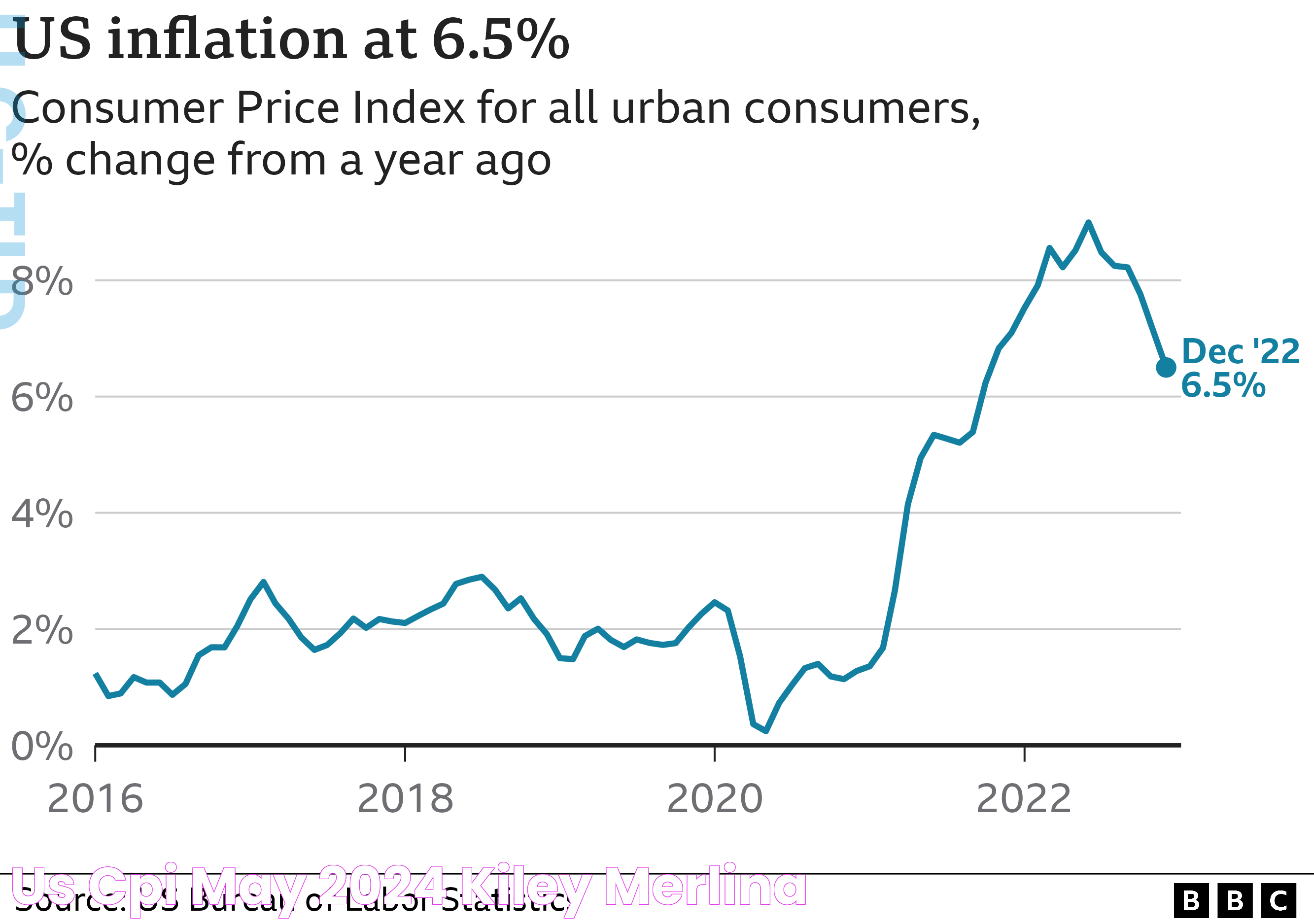
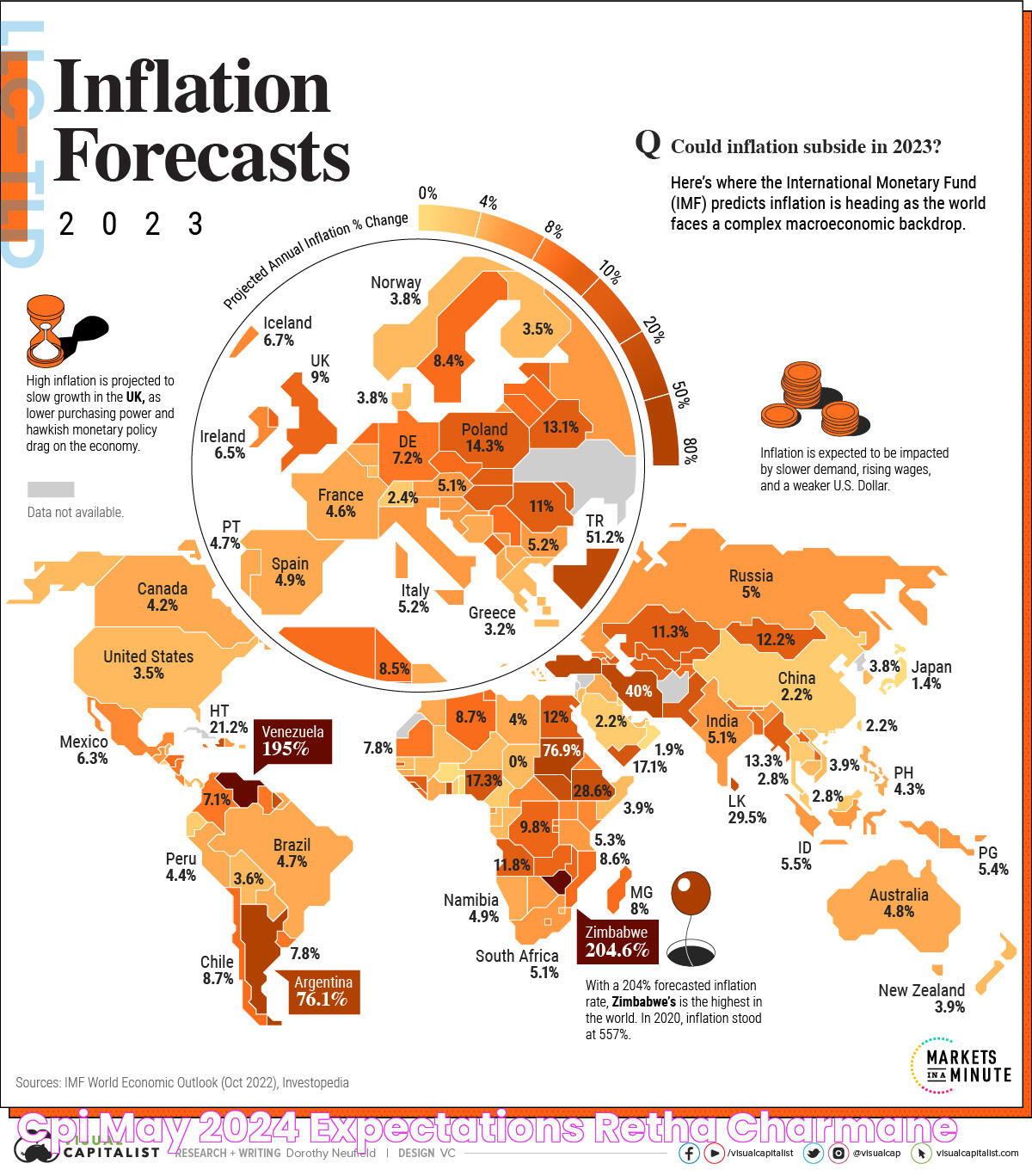
The Consumer Price Index (CPI) is a critical indicator of economic health, reflecting the average change over time in the prices paid by urban consumers for a basket of goods and services. As we approach May 2024, understanding the CPI becomes increasingly important for economists, policymakers, businesses, and consumers alike. The CPI offers insights into inflationary trends, purchasing power, and the overall economic climate. With the global economy facing unprecedented challenges and changes, the CPI for May 2024 is poised to provide valuable data for assessing economic stability and forecasting future financial conditions.
In recent years, the CPI has been a focal point for discussions on economic recovery, inflation control, and fiscal policies. As the world recovers from the disruptions caused by the COVID-19 pandemic, monitoring the CPI helps gauge the effectiveness of economic measures and policy interventions. The CPI for May 2024 is expected to reflect the ongoing adjustments in consumer behavior, supply chain dynamics, and market trends. This period serves as a checkpoint to evaluate whether the economic strategies employed have successfully steered the economy towards steady growth and stability.
As we delve into the specifics of the CPI for May 2024, this article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of its significance, influencing factors, and potential implications for various sectors. By examining historical data, current economic conditions, and expert predictions, we can better understand the trajectory of inflation and its impact on different aspects of the economy. Whether you are an investor, policymaker, or simply a curious reader, this article will equip you with the knowledge needed to navigate the complexities of the CPI and its role in shaping the economic landscape.
Read also:Taylor Swifts Sydney Extravaganza Experience The Magic Down Under
Table of Contents
- Understanding CPI: A Basic Introduction
- CPI May 2024: What to Expect?
- Factors Influencing the CPI in May 2024
- Examining Historical CPI Trends
- How is the CPI Calculated?
- Impact of CPI on the Economy
- CPI and Inflation: What's the Connection?
- Sectoral Analysis: Which Sectors are Most Affected?
- Global Comparison: How Does the CPI in May 2024 Stack Up?
- Policy Implications of the CPI Data
- How Does the CPI Influence Consumer Behavior?
- Predictions for CPI May 2024: Expert Insights
- What are the Challenges in Predicting the CPI?
- CPI and Investment Strategies: What Investors Need to Know?
- Future of CPI: What Lies Ahead?
- FAQs
- Conclusion
Understanding CPI: A Basic Introduction
The Consumer Price Index (CPI) is a measure that examines the weighted average of prices of a basket of consumer goods and services, such as transportation, food, and medical care. It's calculated by taking price changes for each item in the predetermined basket of goods and averaging them. Prices in the CPI are collected by trained government employees in a variety of retail stores, service establishments, rental units, and doctors' offices.
Published monthly by the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) in the United States, the CPI is one of the most frequently used statistics for identifying periods of inflation or deflation. It's a crucial metric that helps policymakers, economists, and the general public understand the economic health of the country. Changes in the CPI are used to assess price changes associated with the cost of living, making it a critical component for adjusting income payments, like Social Security, to maintain their purchasing power.
There are two types of CPI measurements: the CPI for All Urban Consumers (CPI-U) and the CPI for Urban Wage Earners and Clerical Workers (CPI-W). The CPI-U represents the spending habits of approximately 93% of the total U.S. population, while the CPI-W is based on the spending habits of households where more than half of the household's income comes from clerical or wage occupations. This nuanced approach allows for a more comprehensive analysis of inflation across different demographic segments.
CPI May 2024: What to Expect?
As we look forward to May 2024, the CPI is expected to reflect several ongoing economic trends and challenges. With global supply chains still recovering from previous disruptions and new geopolitical tensions, fluctuations in commodity prices, particularly energy and food, are likely to impact the CPI figures. Economists anticipate that these factors, combined with monetary policies, will play a significant role in shaping the inflationary landscape.
The CPI for May 2024 will likely be influenced by the monetary policy decisions made by central banks worldwide. As interest rates continue to adjust, these changes will have a direct impact on borrowing costs, consumer spending, and ultimately, the overall price levels. Additionally, government fiscal policies aimed at stimulating or restraining economic activity can also affect CPI outcomes by altering demand levels for goods and services.
In the U.S., the Federal Reserve's stance on interest rates will be closely monitored, as any changes can lead to shifts in consumer confidence and spending patterns. Similarly, international economic developments, such as trade agreements or tariffs, can have ripple effects on the CPI. Analysts will be paying close attention to these variables as they release their forecasts for the CPI in May 2024.
Read also:Khal Drigo The Charismatic Leader And His Enduring Influence
Factors Influencing the CPI in May 2024
Several factors are expected to influence the CPI in May 2024, ranging from supply chain dynamics to consumer demand and government policies. One of the primary drivers is expected to be the cost of energy. As economies transition to more sustainable energy sources, fluctuations in oil prices and the cost of renewable energy technologies will likely have a significant impact on the CPI.
Another crucial factor is the labor market. Wage growth can contribute to inflationary pressures as businesses pass on increased labor costs to consumers through higher prices. As unemployment rates fluctuate and new labor laws come into effect, the relationship between wages and prices will be a key focus for economists analyzing the CPI.
Additionally, global events such as geopolitical tensions, natural disasters, or pandemics can disrupt supply chains and affect the availability and cost of goods. These disruptions often lead to price volatility, which can be reflected in the CPI. Understanding the interplay between these factors is essential for making accurate predictions about future CPI movements.
Examining Historical CPI Trends
Examining historical CPI trends provides valuable insights into how the index behaves under different economic conditions. Over the past few decades, the CPI has shown periods of both stability and volatility, often reflecting broader economic cycles. For instance, during times of economic growth, the CPI tends to rise as consumer demand increases, leading to higher prices.
Conversely, during economic downturns, the CPI may stabilize or even decrease as consumer spending declines and businesses lower prices to attract customers. Historical data also highlights the impact of major economic events, such as financial crises, on the CPI. Understanding these trends helps economists and policymakers anticipate future changes and develop strategies to manage inflation effectively.
By analyzing past CPI data, we can identify patterns and correlations with other economic indicators, such as employment rates, GDP growth, and interest rates. This analysis provides a framework for predicting how the CPI might respond to current and future economic conditions, offering valuable guidance for decision-makers.
How is the CPI Calculated?
The calculation of the CPI involves several steps, beginning with the selection of a representative basket of goods and services. This basket is designed to reflect the spending patterns of urban consumers and includes categories such as food, housing, apparel, transportation, medical care, recreation, education, and communication.
Once the basket is defined, BLS employees collect price data from various sources, including retail stores, service providers, and online platforms. This data is used to calculate the average price change for each item in the basket, which is then weighted according to its importance in the average consumer's budget. The weights are derived from detailed expenditure surveys conducted by the BLS.
The resulting index is expressed as a percentage change from a base period, allowing for easy comparison across different time frames. Adjustments may be made to account for seasonal variations, quality changes, and other factors that could skew the results. By following this rigorous methodology, the CPI provides a reliable measure of inflation that can inform economic policy and business strategy.
Impact of CPI on the Economy
The CPI is a critical indicator of inflation, which has far-reaching effects on the economy. Inflation can erode purchasing power, reduce consumer confidence, and impact investment decisions. As the CPI rises, consumers may find that their money buys less, leading to changes in spending habits and saving strategies.
For businesses, an increasing CPI can lead to higher production costs as raw materials and labor become more expensive. Companies may pass these costs onto consumers through price increases, potentially reducing demand for their products. Inflation also affects borrowing costs, as lenders adjust interest rates to maintain their profit margins.
On a broader scale, the CPI influences government policy decisions, particularly those related to monetary policy. Central banks, such as the Federal Reserve, use the CPI to set interest rates and control money supply, aiming to achieve a balance between economic growth and price stability. By monitoring the CPI, policymakers can develop strategies to address inflationary pressures and maintain a healthy economy.
CPI and Inflation: What's the Connection?
Inflation is the rate at which the general level of prices for goods and services is rising, and subsequently, purchasing power is falling. The CPI is a key measure of inflation, as it tracks the changes in prices paid by consumers for a basket of goods and services over time. By analyzing the CPI, economists can assess inflationary trends and predict future price movements.
When the CPI increases, it indicates that prices are rising, which may signal inflation. Conversely, a decrease in the CPI suggests deflation or a reduction in the overall price level. The relationship between the CPI and inflation is essential for understanding the economic environment and developing appropriate policy responses.
Inflation can have both positive and negative effects on the economy. Moderate inflation can stimulate economic growth by encouraging spending and investment, as consumers and businesses anticipate higher prices in the future. However, high inflation can lead to uncertainty and instability, reducing confidence in the economy and hindering long-term growth prospects.
Sectoral Analysis: Which Sectors are Most Affected?
The impact of the CPI varies across different sectors of the economy, with some industries more sensitive to price changes than others. For example, the energy sector is particularly affected by fluctuations in oil prices, which can have a significant impact on the overall CPI. As energy prices rise, transportation and production costs increase, affecting a wide range of industries.
The food and beverage sector is also highly responsive to changes in the CPI, as shifts in commodity prices can lead to fluctuations in the cost of raw materials. These changes are often passed on to consumers through higher prices for groceries and dining out, influencing consumer spending patterns.
Other sectors, such as healthcare and education, may experience varying degrees of impact from the CPI. In these industries, prices are often influenced by regulatory changes, technological advancements, and demographic trends, which can affect the overall cost of goods and services.
Global Comparison: How Does the CPI in May 2024 Stack Up?
Comparing the CPI across different countries provides valuable insights into global economic trends and the relative competitiveness of various economies. By examining the CPI for May 2024, we can assess how inflationary pressures are affecting different regions and identify potential challenges and opportunities for international trade and investment.
In developed economies, the CPI is typically more stable, reflecting well-established markets and mature supply chains. However, emerging markets may experience greater volatility in their CPI figures due to factors such as political instability, currency fluctuations, and rapid changes in consumer demand.
By analyzing global CPI data, policymakers and businesses can develop strategies to mitigate risks and capitalize on opportunities in the international market. This information is essential for fostering economic growth and maintaining a competitive edge in an increasingly interconnected world.
Policy Implications of the CPI Data
The CPI data has significant implications for economic policy, as it informs decisions related to monetary policy, fiscal policy, and social programs. Central banks use the CPI to set interest rates and manage money supply, aiming to achieve a balance between economic growth and price stability.
Fiscal policy decisions, such as government spending and taxation, are also influenced by the CPI. Policymakers may adjust these measures to stimulate or restrain economic activity, depending on the inflationary environment. For example, during periods of high inflation, governments may reduce spending or increase taxes to curb demand and stabilize prices.
Social programs, such as Social Security and welfare benefits, are often indexed to the CPI to maintain their purchasing power over time. By adjusting payments in line with the CPI, governments can ensure that these programs continue to provide adequate support to beneficiaries, even as prices rise.
How Does the CPI Influence Consumer Behavior?
The CPI plays a crucial role in shaping consumer behavior, as it reflects changes in the cost of living and influences purchasing decisions. When the CPI rises, consumers may adjust their spending habits to accommodate higher prices, prioritizing essential goods and services while cutting back on discretionary items.
This shift in consumer behavior can have a ripple effect on the economy, as changes in demand influence production levels, employment, and investment. Businesses must adapt to these changes by adjusting their pricing strategies, product offerings, and marketing efforts to remain competitive in a dynamic market environment.
By understanding the relationship between the CPI and consumer behavior, companies can develop strategies to anticipate and respond to changes in demand, ensuring their long-term success in an ever-evolving market.
Predictions for CPI May 2024: Expert Insights
As we look ahead to May 2024, experts predict that the CPI will continue to reflect ongoing economic challenges and opportunities. While inflationary pressures are expected to persist, the rate of increase may moderate as supply chains stabilize and consumer demand adjusts to new market conditions.
Economists anticipate that the CPI will be influenced by several factors, including energy prices, labor market dynamics, and government policies. As central banks and governments implement measures to manage inflation, the CPI is likely to provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of these interventions and the overall health of the economy.
By analyzing expert predictions and monitoring key economic indicators, businesses and policymakers can develop strategies to navigate the complexities of the CPI and ensure long-term stability and growth.
What are the Challenges in Predicting the CPI?
Predicting the CPI is a complex task, as it involves analyzing a wide range of factors that influence price levels. One of the primary challenges is the inherent volatility of certain components, such as energy and food prices, which can be affected by unpredictable global events and natural disasters.
Another challenge is the dynamic nature of consumer behavior, as shifts in preferences and spending patterns can impact demand and pricing strategies. This unpredictability makes it difficult to accurately forecast the CPI and develop reliable economic models.
Additionally, changes in government policies, such as trade agreements and regulatory measures, can have significant implications for the CPI. As these policies continue to evolve, economists must constantly update their models and assumptions to ensure accurate predictions.
CPI and Investment Strategies: What Investors Need to Know?
Investors must consider the CPI when developing their investment strategies, as inflation can have a significant impact on asset values and returns. Rising CPI figures may signal increasing inflation, which can erode the purchasing power of fixed-income investments and reduce the real value of returns.
To mitigate these risks, investors may consider diversifying their portfolios to include assets that are less sensitive to inflationary pressures, such as equities, real estate, and commodities. These investments can provide a hedge against inflation, as their value may increase in line with rising prices.
By incorporating CPI data into their investment decision-making process, investors can develop strategies to protect their portfolios from inflationary risks and capitalize on opportunities in a changing economic environment.
Future of CPI: What Lies Ahead?
The future of the CPI is likely to be shaped by several key trends and developments, including technological advancements, demographic shifts, and evolving consumer preferences. As new technologies continue to transform industries and supply chains, the CPI may need to adapt to accurately reflect these changes.
Demographic trends, such as aging populations and urbanization, will also have implications for the CPI, as they influence spending patterns and demand for goods and services. As these trends continue to evolve, the CPI will need to adapt to ensure its continued relevance as a measure of inflation.
By staying informed about these trends and developments, policymakers and businesses can ensure that the CPI remains a valuable tool for understanding and managing inflation in an increasingly complex economic landscape.
FAQs
What is the CPI, and why is it important?
The Consumer Price Index (CPI) is a measure that examines the weighted average of prices of a basket of consumer goods and services. It's important because it helps identify periods of inflation or deflation, guiding economic policy and business strategy.
How is the CPI calculated?
The CPI is calculated by collecting price data for a representative basket of goods and services, averaging the price changes, and weighting them according to their importance in the average consumer's budget.
What factors influence the CPI in May 2024?
Factors influencing the CPI in May 2024 include energy prices, labor market dynamics, global events, and government policies, all of which can impact price levels and inflation.
How does the CPI affect the economy?
The CPI affects the economy by influencing purchasing power, consumer confidence, business costs, and government policy decisions, all of which have far-reaching implications for economic growth and stability.
What are the challenges in predicting the CPI?
Challenges in predicting the CPI include volatility in certain components, dynamic consumer behavior, and evolving government policies, all of which contribute to the complexity of forecasting price levels.
How can investors use CPI data in their strategies?
Investors can use CPI data to develop strategies that protect their portfolios from inflationary risks and capitalize on opportunities in a changing economic environment, such as diversifying into assets less sensitive to inflation.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Consumer Price Index for May 2024 will be a critical indicator of economic health, reflecting the ongoing challenges and opportunities facing the global economy. By understanding the factors influencing the CPI, examining historical trends, and considering expert predictions, we can gain valuable insights into the trajectory of inflation and its impact on various sectors.
As we navigate the complexities of the CPI, it's essential to remain informed and adaptable, continuously updating our strategies to ensure long-term stability and growth in an ever-evolving economic landscape. By leveraging the insights provided by the CPI, policymakers, businesses, and investors can make informed decisions that support a prosperous future.