. As the chief designer of the Soviet space program, Korolev was instrumental in realizing the dream of launching the first artificial satellite into orbit. Under his leadership, the Soviet Union embarked on an ambitious project to design and build a satellite that would orbit the Earth, demonstrating the country's technological prowess and challenging the United States in the burgeoning space race.
Sputnik 1 was conceived as a simple yet effective satellite, designed to transmit radio signals that could be received by ground stations around the world. The development of the satellite was marked by a series of technical challenges, including the need to design a reliable launch vehicle capable of delivering the satellite into orbit. Despite these challenges, the Soviet team, led by Korolev, worked tirelessly to ensure the successful launch of Sputnik 1. The satellite's design was finalized in 1956, and construction began shortly thereafter. By 1957, all components of Sputnik 1 were assembled and tested, paving the way for its historic launch.
The successful launch of Sputnik 1 marked a turning point in the history of space exploration, demonstrating the feasibility of launching artificial satellites into orbit and opening the door to future space missions. The satellite's design and development were a testament to the ingenuity and determination of the Soviet scientists and engineers who worked tirelessly to achieve this milestone. The launch of Sputnik 1 was not only a technological triumph but also a symbol of the Soviet Union's commitment to advancing human knowledge and exploration beyond the confines of Earth.
Technical Specifications of Sputnik 1
Sputnik 1 was a marvel of engineering, characterized by its simple yet effective design. The satellite was a metal sphere with a diameter of 58 centimeters and a weight of approximately 83.6 kilograms. Its surface was polished to a high sheen, allowing it to reflect sunlight and be visible from Earth as it orbited the planet. The sphere was equipped with four protruding radio antennas, which were designed to transmit signals back to Earth. These signals, consisting of a series of beeps, were broadcast on two frequencies: 20.005 and 40.002 MHz. The simplicity of Sputnik 1's design belied its significant impact on science and technology.
The satellite's internal components were designed to withstand the harsh conditions of space, including extreme temperatures and radiation. Sputnik 1 was equipped with a thermal control system to maintain a stable internal temperature, ensuring the proper functioning of its electronic components. The satellite's power source consisted of three silver-zinc batteries, which provided the necessary energy to operate its radio transmitters for approximately 21 days. Beyond this period, the satellite continued to orbit the Earth, but its radio transmissions ceased.
Sputnik 1's launch vehicle, the R-7 Semyorka, was a remarkable achievement in its own right. Originally developed as an intercontinental ballistic missile, the R-7 was modified to serve as a launch vehicle for the satellite. It was equipped with four strap-on boosters and a core stage, providing the necessary thrust to propel Sputnik 1 into orbit. The successful launch of Sputnik 1 demonstrated the reliability and effectiveness of the R-7, which would later serve as the basis for future Soviet space missions.
Read also:Magi Names Unraveling The Mystical Symbols Of Ancient Wisdom
The Launch of Sputnik 1
The launch of Sputnik 1 took place at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan, a remote launch site that had been constructed specifically for the Soviet space program. On October 4, 1957, at precisely 19:28:34 UTC, the R-7 Semyorka rocket carrying Sputnik 1 lifted off from the launch pad, beginning its journey into orbit. The launch was a meticulously planned operation, with every detail carefully considered to ensure the success of the mission. As the rocket ascended into the sky, the world watched in awe, recognizing the significance of this historic moment.
The launch of Sputnik 1 was a flawless execution of engineering and technology, with the satellite successfully entering a low Earth orbit approximately 96 minutes after liftoff. Once in orbit, Sputnik 1 began transmitting its iconic radio signals, which were received by ground stations around the world. The success of the launch was a monumental achievement for the Soviet Union, affirming its position as a leader in space exploration and igniting a fervent interest in space technology and science.
The launch of Sputnik 1 had a profound impact on international relations, particularly between the United States and the Soviet Union. The success of the Soviet satellite underscored the need for the United States to invest in its own space program, leading to the creation of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) in 1958. The launch of Sputnik 1 marked the beginning of the space race, a period of intense competition between the United States and the Soviet Union to achieve dominance in space exploration.
How Did Sputnik 1 Impact the World?
Sputnik 1's launch had far-reaching implications for science, technology, and international relations. The successful deployment of the first artificial satellite demonstrated the feasibility of space exploration and sparked a global interest in space science and engineering. The satellite's radio signals provided valuable data on the density of the Earth's upper atmosphere, contributing to our understanding of the planet's environment and laying the groundwork for future space missions.
The launch of Sputnik 1 also had a profound impact on the geopolitical landscape of the time, particularly in the context of the Cold War. The Soviet Union's success in launching the first artificial satellite was perceived as a significant technological and political victory, challenging the United States' position as a global leader in science and technology. The event prompted the United States to accelerate its own space program, leading to increased investment in science and technology education and the establishment of NASA.
The impact of Sputnik 1 extended beyond the realm of politics and science, influencing popular culture and inspiring a generation of scientists, engineers, and dreamers to pursue careers in space exploration. The satellite's iconic radio signals became a symbol of human achievement and the limitless possibilities of space exploration. Sputnik 1's legacy continues to inspire and motivate individuals to push the boundaries of human knowledge and exploration.
Scientific Contributions of Sputnik 1
Sputnik 1 made significant contributions to the field of science, providing valuable data that advanced our understanding of the Earth's environment and the challenges of space exploration. The satellite's radio signals, transmitted on two frequencies, allowed scientists to study the characteristics of the ionosphere, a region of the Earth's atmosphere that reflects radio waves. By analyzing the changes in signal strength, researchers were able to gather information about the density and composition of the ionosphere, contributing to our understanding of this important atmospheric layer.
The orbit of Sputnik 1 also provided insights into the behavior of artificial satellites in space, helping scientists to develop models of satellite motion and predict their trajectories. The data collected from Sputnik 1's orbit informed the design and development of future satellites, paving the way for more advanced space missions. The success of Sputnik 1 demonstrated the feasibility of using artificial satellites for scientific research, leading to the development of new technologies and methodologies for studying the Earth's environment and the broader cosmos.
Sputnik 1's contributions to science extended beyond the immediate data it provided, inspiring a new era of exploration and discovery. The satellite's success encouraged governments and institutions around the world to invest in space research, leading to the development of new technologies and the expansion of scientific knowledge. Sputnik 1's legacy continues to shape the field of space science, influencing the design of modern satellites and contributing to our understanding of the universe.
Sputnik 1 and the Cold War
The launch of Sputnik 1 occurred at the height of the Cold War, a period of intense rivalry between the United States and the Soviet Union. This geopolitical tension added a layer of complexity to the satellite's launch, as it was seen not only as a scientific achievement but also as a demonstration of military and technological superiority. The success of Sputnik 1 was perceived as a significant victory for the Soviet Union, challenging the United States' position as a global leader in science and technology.
The launch of Sputnik 1 had a profound impact on the United States, prompting a reevaluation of its space program and leading to increased investment in science and technology education. The event highlighted the need for the United States to compete with the Soviet Union in the field of space exploration, resulting in the creation of NASA in 1958. The space race became a defining aspect of the Cold War, with both superpowers striving to achieve significant milestones in space exploration.
The launch of Sputnik 1 also had a broader impact on international relations, influencing the development of space policies and agreements. The satellite's success underscored the importance of international cooperation in space exploration, leading to discussions on the peaceful use of outer space and the establishment of frameworks for international collaboration. Sputnik 1's legacy continues to influence international space policy, promoting cooperation and collaboration in the exploration of the cosmos.
Who Was Behind the Success of Sputnik 1?
The success of Sputnik 1 was the result of the collective efforts of a dedicated team of scientists, engineers, and visionaries who worked tirelessly to achieve this historic milestone. At the forefront of this effort was Sergei Korolev, a brilliant engineer and scientist who served as the chief designer of the Soviet space program. Korolev's leadership and vision were instrumental in the development and launch of Sputnik 1, guiding the project from its inception to its successful completion.
Korolev's team consisted of a diverse group of experts, each contributing their unique skills and expertise to the development of Sputnik 1. This team included prominent figures such as Mstislav Keldysh, a mathematician who played a key role in developing the theoretical models for satellite motion, and Valentin Glushko, a propulsion specialist who contributed to the design of the rocket engines used in the launch vehicle. The collaborative efforts of these individuals, along with countless others, were essential to the success of Sputnik 1.
The launch of Sputnik 1 was also supported by the broader Soviet government, which recognized the importance of space exploration in demonstrating the country's technological prowess and political influence. The success of Sputnik 1 was a testament to the dedication and determination of the individuals behind the project, who overcame numerous challenges to achieve this historic milestone. Their legacy continues to inspire future generations of scientists and engineers, motivating them to pursue the exploration of the cosmos.
Challenges Faced During Sputnik 1 Development
The development of Sputnik 1 was fraught with challenges, as the Soviet team faced numerous technical and logistical obstacles in their quest to launch the first artificial satellite. One of the primary challenges was the design and construction of a reliable launch vehicle capable of delivering the satellite into orbit. The R-7 Semyorka rocket, originally developed as an intercontinental ballistic missile, had to be modified to accommodate the satellite and ensure a successful launch.
In addition to the challenges associated with the launch vehicle, the team also faced difficulties in designing and constructing the satellite itself. Sputnik 1 had to be lightweight yet durable, with the ability to withstand the harsh conditions of space. The satellite's radio transmitters needed to be powerful enough to send signals back to Earth, while its power source had to be efficient and long-lasting. Despite these challenges, the Soviet team worked tirelessly to overcome each obstacle, utilizing their expertise and ingenuity to ensure the success of the mission.
The development of Sputnik 1 also required significant coordination and collaboration among various government agencies and institutions, each contributing their resources and expertise to the project. The logistical challenges of managing such a large and complex operation were significant, requiring careful planning and execution to ensure that each component of the mission was completed on time and to the highest standards. Despite these challenges, the Soviet team succeeded in launching Sputnik 1, setting the stage for future space exploration missions.
Sputnik 1 in Popular Culture
The launch of Sputnik 1 captured the imagination of people around the world, becoming a cultural icon and symbol of human achievement. The satellite's iconic radio signals, heard by radio operators across the globe, became emblematic of the dawn of the space age and the limitless possibilities of space exploration. Sputnik 1's launch was widely covered in the media, inspiring countless articles, books, and films that celebrated its significance and impact.
Sputnik 1's influence extended beyond the realm of science and technology, permeating popular culture and inspiring a new generation of artists, writers, and musicians. The satellite's success was celebrated in music and literature, with artists drawing inspiration from its historic achievement to create works that captured the excitement and wonder of space exploration. Sputnik 1's legacy continues to inspire creative expression, serving as a symbol of innovation and the pursuit of knowledge.
The cultural impact of Sputnik 1 also extended to the realm of education, inspiring a renewed interest in science and technology among students and educators. The satellite's success underscored the importance of investing in science education, leading to increased funding and support for programs that encouraged young people to pursue careers in the fields of science and engineering. Sputnik 1's legacy continues to inspire and motivate individuals to explore the wonders of the cosmos, fostering a sense of curiosity and wonder that transcends generations.
The Legacy of Sputnik 1
The legacy of Sputnik 1 extends far beyond its historic launch, influencing the course of space exploration and shaping the future of science and technology. The satellite's success demonstrated the feasibility of space exploration, paving the way for future missions and advancing our understanding of the universe. Sputnik 1's contributions to science and technology continue to resonate, inspiring new generations to push the boundaries of human knowledge and exploration.
Sputnik 1's impact on international relations and the geopolitical landscape of the time was significant, shaping the development of space policies and agreements that continue to influence international collaboration in space exploration. The satellite's success underscored the importance of cooperation and competition in advancing human knowledge, highlighting the potential for space exploration to serve as a unifying force for humanity.
The legacy of Sputnik 1 is also reflected in the continued exploration of space, with modern satellites and space missions building upon the foundation established by this historic achievement. The satellite's success inspired a renewed interest in science and technology, fostering a culture of innovation and discovery that continues to drive advancements in the fields of space science and engineering. Sputnik 1's legacy serves as a testament to the power of human ingenuity and the enduring spirit of exploration.
What Lessons Did We Learn from Sputnik 1?
The launch of Sputnik 1 provided valuable lessons that continue to inform the field of space exploration and the broader scientific community. One of the key lessons learned from Sputnik 1 was the importance of collaboration and teamwork in achieving complex scientific and technological goals. The success of Sputnik 1 was the result of the collective efforts of a diverse group of scientists, engineers, and visionaries, each contributing their unique skills and expertise to the project.
Another important lesson from Sputnik 1 was the significance of perseverance and determination in overcoming challenges and achieving success. The development of Sputnik 1 was marked by numerous technical and logistical obstacles, yet the Soviet team remained committed to their goal, working tirelessly to overcome each challenge and ensure the success of the mission.
Sputnik 1 also underscored the importance of investing in education and fostering a culture of innovation and discovery. The satellite's success inspired a renewed interest in science and technology, highlighting the need for continued investment in education and research to drive advancements and push the boundaries of human knowledge.
Finally, Sputnik 1 demonstrated the potential for space exploration to serve as a unifying force for humanity, highlighting the importance of international cooperation and collaboration in advancing our understanding of the universe. The satellite's success underscored the potential for space exploration to transcend geopolitical boundaries and serve as a catalyst for global cooperation and understanding.
Frequently Asked Questions About Sputnik 1
1. What was the purpose of Sputnik 1?
Sputnik 1 was launched to demonstrate the feasibility of artificial satellites and gather data on the upper atmosphere. Its success marked the beginning of the space age and inspired future space exploration missions.
2. How long did Sputnik 1 remain in orbit?
Sputnik 1 remained in orbit for approximately three months, completing 1,440 orbits before re-entering Earth's atmosphere and burning up on January 4, 1958.
3. What impact did Sputnik 1 have on the United States?
The launch of Sputnik 1 prompted the United States to accelerate its space program, leading to the creation of NASA in 1958 and increased investment in science and technology education.
4. How did Sputnik 1 contribute to scientific research?
Sputnik 1 provided valuable data on the density and composition of the ionosphere, contributing to our understanding of the Earth's atmosphere and informing the design of future satellites.
5. What challenges were faced during Sputnik 1's development?
The development of Sputnik 1 was marked by technical challenges, including designing a reliable launch vehicle and ensuring the satellite's components could withstand the harsh conditions of space.
6. Who was Sergei Korolev, and what was his role in Sputnik 1's success?
Sergei Korolev was the chief designer of the Soviet space program and played a pivotal role in the development and launch of Sputnik 1. His leadership and vision were instrumental in the success of the mission.
Conclusion
The launch of Sputnik 1 was a defining moment in the history of space exploration, marking the beginning of the space age and inspiring a new era of discovery and innovation. The satellite's success demonstrated the feasibility of space exploration, paving the way for future missions and advancing our understanding of the universe. Sputnik 1's legacy continues to resonate, inspiring new generations to push the boundaries of human knowledge and exploration.
Sputnik 1's impact extended beyond the realm of science and technology, influencing international relations and shaping the development of space policies and agreements. The satellite's success underscored the importance of cooperation and competition in advancing human knowledge, highlighting the potential for space exploration to serve as a unifying force for humanity.
As we reflect on the achievements of Sputnik 1, we recognize the enduring legacy of this historic milestone and its role in inspiring future generations to explore the wonders of the cosmos. Sputnik 1's success serves as a testament to the power of human ingenuity and the enduring spirit of exploration, motivating us to continue our quest to understand and explore the universe.