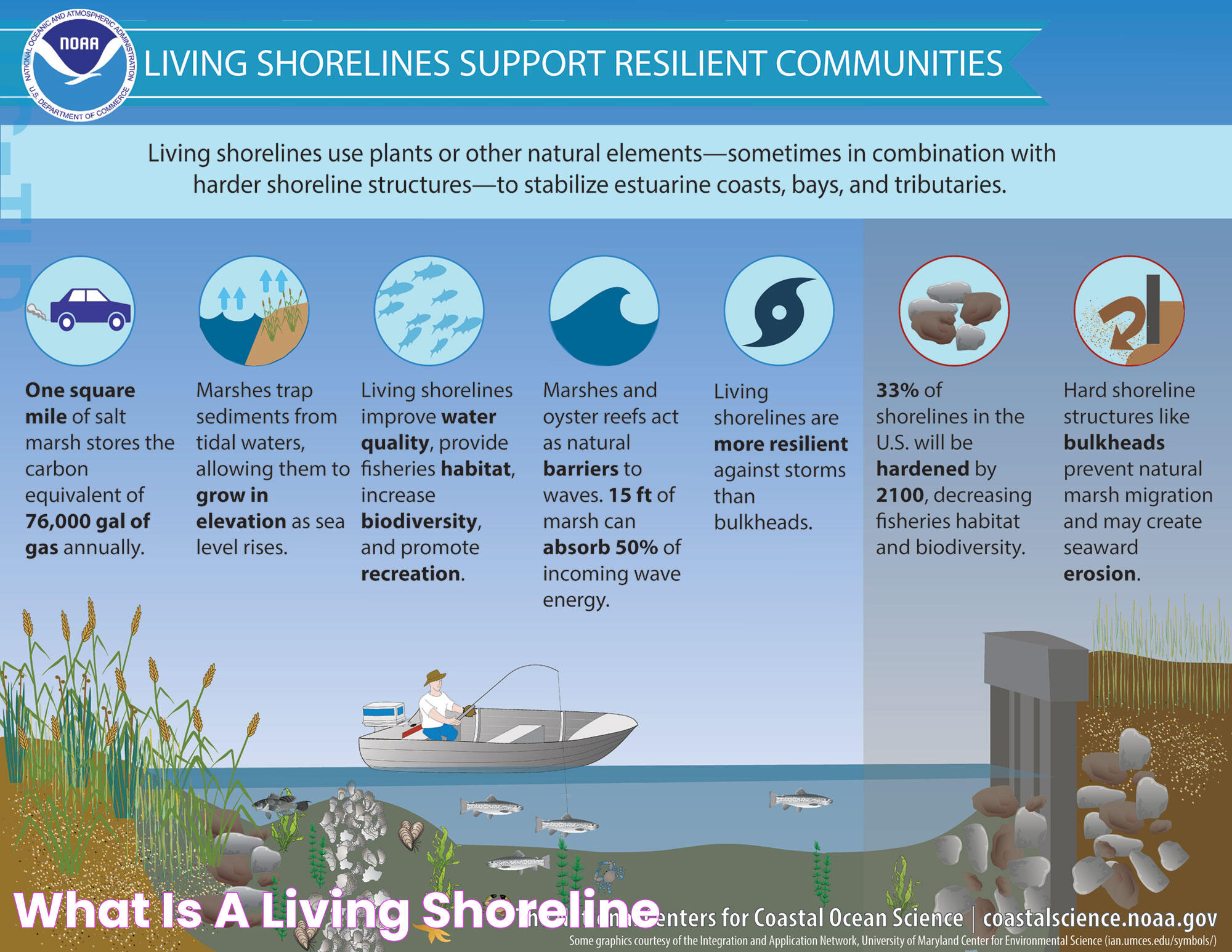
The weather along coastlines can vary significantly from one region to another, shaped by geographical features, ocean currents, and atmospheric conditions. Shoreline weather is characterized by its dynamic nature, often changing rapidly and unpredictably. Whether you're a beachgoer, a sailor, or simply someone interested in meteorology, gaining insights into shoreline weather can enhance your appreciation of these enchanting landscapes. This article delves into the fascinating world of shoreline weather, exploring the factors that influence it, its impact on human activities, and how it might change in the future. With a focus on providing clear and informative content, we'll guide you through the intricacies of coastal climates, offering a comprehensive understanding of the subject.
| Content | Subsection | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. What Defines Shoreline Weather? | 1.1 Factors Influencing Shoreline Weather | 1.2 Common Shoreline Weather Patterns |
| 2. How Do Ocean Currents Affect Shoreline Weather? | 2.1 The Role of Warm and Cold Currents | 2.2 Impact on Local Climate |
| 3. What is the Influence of Geography on Shoreline Weather? | 3.1 Coastal Topography | 3.2 The Role of Elevation and Latitude |
| 4. How Does Shoreline Weather Impact Human Activities? | 4.1 Tourism and Recreation | 4.2 Fishing and Marine Transportation |
| 5. What are the Challenges of Predicting Shoreline Weather? | 5.1 Technological Advances in Meteorology | 5.2 Limitations and Uncertainties |
| 6. How is Shoreline Weather Affected by Climate Change? | 6.1 Rising Sea Levels | 6.2 Increasing Storm Intensity |
| 7. How Can Communities Adapt to Changing Shoreline Weather? | 7.1 Infrastructure and Urban Planning | 7.2 Emergency Preparedness |
| 8. What Technologies Help Monitor Shoreline Weather? | 8.1 Satellite Imagery | 8.2 Weather Buoys and Sensors |
| 9. How Does Shoreline Weather Influence Wildlife and Ecosystems? | 9.1 Coastal Habitats | 9.2 Migration Patterns |
| 10. Shoreline Weather and Renewable Energy | 10.1 Wind and Solar Power | 10.2 Tidal and Wave Energy |
| 11. What are Some Famous Shoreline Weather Events? | 11.1 Historic Hurricanes and Typhoons | 11.2 Notable Storm Surges |
| 12. How Do Cultural Practices Relate to Shoreline Weather? | 12.1 Indigenous Knowledge and Traditions | 12.2 Festivals and Celebrations |
| 13. Shoreline Weather in Literature and Art | 13.1 Symbolism and Inspiration | 13.2 Representations in Media |
| 14. FAQs About Shoreline Weather | 14.1 Understanding Weather Alerts | 14.2 Preparing for Coastal Storms |
| 15. Conclusion |
1. What Defines Shoreline Weather?
Shoreline weather is defined by the unique climatic conditions that occur along coastlines, where land meets the ocean. This type of weather is influenced by a combination of atmospheric and oceanic factors that are distinct from those affecting inland areas. Due to the proximity of large bodies of water, shoreline weather is often characterized by higher humidity levels, more moderate temperatures, and frequent precipitation. The interaction between the ocean and the atmosphere plays a crucial role in shaping the weather along coastlines.
1.1 Factors Influencing Shoreline Weather
Several factors influence shoreline weather, contributing to its variability and complexity. Some of the key factors include:
Read also:Rich Traditions Cajun Or Creole Culture And Cuisine
- Ocean Currents: These large-scale water movements can warm or cool the air above them, affecting local weather conditions.
- Wind Patterns: Coastal areas are often subject to sea breezes and land breezes, which can influence temperature and precipitation.
- Geography: The topography of the coastline, including its elevation and proximity to mountains, can alter weather patterns.
- Latitude: The position of a coastline relative to the equator affects its exposure to sunlight and seasonal changes.
1.2 Common Shoreline Weather Patterns
Shoreline weather patterns can vary widely, but some common features include:
- Sea Breezes: These occur when cool air from the ocean moves inland, often leading to cooler temperatures and increased humidity.
- Fog: Coastal fog is a frequent phenomenon in many shoreline areas, resulting from the interaction of warm air and cool ocean waters.
- Tropical Cyclones: Hurricanes and typhoons can have a significant impact on shoreline weather, bringing heavy rain, strong winds, and storm surges.
- Precipitation: Shoreline areas may experience frequent rainfall due to the influence of moist oceanic air masses.
2. How Do Ocean Currents Affect Shoreline Weather?
Ocean currents are powerful drivers of shoreline weather, affecting temperature, precipitation, and wind patterns. These currents can carry warm or cold water over long distances, influencing the climate of coastal regions. Understanding the role of ocean currents is essential for predicting shoreline weather and its impacts.
2.1 The Role of Warm and Cold Currents
Warm and cold ocean currents play distinct roles in shaping shoreline weather:
- Warm Currents: These currents, such as the Gulf Stream, transport warm water from the equator toward the poles. They can raise temperatures along coastlines, leading to milder winters and more humid conditions.
- Cold Currents: Cold currents, like the California Current, bring cooler water from polar regions toward the equator. They can result in cooler coastal temperatures and reduced humidity.
2.2 Impact on Local Climate
The impact of ocean currents on local climate is profound, affecting everything from temperature to precipitation patterns. For instance:
- Temperature Moderation: Ocean currents help moderate temperatures along coastlines, reducing the temperature extremes often seen in inland areas.
- Precipitation Patterns: Currents can influence the distribution of rainfall, leading to wetter or drier conditions depending on the current's characteristics.
- Wind Patterns: The interaction between ocean currents and atmospheric systems can generate wind patterns that influence local weather conditions.
3. What is the Influence of Geography on Shoreline Weather?
Geography plays a critical role in determining shoreline weather, as the physical characteristics of a coastline can dramatically affect local climatic conditions. The interplay between geographic features and atmospheric processes can create unique weather patterns that distinguish one coastal region from another.
3.1 Coastal Topography
Coastal topography, including features such as cliffs, bays, and peninsulas, can influence weather in several ways:
Read also:Stamp Costs Demystified Pricing History And More
- Wind Barriers: Cliffs and mountains can act as barriers to prevailing winds, altering wind patterns and creating microclimates.
- Temperature Variation: The presence of bodies of water, such as bays and estuaries, can moderate temperatures, leading to milder conditions.
- Localized Weather Phenomena: Unique geographic features can result in localized weather phenomena, such as sea breezes and coastal fog.
3.2 The Role of Elevation and Latitude
Elevation and latitude also have significant impacts on shoreline weather:
- Elevation: Higher elevations can lead to cooler temperatures and increased precipitation due to orographic lift.
- Latitude: The position of a coastline relative to the equator affects its exposure to solar radiation and seasonal variations, influencing temperature and precipitation.
4. How Does Shoreline Weather Impact Human Activities?
Shoreline weather has a profound impact on human activities, influencing everything from tourism and recreation to fishing and marine transportation. Understanding the implications of shoreline weather is essential for those living and working in coastal areas.
4.1 Tourism and Recreation
Tourism and recreation are heavily influenced by shoreline weather, as visitors are often drawn to coastal areas for their natural beauty and outdoor opportunities. Key considerations include:
- Seasonal Variability: Weather conditions can vary significantly by season, affecting the availability of activities such as swimming, surfing, and boating.
- Weather-Related Hazards: Understanding and preparing for weather-related hazards, such as hurricanes and rip currents, is crucial for ensuring visitor safety.
- Economic Impact: Favorable weather conditions can boost tourism revenue, while adverse weather can lead to economic losses.
4.2 Fishing and Marine Transportation
Fishing and marine transportation are also affected by shoreline weather, as these activities rely on stable and predictable conditions. Key factors include:
- Weather Forecasting: Accurate weather forecasting is essential for ensuring the safety of fishing vessels and cargo ships.
- Extreme Weather Events: Storms and high winds can disrupt fishing and transportation operations, leading to delays and potential hazards.
- Environmental Impact: Changes in shoreline weather can affect marine ecosystems, impacting fish populations and the sustainability of fishing practices.
5. What are the Challenges of Predicting Shoreline Weather?
Predicting shoreline weather presents unique challenges due to the complex interactions between oceanic and atmospheric systems. While advances in meteorology have improved our ability to forecast weather, several limitations and uncertainties remain.
5.1 Technological Advances in Meteorology
Technological advances have enhanced our ability to predict shoreline weather, including:
- Numerical Weather Models: These models simulate atmospheric conditions and provide forecasts based on current data and trends.
- Remote Sensing Technologies: Satellite imagery and radar systems offer real-time data on weather patterns, improving accuracy and timeliness.
- Data Assimilation: Integrating data from various sources allows for more comprehensive and accurate weather predictions.
5.2 Limitations and Uncertainties
Despite these advances, several limitations and uncertainties remain in predicting shoreline weather:
- Data Gaps: Incomplete data, particularly in remote or inaccessible areas, can limit the accuracy of weather forecasts.
- Model Limitations: Weather models may struggle to accurately represent complex interactions between oceanic and atmospheric systems.
- Unpredictable Weather Events: Sudden and extreme weather events, such as hurricanes, can be difficult to predict with precision.
6. How is Shoreline Weather Affected by Climate Change?
Climate change is having a significant impact on shoreline weather, altering patterns and intensifying extreme events. Understanding these changes is crucial for adapting to future challenges and mitigating their effects on coastal communities.
6.1 Rising Sea Levels
Rising sea levels, a consequence of climate change, are affecting shoreline weather in several ways:
- Increased Flooding: Higher sea levels increase the risk of coastal flooding, particularly during storms and high tides.
- Coastal Erosion: Erosion of coastlines is accelerated by rising sea levels, threatening infrastructure and ecosystems.
- Saltwater Intrusion: Saltwater can infiltrate freshwater resources, impacting agriculture and drinking water supplies.
6.2 Increasing Storm Intensity
Climate change is also contributing to an increase in the intensity of storms affecting shorelines:
- Stronger Hurricanes: Warmer ocean temperatures provide more energy for hurricanes, leading to more intense and destructive storms.
- More Frequent Storm Surges: Storm surges, driven by powerful winds and low pressure, are becoming more frequent and severe.
- Increased Precipitation: Climate change is leading to more intense rainfall events, which can exacerbate flooding and erosion.
7. How Can Communities Adapt to Changing Shoreline Weather?
Adapting to changing shoreline weather is essential for protecting life, property, and ecosystems. Communities must implement strategies to mitigate risks and enhance resilience to future challenges.
7.1 Infrastructure and Urban Planning
Infrastructure and urban planning play a critical role in adapting to changing shoreline weather:
- Building Resilient Structures: Designing and constructing buildings and infrastructure to withstand extreme weather events is essential.
- Implementing Flood Defenses: Sea walls, levees, and other flood defenses can help protect communities from rising sea levels and storm surges.
- Integrating Green Spaces: Incorporating green spaces and natural barriers can reduce the impact of flooding and erosion.
7.2 Emergency Preparedness
Emergency preparedness is vital for responding effectively to extreme shoreline weather events:
- Developing Emergency Plans: Communities should establish comprehensive emergency plans that outline evacuation routes and response procedures.
- Conducting Drills and Training: Regular drills and training exercises can ensure communities are ready to respond to emergencies.
- Raising Awareness: Public education campaigns can increase awareness of shoreline weather risks and encourage preparedness.
8. What Technologies Help Monitor Shoreline Weather?
Monitoring shoreline weather requires advanced technologies that provide accurate and timely data on atmospheric and oceanic conditions. These technologies are essential for predicting weather patterns and mitigating risks to coastal communities.
8.1 Satellite Imagery
Satellite imagery is a powerful tool for monitoring shoreline weather:
- Real-Time Data: Satellites provide real-time data on cloud cover, precipitation, and temperature, aiding in weather forecasting.
- Global Coverage: Satellites offer global coverage, enabling the monitoring of weather systems across vast ocean areas.
- Predictive Modeling: Satellite data is used in predictive modeling to forecast weather patterns and track storm systems.
8.2 Weather Buoys and Sensors
Weather buoys and sensors provide valuable data on oceanic and atmospheric conditions:
- Ocean Temperature and Currents: Buoys measure ocean temperature and currents, providing data critical for understanding shoreline weather.
- Wind and Wave Data: Sensors on buoys collect data on wind speed and wave height, aiding in the prediction of extreme weather events.
- Continuous Monitoring: Buoys and sensors provide continuous monitoring, offering valuable insights into changing conditions.
9. How Does Shoreline Weather Influence Wildlife and Ecosystems?
Shoreline weather plays a significant role in shaping wildlife and ecosystems along coastlines, influencing habitat conditions, migration patterns, and species interactions. Understanding these impacts is vital for conserving biodiversity and maintaining ecosystem health.
9.1 Coastal Habitats
Coastal habitats, such as beaches, estuaries, and wetlands, are directly affected by shoreline weather:
- Habitat Creation and Maintenance: Shoreline weather influences the creation and maintenance of habitats, such as sand dunes and tidal pools.
- Temperature and Precipitation: Variations in temperature and precipitation affect the distribution and abundance of plant and animal species.
- Storm Impacts: Storms can cause habitat destruction, altering the composition and structure of ecosystems.
9.2 Migration Patterns
Migration patterns of wildlife are influenced by shoreline weather, as animals move in response to changing conditions:
- Seasonal Migrations: Many species, such as birds and marine mammals, undertake seasonal migrations influenced by shoreline weather.
- Climate Change Effects: Changes in shoreline weather due to climate change can disrupt migration patterns, affecting species survival.
- Ecosystem Connectivity: Understanding migration patterns is essential for maintaining ecosystem connectivity and biodiversity.
10. Shoreline Weather and Renewable Energy
Shoreline weather offers opportunities for harnessing renewable energy, such as wind, solar, tidal, and wave energy. These renewable sources can contribute to sustainable energy production and reduce reliance on fossil fuels.
10.1 Wind and Solar Power
Wind and solar power are viable renewable energy options in shoreline areas:
- Wind Energy Potential: Coastal areas often experience strong and consistent winds, providing ideal conditions for wind energy generation.
- Solar Energy Opportunities: Sunny coastal regions can harness solar energy, contributing to renewable energy production.
- Environmental Benefits: Wind and solar energy offer environmental benefits by reducing greenhouse gas emissions and environmental degradation.
10.2 Tidal and Wave Energy
Tidal and wave energy are promising renewable energy sources along shorelines:
- Tidal Energy Generation: Tidal energy harnesses the power of ocean tides, providing a reliable and predictable energy source.
- Wave Energy Potential: Wave energy captures the kinetic energy of ocean waves, offering a continuous and sustainable energy source.
- Integration with Other Renewables: Tidal and wave energy can complement other renewable sources, enhancing energy security and sustainability.
11. What are Some Famous Shoreline Weather Events?
Throughout history, numerous famous shoreline weather events have captured public attention and had significant impacts on coastal communities. Understanding these events provides insights into the power and unpredictability of shoreline weather.
11.1 Historic Hurricanes and Typhoons
Historic hurricanes and typhoons have left lasting legacies along many shorelines:
- Hurricane Katrina (2005): One of the most devastating hurricanes in U.S. history, Katrina caused widespread destruction along the Gulf Coast.
- Typhoon Haiyan (2013): A powerful typhoon that struck the Philippines, Haiyan resulted in significant loss of life and extensive damage.
- Hurricane Sandy (2012): Known as "Superstorm Sandy," this hurricane affected the Eastern United States, causing severe flooding and damage.
11.2 Notable Storm Surges
Storm surges are among the most dangerous aspects of shoreline weather events:
- The North Sea Flood (1953): This storm surge caused widespread flooding in the Netherlands and the United Kingdom, leading to significant loss of life.
- Cyclone Nargis (2008): A severe storm surge associated with Cyclone Nargis caused extensive flooding and destruction in Myanmar.
- Hurricane Ike (2008): Ike's storm surge heavily impacted the Texas coastline, resulting in significant damage and economic losses.
12. How Do Cultural Practices Relate to Shoreline Weather?
Cultural practices often have deep connections to shoreline weather, as coastal communities have historically adapted to and celebrated the unique conditions of their environment. These practices reflect the interplay between human culture and natural phenomena.
12.1 Indigenous Knowledge and Traditions
Indigenous knowledge and traditions often incorporate a deep understanding of shoreline weather:
- Traditional Weather Forecasting: Indigenous communities have long used environmental cues to predict weather patterns and prepare for changes.
- Resource Management: Traditional practices often include sustainable resource management, reflecting an understanding of shoreline weather impacts.
- Cultural Heritage: Shoreline weather is often woven into cultural stories, rituals, and practices, reflecting its importance to community identity.
12.2 Festivals and Celebrations
Festivals and celebrations often highlight the relationship between shoreline weather and cultural practices:
- Seasonal Festivals: Many coastal communities celebrate festivals that coincide with seasonal weather changes, such as harvests and fishing seasons.
- Weather-Related Traditions: Traditions and rituals may be linked to weather phenomena, such as storms and tides, reflecting their significance to the community.
- Tourism and Economic Impact: Festivals and celebrations can attract tourists and boost local economies, reflecting the importance of shoreline weather to community life.
13. Shoreline Weather in Literature and Art
Shoreline weather has long been a source of inspiration for literature and art, providing a rich tapestry of imagery and symbolism. The dynamic and often dramatic nature of shoreline weather is reflected in a wide range of creative works.
13.1 Symbolism and Inspiration
Shoreline weather often serves as a powerful symbol and source of inspiration in literature and art:
- Symbolism of Change and Transformation: The ever-changing nature of shoreline weather can symbolize change, transformation, and renewal.
- Imagery of Beauty and Power: The beauty and power of coastal storms, sunsets, and seascapes have been captured in countless works of art and literature.
- Emotional Resonance: The emotional impact of shoreline weather, from calm and serenity to chaos and destruction, is a common theme in creative expression.
13.2 Representations in Media
Shoreline weather is often represented in various forms of media, reflecting its cultural and artistic significance:
- Film and Television: Coastal settings and weather events are frequently depicted in film and television, adding drama and visual interest.
- Photography and Visual Arts: Photographers and visual artists capture the beauty and power of shoreline weather, creating iconic images.
- Literary Works: Shoreline weather serves as a backdrop and motif in literature, enriching narratives and character development.
14. FAQs About Shoreline Weather
14.1 Understanding Weather Alerts
Weather alerts are issued to inform the public of potential hazards related to shoreline weather. These alerts can include warnings for storms, high winds, and flooding. Understanding these alerts and taking appropriate action is essential for ensuring safety.
14.2 Preparing for Coastal Storms
Preparing for coastal storms involves taking steps to protect life and property. This can include securing outdoor items, stocking emergency supplies, and having an evacuation plan in place. Staying informed about weather conditions and heeding official warnings is critical during storm events.
14.3 How Do Ocean Currents Influence Shoreline Weather?
Ocean currents play a significant role in shaping shoreline weather by transporting warm or cold water, which influences local temperatures, wind patterns, and precipitation. Understanding the impact of ocean currents is essential for predicting and responding to shoreline weather.
14.4 What Strategies Can Communities Use to Adapt to Changing Shoreline Weather?
Communities can adapt to changing shoreline weather by implementing strategies such as building resilient infrastructure, developing emergency preparedness plans, and integrating green spaces to mitigate flooding and erosion. These measures enhance resilience to future weather challenges.
14.5 How Does Climate Change Affect Shoreline Weather?
Climate change affects shoreline weather by contributing to rising sea levels, increasing storm intensity, and altering precipitation patterns. These changes pose significant risks to coastal communities, making adaptation and mitigation efforts critical.
14.6 What Role Do Satellite Technologies Play in Monitoring Shoreline Weather?
Satellite technologies play a crucial role in monitoring shoreline weather by providing real-time data on atmospheric and oceanic conditions. This data is essential for forecasting weather patterns, tracking storm systems, and informing emergency response efforts.
15. Conclusion
Shoreline weather is a complex and dynamic subject that encompasses the unique climatic conditions experienced along coastlines. Influenced by factors such as ocean currents, geography, and climate change, shoreline weather has profound implications for human activities, wildlife, and ecosystems. Understanding and adapting to these conditions is essential for safeguarding coastal communities and promoting sustainable development. By leveraging advanced technologies and implementing strategic adaptation measures, we can enhance resilience to future weather challenges and harness the potential of renewable energy in shoreline areas.