, commonly known as the pork tapeworm, is a parasitic worm that has captivated the attention of scientists and health professionals around the world. This complex organism is responsible for a range of health issues in humans, primarily through its life cycle as a tapeworm in the intestines. The lifecycle of Taenia solium involves various stages, including a fascinating transition from pigs to humans, making it a subject of study in parasitology and public health. Understanding Taenia solium is crucial for preventing and controlling infections, especially in regions where it is endemic. The life cycle of Taenia solium is intricate and involves two main hosts: pigs and humans. Pigs act as intermediate hosts when they ingest eggs that are shed by humans in feces. Once inside the pig, the eggs develop into larvae, which then form cysts within the pig's muscles. Humans become infected when they consume undercooked or raw pork containing these cysts. Upon ingestion, the larvae are released in the human digestive system, where they mature into adult tapeworms, leading to a condition known as taeniasis. In some cases, the larvae can migrate to various tissues in the human body, causing cysticercosis, a more severe condition. The widespread distribution of Taenia solium is a significant public health issue, particularly in developing countries where sanitation and animal husbandry practices may be inadequate. The World Health Organization recognizes the importance of controlling Taenia solium infections due to their impact on human health and economic development. By implementing effective control measures, such as improving sanitation, educating communities, and treating infected individuals, it is possible to reduce the prevalence of this parasite. In this article, we will explore the biology, life cycle, symptoms, diagnosis, and prevention strategies related to Taenia solium, providing a comprehensive understanding of this fascinating yet concerning organism. Table of Contents: 1. What is Taenia Solium? 2. The Life Cycle of Taenia Solium 1. How does Taenia Solium infect humans? 2. What are the stages of Taenia Solium's life cycle? 3. Symptoms of Taeniasis and Cysticercosis 1. How does Taeniasis manifest in humans? 2. What are the effects of Cysticercosis? 4. Diagnosis of Taenia Solium Infections 5. Treatment Options for Taenia Solium 6. Prevention and Control Measures 7. Impact of Taenia Solium on Public Health 8. Taenia Solium in Pigs: A Closer Look 9. The Global Distribution of Taenia Solium 10. Taenia Solium and Food Safety 11. Research and Developments in Taenia Solium Control 12. Frequently Asked Questions 13. Conclusion
1. What is Taenia Solium?
Taenia solium, also known as the pork tapeworm, is a parasitic flatworm belonging to the class Cestoda. It primarily infects pigs and humans, causing two major health conditions: taeniasis and cysticercosis. The adult tapeworm resides in the small intestine of humans, while the larval stage, or cysticercus, can form cysts in the tissues of both humans and pigs.
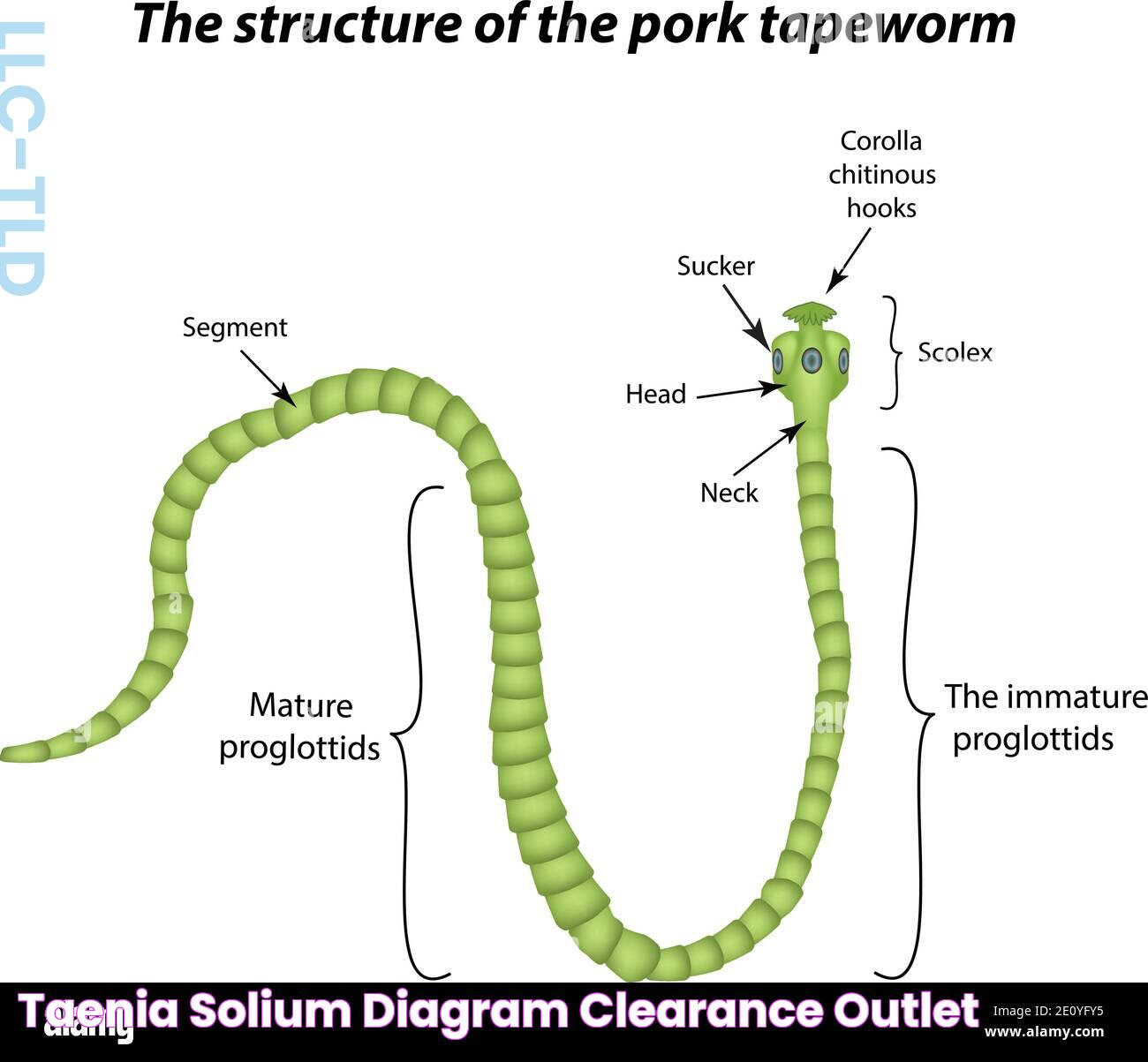
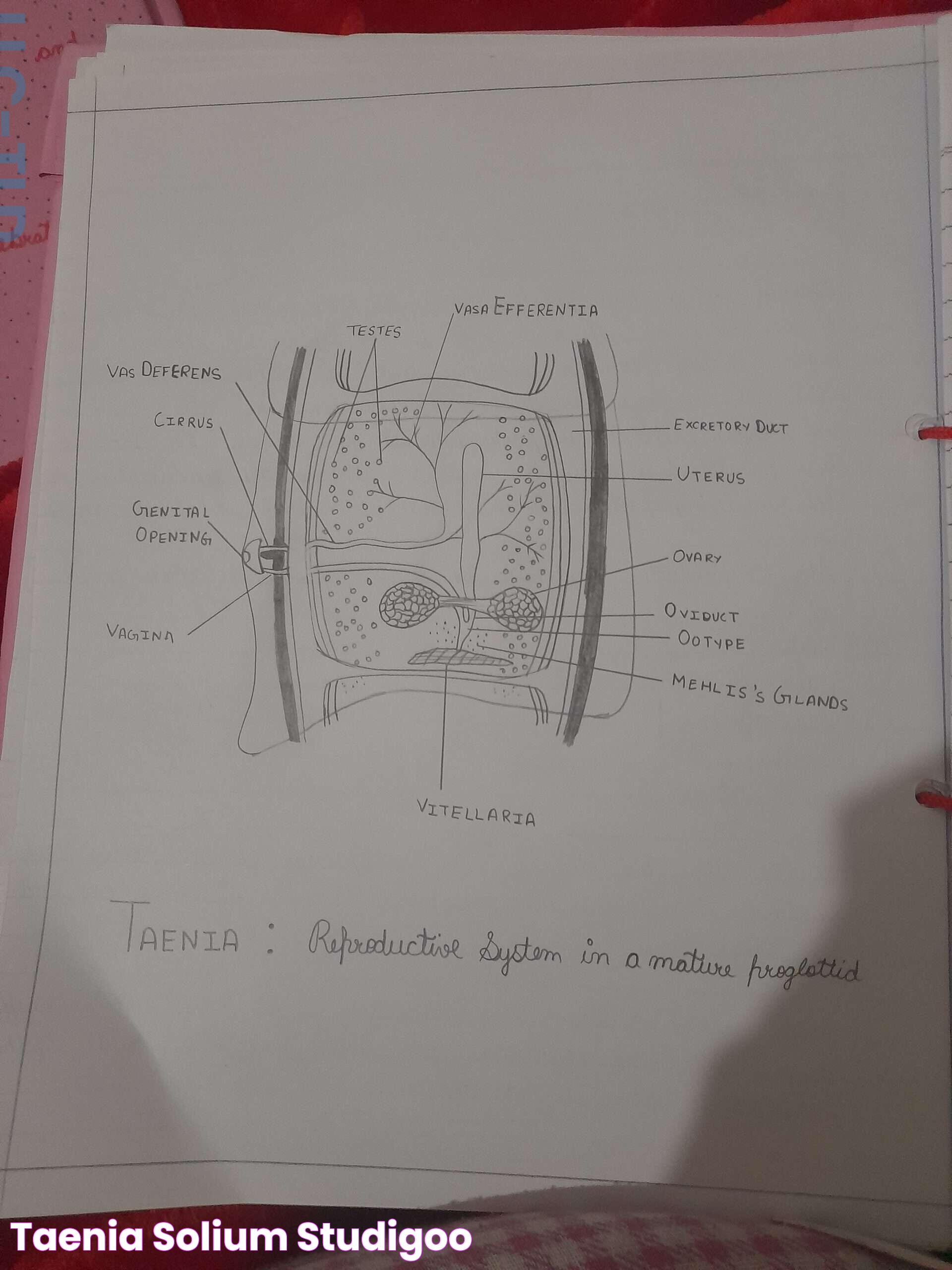
Taenia solium has a complex morphology characterized by a scolex (head) with hooks and suckers, a neck, and a series of proglottids (segments) that contain reproductive organs. This structure allows the tapeworm to attach to the intestinal wall and absorb nutrients directly from the host's digested food.
Read also:Ultimate Guide To Dining At Carmines Italian Restaurant
The significance of Taenia solium lies in its impact on human health and its role in zoonotic transmission. It is prevalent in areas with poor sanitation and where pigs are raised in close proximity to humans. Understanding Taenia solium's biology is crucial for developing effective control strategies to minimize its transmission and associated health risks.
2. The Life Cycle of Taenia Solium
2.1 How does Taenia Solium infect humans?
Humans become infected with Taenia solium through the consumption of undercooked or raw pork contaminated with cysticerci, the larval form of the tapeworm. These cysticerci are present in the muscles of pigs that have ingested tapeworm eggs, which are excreted in the feces of infected humans.
Upon ingestion, the cysticerci are released in the human digestive tract, where they attach to the intestinal wall and mature into adult tapeworms. This results in taeniasis, a condition where the adult tapeworm resides in the intestines, often causing mild symptoms or remaining asymptomatic.
2.2 What are the stages of Taenia Solium's life cycle?
The life cycle of Taenia solium involves several stages, each crucial for its transmission and survival:
- Egg Stage: Eggs are released into the environment through the feces of an infected human host.
- Larval Stage: Pigs ingest the eggs, which hatch into larvae and penetrate the intestinal wall to reach the bloodstream.
- Cysticercus Stage: Larvae develop into cysticerci within the pig's muscles, forming cysts that are infectious to humans.
- Adult Stage: Humans ingest cysticerci by eating contaminated pork, leading to the development of adult tapeworms in the intestines.
This cycle perpetuates the transmission of Taenia solium between pigs and humans, underscoring the importance of controlling both stages to prevent infections.
3. Symptoms of Taeniasis and Cysticercosis
3.1 How does Taeniasis manifest in humans?
Taeniasis is caused by the presence of adult Taenia solium tapeworms in the human intestines. The symptoms are often mild or non-existent, but some individuals may experience:
Read also:Reflective Moments The Impact Of If I Turn Back Time
- Abdominal pain
- Nausea
- Diarrhea
- Unexplained weight loss
- Digestive disturbances
In many cases, individuals may be unaware of the infection until they pass segments of the tapeworm in their stool.
3.2 What are the effects of Cysticercosis?
Cysticercosis occurs when Taenia solium larvae migrate to tissues outside the intestines, forming cysts in various parts of the body. This condition is more severe and can lead to complications, particularly when cysts form in the central nervous system:
- Seizures and neurological symptoms
- Headaches
- Vision problems
- Confusion and difficulty with balance
- Chronic pain in muscles or other tissues
Neurocysticercosis, the presence of cysts in the brain, is a significant cause of epilepsy and other neurological disorders in endemic regions.
4. Diagnosis of Taenia Solium Infections
Diagnosing Taenia solium infections involves several methods, each aimed at detecting either the adult tapeworm or larval cysts:
- Stool Examination: Identifying tapeworm eggs or proglottids in stool samples to confirm taeniasis.
- Serological Tests: Detecting antibodies against Taenia solium in the blood, particularly for cysticercosis.
- Imaging Techniques: MRI or CT scans to visualize cysts in tissues, especially in cases of neurocysticercosis.
- Biopsy: In some cases, a tissue biopsy may be necessary to confirm the presence of cysts.
Early and accurate diagnosis is essential for effective treatment and management of Taenia solium infections.
5. Treatment Options for Taenia Solium
Treatment for Taenia solium infections varies depending on the type of infection and its severity:
- Taeniasis: Antiparasitic medications such as praziquantel or niclosamide are commonly used to eliminate adult tapeworms from the intestines.
- Cysticercosis: Treatment may include a combination of antiparasitic drugs, anti-inflammatory medications, and supportive care. In cases of neurocysticercosis, antiepileptic drugs may be prescribed to manage seizures.
Surgical intervention may be necessary to remove cysts in certain cases, particularly when they cause significant symptoms or complications.
6. Prevention and Control Measures
Effective prevention and control of Taenia solium infections require a comprehensive approach, addressing both human and animal hosts:
- Improving Sanitation: Ensuring proper disposal of human waste to prevent contamination of the environment and pig feed.
- Health Education: Raising awareness about the risks of consuming undercooked pork and promoting safe food handling practices.
- Regular Deworming: Implementing deworming programs for both humans and pigs in endemic areas.
- Veterinary Surveillance: Monitoring and treating pigs for Taenia solium infections to reduce the risk of transmission to humans.
Public health initiatives focused on education and infrastructure improvements are crucial for reducing the prevalence of Taenia solium and its associated health impacts.
7. Impact of Taenia Solium on Public Health
Taenia solium infections pose significant public health challenges, particularly in regions with limited resources. The parasite contributes to morbidity and mortality through conditions like cysticercosis, which can lead to chronic health issues and economic burdens for affected communities.
The World Health Organization has identified Taenia solium as a neglected tropical disease, highlighting the need for increased awareness, research, and control measures. Addressing the public health impact of this parasite requires a coordinated effort involving governments, health organizations, and communities.
8. Taenia Solium in Pigs: A Closer Look
Pigs play a crucial role in the life cycle of Taenia solium as intermediate hosts. Ingestion of contaminated feed or water leads to infection, with larvae forming cysts within the pig's muscles. These cysticerci are the primary source of human infections when pork is not cooked properly.
Improving pig husbandry practices, such as providing safe and clean feed, regular veterinary care, and confinement to prevent access to human waste, can significantly reduce the prevalence of Taenia solium in pigs and, consequently, in humans.
9. The Global Distribution of Taenia Solium
Taenia solium is prevalent in many parts of the world, particularly in regions with poor sanitation and where pigs are a common source of food. Areas most affected include parts of Latin America, Africa, and Asia. Understanding the distribution patterns of Taenia solium is essential for targeting control efforts and resources effectively.
Global initiatives aim to map the prevalence of Taenia solium and implement region-specific strategies to combat its spread, improve sanitation, and promote food safety.
10. Taenia Solium and Food Safety
Food safety plays a critical role in preventing Taenia solium infections. Proper cooking and preparation of pork, adherence to hygienic practices, and food inspection are essential components of food safety measures.
Educating communities about the importance of thoroughly cooking pork and avoiding raw or undercooked meat is vital in reducing the risk of taeniasis and cysticercosis. For food safety professionals and industries, implementing rigorous inspection and quality control standards is key to ensuring the safety of pork products.
11. Research and Developments in Taenia Solium Control
Ongoing research and technological advancements are enhancing our understanding of Taenia solium and improving control measures. Innovations in diagnostics, treatment options, and preventive strategies hold promise for reducing the burden of Taenia solium infections worldwide.
Collaborative efforts between researchers, health organizations, and governments are crucial in developing and implementing effective interventions, sharing knowledge, and ultimately eradicating Taenia solium as a public health concern.
12. Frequently Asked Questions
12.1 What is Taenia solium?
Taenia solium, commonly known as the pork tapeworm, is a parasitic flatworm that primarily infects pigs and humans, causing taeniasis and cysticercosis.
12.2 How do humans get infected with Taenia solium?
Humans become infected by consuming undercooked or raw pork containing cysticerci, the larval stage of Taenia solium.
12.3 What are the symptoms of Taeniasis?
Symptoms of taeniasis may include abdominal pain, nausea, diarrhea, and unexplained weight loss, though it can also be asymptomatic.
12.4 How is cysticercosis diagnosed?
Cysticercosis is diagnosed through serological tests, imaging techniques like MRI or CT scans, and sometimes tissue biopsies.
12.5 What are the treatment options for Taenia solium infections?
Treatment includes antiparasitic medications for taeniasis and a combination of drugs and supportive care for cysticercosis.
12.6 How can Taenia solium infections be prevented?
Prevention involves improving sanitation, educating communities, regular deworming, and ensuring proper cooking and handling of pork.
13. Conclusion
Taenia solium presents a complex challenge for public health, with its intricate life cycle and significant impact on human health. Understanding its biology, transmission, and effects is crucial for developing effective control measures. Through improved sanitation, education, and food safety practices, it is possible to reduce the prevalence of Taenia solium infections and mitigate their impact on affected communities. Continued research and collaboration are essential for advancing our knowledge and strategies to combat this parasitic threat.
For further reading on parasitic diseases and their impact on global health, refer to resources provided by the World Health Organization and other leading health organizations.