Rus country, a term that holds a profound historical and cultural significance, refers to the early medieval region in Eastern Europe that laid the foundation for modern-day Russia, Ukraine, and Belarus. This fascinating area, often shrouded in mystery, has captured the imagination of historians, travelers, and cultural enthusiasts alike. With a rich tapestry of cultural heritage, historical events, and societal evolution, Rus country offers a glimpse into a world that has shaped the identity of many Eastern European nations.
Throughout its history, Rus country has been a melting pot of peoples, traditions, and influences. From the Viking settlers who first established their presence in the region to the Byzantine cultural influx, the history of Rus country is marked by a series of dynamic interactions. These interactions have given rise to a unique cultural identity that continues to influence the societal norms and values of the region today. The legacy of Rus country is not only preserved in the historical narratives but can also be seen in the architecture, art, and literature that have emerged from this storied land.
As we delve deeper into the intriguing aspects of Rus country, we will explore its historical evolution, the cultural richness that defines it, and the lasting impact it has had on contemporary society. This exploration will provide a comprehensive understanding of the forces that have shaped Rus country, offering insights into its past, present, and future. Join us on this fascinating journey as we uncover the layers of history and culture that make Rus country a truly remarkable place.
Read also:Resolving The P0171 Code Toyotas Guide To Efficient Engine Performance
Table of Contents
- Early History of Rus Country
- Significance of Viking Settlers
- Cultural Influences in Rus Country
- How Did Byzantine Culture Impact Rus Country?
- Religious Evolution and Its Impact
- What Were the Major Historical Events?
- Architectural Marvels of Rus Country
- Rus Country in Literature and Arts
- Modern-Day Legacy of Rus Country
- How Has Rus Country Influenced Modern Culture?
- Economic Contributions of Rus Country
- What Are the Current Challenges Facing Rus Country?
- Future Prospects for Rus Country
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
Early History of Rus Country
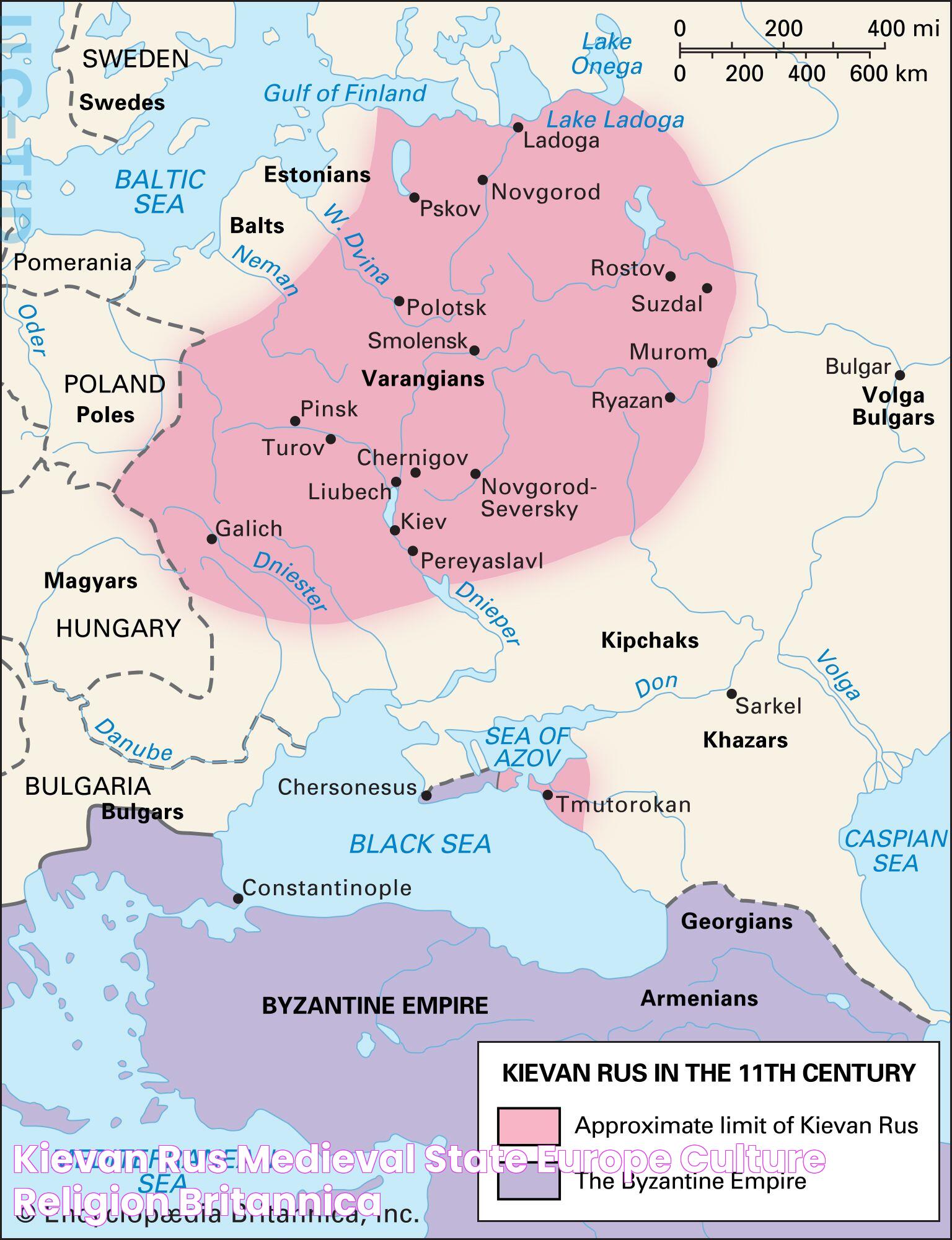
The early history of Rus country is marked by its strategic geographical location, which facilitated trade and cultural exchanges between various civilizations. The region, which encompasses parts of present-day Russia, Ukraine, and Belarus, was initially inhabited by Slavic tribes. These tribes engaged in trade with neighboring regions, contributing to the cultural and economic development of the area.
By the 9th century, the region became known as the land of the Rus, a name derived from the Viking settlers who established trade routes and settlements along the rivers. The Vikings, known as the Varangians, played a crucial role in shaping the early political and cultural landscape of Rus country. Their influence extended beyond commerce, as they established the Rurik dynasty, which would go on to rule the region for centuries.
The formation of Kievan Rus, a loose federation of Slavic tribes under the rule of the Rurik dynasty, marked a significant milestone in the history of Rus country. This political entity became a powerful trading hub, facilitating the exchange of goods and ideas between the Byzantine Empire and the Nordic regions. The prosperity and cultural richness of Kievan Rus laid the foundation for the future development of the region.
Significance of Viking Settlers
The arrival of Viking settlers, also known as the Varangians, in Rus country was a turning point in the region's history. The Vikings, known for their seafaring prowess and trading expertise, established key trade routes that connected the Baltic Sea with the Byzantine Empire. These routes, known as the Varangian trade routes, facilitated the exchange of goods such as furs, silver, and luxury items, contributing to the economic prosperity of the region.
The Vikings also played a significant role in the political landscape of Rus country. Under the leadership of the legendary Viking chieftain Rurik, they established a ruling dynasty that would govern the region for centuries. The Rurik dynasty laid the groundwork for the unification of the Slavic tribes, creating a centralized political entity known as Kievan Rus.
In addition to their economic and political contributions, the Vikings left a lasting cultural impact on Rus country. Their interactions with the local Slavic population led to a blending of cultural traditions, resulting in a unique cultural identity that is still evident today. The influence of Viking art, architecture, and mythology can be seen in the region's cultural heritage.
Read also:Ultimate Guide To Dining At Carmines Italian Restaurant
Cultural Influences in Rus Country
Rus country has been a crossroads of cultures, with various influences shaping its identity over the centuries. One of the most significant cultural influences came from the Byzantine Empire, which played a crucial role in the region's religious and cultural development. The introduction of Christianity in the 10th century, under the rule of Prince Vladimir the Great, marked a transformative period in Rus country's history.
Christianity brought with it Byzantine religious practices, art, and architecture, which left a lasting impact on the cultural landscape of Rus country. The construction of grand churches and cathedrals, adorned with intricate mosaics and frescoes, reflected the Byzantine influence on Rus architecture. The adoption of the Cyrillic script, developed by the Byzantine missionaries Cyril and Methodius, further solidified the cultural ties between Rus country and the Byzantine Empire.
In addition to Byzantine influences, Rus country also absorbed cultural elements from neighboring regions, including the Khazar Khaganate, the Islamic Caliphates, and the Mongol Empire. These interactions contributed to the rich tapestry of cultural traditions that define Rus country, creating a unique blend of Eastern and Western influences.
How Did Byzantine Culture Impact Rus Country?
The influence of Byzantine culture on Rus country is evident in various aspects of its society, from religion to art and architecture. The conversion to Christianity under Prince Vladimir the Great in 988 AD marked a significant turning point, as it established the Byzantine Orthodox Church as the dominant religious institution in the region.
The adoption of Byzantine religious practices and liturgy had a profound impact on the spiritual and cultural life of Rus country. The construction of churches and cathedrals, inspired by Byzantine architectural styles, became a hallmark of the region's cultural landscape. Notable examples include the Saint Sophia Cathedral in Kyiv, which showcases the grandeur of Byzantine architectural influence.
Byzantine art also left an indelible mark on Rus country, with the use of mosaics and frescoes becoming prevalent in religious and secular spaces. The artistic techniques and themes introduced by Byzantine artists were adapted and transformed by local artisans, resulting in a distinctive style that characterized Rus art.
Religious Evolution and Its Impact
The religious evolution of Rus country has played a pivotal role in shaping its cultural and societal identity. The introduction of Christianity in the 10th century marked a significant departure from the pagan beliefs that had previously dominated the region. This transition was spearheaded by Prince Vladimir the Great, who, after converting to Christianity, embarked on a campaign to Christianize his subjects.
The adoption of Christianity brought about significant changes in the social and cultural fabric of Rus country. It facilitated the establishment of religious institutions, such as monasteries and churches, which became centers of learning and cultural preservation. The church also played a crucial role in the unification of the Slavic tribes, providing a common religious and cultural framework that transcended regional differences.
The impact of religious evolution extended beyond the spiritual realm, influencing various aspects of daily life, including art, education, and governance. The church's involvement in education and literacy initiatives helped preserve and disseminate knowledge, contributing to the cultural and intellectual development of Rus country.
What Were the Major Historical Events?
Rus country has witnessed a series of major historical events that have shaped its development and legacy. One of the most significant events was the establishment of the Kievan Rus, a powerful federation of Slavic tribes under the rule of the Rurik dynasty. This political entity became a major center of trade and culture, facilitating exchanges with the Byzantine Empire and other neighboring regions.
The Mongol invasion in the 13th century marked another pivotal moment in the history of Rus country. The Mongols, led by Batu Khan, conquered much of the region, establishing the Golden Horde. This period of Mongol rule brought about significant changes in the political and social structure of Rus country, influencing its development for centuries to come.
The rise of the Grand Duchy of Moscow in the late medieval period marked a new chapter in the history of Rus country. Moscow emerged as a powerful political and cultural center, eventually leading to the establishment of the Tsardom of Russia. This transformation laid the foundation for the emergence of the modern Russian state, with Rus country's legacy continuing to influence its development.
Architectural Marvels of Rus Country
The architectural heritage of Rus country is a testament to its rich cultural and historical legacy. The region is home to a wealth of architectural marvels that reflect the diverse influences that have shaped its development over the centuries. From the grandeur of Byzantine-inspired cathedrals to the intricate wooden structures of rural villages, Rus country's architecture offers a glimpse into its storied past.
One of the most iconic architectural landmarks of Rus country is the Saint Sophia Cathedral in Kyiv. Built in the 11th century, the cathedral is a masterpiece of Byzantine architecture, adorned with stunning mosaics and frescoes that depict religious and historical scenes. Its architectural style served as a model for subsequent church constructions throughout the region.
In addition to religious structures, Rus country boasts a rich tradition of wooden architecture, particularly in rural areas. These structures, often characterized by intricate carvings and decorative elements, reflect the craftsmanship and artistic sensibilities of the local population. The wooden churches and houses of Rus country are celebrated for their unique style and cultural significance.
Rus Country in Literature and Arts
Rus country's rich cultural heritage is vividly captured in its literature and arts, which have played a vital role in preserving and promoting the region's identity. The literary tradition of Rus country dates back to the medieval period, with the "Primary Chronicle" serving as one of the earliest and most significant historical texts. This chronicle provides a comprehensive account of the history of Rus country, offering valuable insights into its cultural and societal evolution.
The epic poem "The Tale of Igor's Campaign" is another notable example of Rus country literature. This literary masterpiece, which recounts the military campaign of Prince Igor, is celebrated for its poetic beauty and historical significance. It reflects the values, beliefs, and cultural traditions of the medieval Rus society, serving as a testament to the region's rich literary heritage.
In addition to literature, Rus country has a thriving artistic tradition that encompasses various forms of visual arts, including painting, iconography, and decorative crafts. The region's art is characterized by its vibrant colors, intricate details, and religious themes, reflecting the deep spiritual and cultural influences that have shaped its development.
Modern-Day Legacy of Rus Country
The legacy of Rus country continues to resonate in contemporary society, influencing various aspects of culture, politics, and identity in Eastern Europe. The historical and cultural heritage of Rus country is celebrated and preserved through various initiatives, including the restoration of historical sites, the promotion of traditional arts and crafts, and the celebration of cultural festivals.
In modern-day Russia, Ukraine, and Belarus, the legacy of Rus country is evident in the shared cultural traditions, language, and historical narratives that bind these nations together. The region's historical sites, such as the ancient city of Kyiv and the architectural marvels of Novgorod, serve as reminders of the rich cultural heritage that defines Rus country.
The influence of Rus country extends beyond its borders, with its cultural and historical legacy contributing to the broader European cultural landscape. The region's contributions to art, literature, and architecture continue to inspire and captivate audiences worldwide, highlighting the enduring impact of Rus country's legacy.
How Has Rus Country Influenced Modern Culture?
Rus country's influence on modern culture is evident in various aspects of contemporary society, from language and literature to art and architecture. The region's rich cultural heritage has left an indelible mark on the cultural identity of Eastern Europe, shaping the traditions and values of modern-day Russia, Ukraine, and Belarus.
The linguistic legacy of Rus country is particularly significant, with the Old East Slavic language serving as the foundation for the modern Russian, Ukrainian, and Belarusian languages. This shared linguistic heritage has facilitated cultural exchanges and communication between these nations, fostering a sense of unity and shared identity.
In the realm of art and architecture, Rus country's influence is seen in the continued appreciation and preservation of traditional artistic forms and architectural styles. The region's artistic legacy is celebrated through exhibitions, cultural festivals, and educational initiatives, ensuring that the rich cultural heritage of Rus country is passed down to future generations.
Economic Contributions of Rus Country
Throughout its history, Rus country has made significant contributions to the economic development of Eastern Europe. The region's strategic geographical location, abundant natural resources, and thriving trade networks have played a crucial role in shaping its economic landscape.
In the medieval period, Rus country became a major center of trade, with the Varangian trade routes facilitating the exchange of goods between the Baltic Sea and the Byzantine Empire. This economic prosperity contributed to the growth of cities such as Kyiv and Novgorod, which became important cultural and economic hubs.
In modern times, Rus country's economic contributions continue to be significant, with the region's natural resources, including oil, gas, and minerals, playing a crucial role in the global economy. The industrial and technological advancements in the region have also contributed to its economic growth, making Rus country an important player in the international economic landscape.
What Are the Current Challenges Facing Rus Country?
Despite its rich cultural heritage and historical significance, Rus country faces a number of contemporary challenges that impact its development and legacy. One of the primary challenges is the preservation of its cultural heritage in the face of modernization and globalization. Efforts to maintain and restore historical sites, promote traditional arts and crafts, and preserve cultural traditions are crucial in ensuring that the legacy of Rus country is not lost.
Another significant challenge is the geopolitical tensions and conflicts that affect the region. The complex political landscape of Eastern Europe, marked by historical grievances and territorial disputes, poses a threat to the stability and unity of Rus country. Addressing these challenges requires diplomatic efforts and cooperation among the nations of the region.
Economic challenges, including resource management, technological advancements, and global competition, also impact the development of Rus country. Balancing economic growth with environmental sustainability and social equity is essential for ensuring the long-term prosperity of the region.
Future Prospects for Rus Country
As Rus country continues to navigate the complexities of the modern world, its future prospects remain promising. The region's rich cultural heritage and historical legacy provide a strong foundation for its continued development and growth. Efforts to preserve and promote the cultural identity of Rus country will play a crucial role in shaping its future.
In the realm of economic development, Rus country's abundant natural resources and strategic geographical location offer significant opportunities for growth and prosperity. Investments in technology, infrastructure, and education will be key to unlocking the region's economic potential and ensuring its competitiveness in the global market.
The future of Rus country also depends on its ability to address contemporary challenges, including geopolitical tensions, environmental sustainability, and social equity. By fostering cooperation and dialogue among the nations of the region, Rus country can work towards a more stable and prosperous future, ensuring that its rich cultural and historical legacy continues to inspire and captivate generations to come.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is Rus country? Rus country refers to the early medieval region in Eastern Europe that laid the foundation for modern-day Russia, Ukraine, and Belarus.
- Who were the Viking settlers in Rus country? The Vikings, also known as the Varangians, were seafaring traders and warriors who established trade routes and settlements in Rus country during the 9th century.
- How did Christianity impact Rus country? The introduction of Christianity in the 10th century brought significant changes to Rus country, including the establishment of religious institutions, cultural exchanges with the Byzantine Empire, and the unification of the Slavic tribes.
- What are some notable architectural landmarks in Rus country? Notable architectural landmarks include the Saint Sophia Cathedral in Kyiv and the wooden churches of rural Rus country, which reflect the region's rich architectural heritage.
- How has Rus country influenced modern Eastern European culture? Rus country's influence is seen in the shared cultural traditions, language, and historical narratives of modern-day Russia, Ukraine, and Belarus, as well as its contributions to art, literature, and architecture.
- What challenges does Rus country face today? Contemporary challenges include the preservation of cultural heritage, geopolitical tensions, and economic development, requiring cooperation and dialogue among the nations of the region.
Conclusion
The story of Rus country is one of rich cultural heritage, historical significance, and enduring influence. From its early days as a center of trade and cultural exchange to its role in shaping the cultural identity of Eastern Europe, Rus country has left an indelible mark on the world. As we look to the future, the legacy of Rus country continues to inspire and captivate, offering valuable insights into the forces that have shaped our world.
By exploring the history, culture, and contributions of Rus country, we gain a deeper understanding of the region's identity and legacy. The preservation and promotion of this rich cultural heritage are essential for ensuring that the story of Rus country continues to be told for generations to come. As we celebrate the achievements and contributions of Rus country, we are reminded of the importance of cultural diversity, historical legacy, and shared identity in shaping our world.