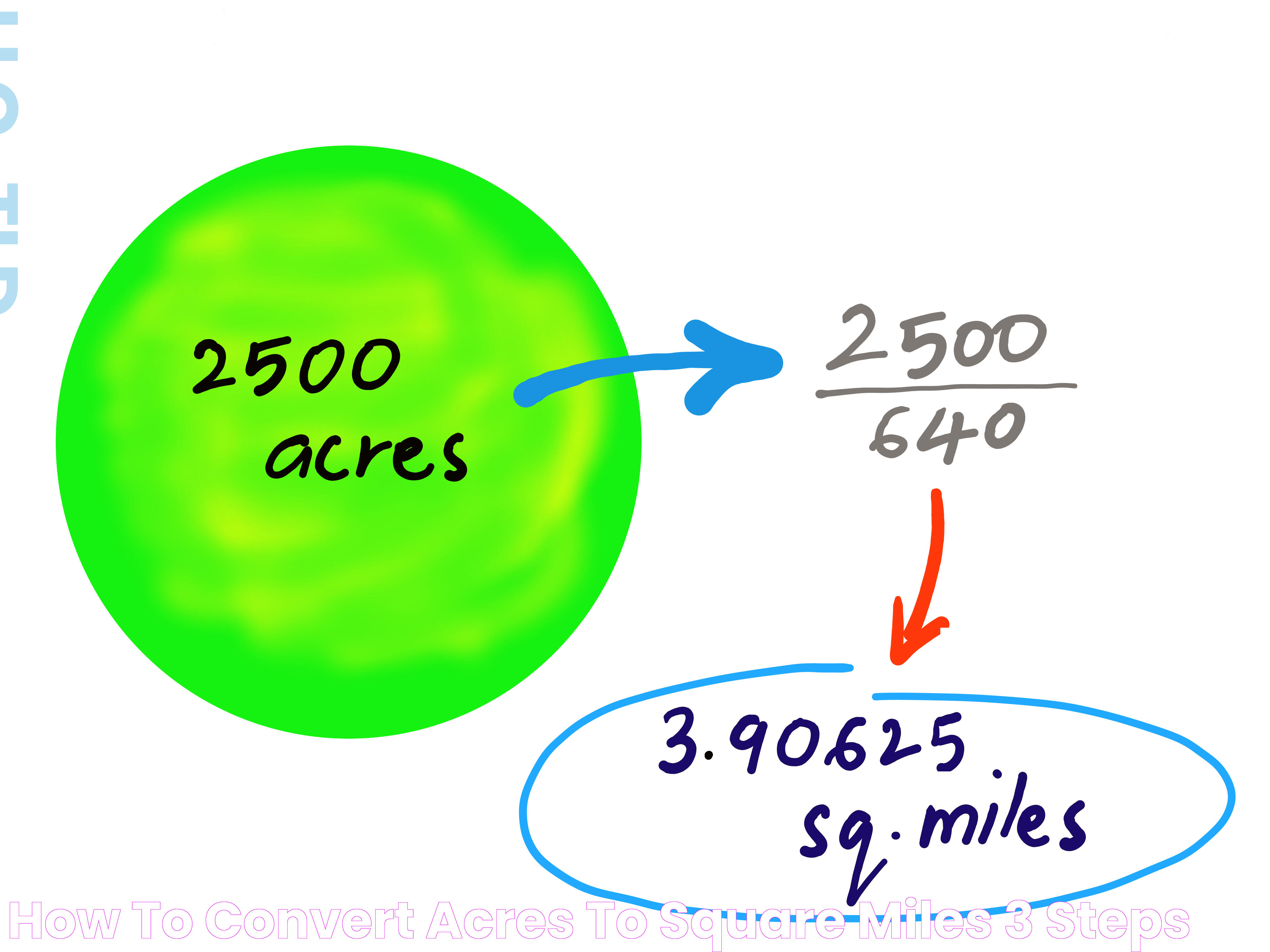
With such a large land area, Texas boasts a variety of ecosystems and wildlife. From the arid deserts of West Texas to the lush piney woods of the east, the state's geographical diversity is one of its most defining features. Rivers like the Rio Grande and the Red River carve through the land, providing water for agriculture and supporting a wide range of biodiversity. The state's landscape is not only a natural wonder but also a critical factor in its economic development, influencing industries such as agriculture, oil, and tourism. Understanding the sheer size of Texas in square miles offers insight into the state's cultural and historical significance. The vastness of Texas has shaped its identity, from the cowboy culture of the ranchlands to the vibrant urban life in cities like Houston and Dallas. Exploring Texas's square miles reveals a rich history of settlement, conflict, and growth, contributing to its reputation as a land of opportunity and adventure.
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Statehood | December 29, 1845 |
| Capital | Austin |
| Nickname | The Lone Star State |
| Population (2020) | 29.15 million |
| Total Area | 268,596 square miles |
Table of Contents
- Geographic Overview of Texas
- What is the Historical Significance of Texas's Size?
- Texas Ecosystems: A Diverse Landscape
- How Does Texas's Size Impact Its Economy?
- Cultural Diversity within Texas's Square Miles
- Urban vs. Rural: How Does Texas's Size Influence Settlement Patterns?
- Climatic Variations Across Texas Square Miles
- Wildlife and Biodiversity in Texas
- What are the Transportation Challenges in Texas?
- Tourism Attractions Across Texas
- Natural Resources and Their Management
- Education and Research Opportunities in Texas
- Future Prospects: What Lies Ahead for Texas?
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
Geographic Overview of Texas
Texas is a land of geographic extremes, stretching over 268,596 square miles. The state is bordered by four states: New Mexico to the west, Oklahoma to the north, Arkansas to the northeast, and Louisiana to the east, with the Gulf of Mexico lying to the southeast. The diverse topography includes the Guadalupe Mountains, the Chihuahuan Desert, the Great Plains, and the Piney Woods. Each region presents unique characteristics, from the high desert plains to the coastal marshes.
The state's geography is marked by significant landmarks, such as the Balcones Fault, which runs through central Texas, creating a division between the flatlands of the coastal plains and the hillier terrain of the Edwards Plateau. Additionally, the Rio Grande forms a natural border with Mexico, stretching over 1,254 miles. These features contribute to Texas's reputation as a land of contrasts, offering opportunities for various outdoor activities and exploration.
Read also:How Many People Can You Gameshare With On Ps5 A Comprehensive Guide
Texas's vast land area also means a wide range of climates. The western part of the state is arid, while the eastern regions experience humid subtropical conditions. This climatic diversity influences not only the natural environment but also agriculture, urban development, and lifestyle. Understanding Texas's geography is essential for appreciating the state's role in the nation's history and economy.
What is the Historical Significance of Texas's Size?
The historical significance of Texas's large size is deeply rooted in its past. Before becoming a state, Texas was an independent republic from 1836 to 1845, following its independence from Mexico. The vast land area was both a blessing and a challenge for settlers, offering ample space for agriculture and ranching, but also posing difficulties in terms of governance and defense.
Throughout history, Texas's size has played a pivotal role in its economic and political development. The discovery of oil in the early 20th century transformed Texas into a major economic powerhouse, with vast areas dedicated to oil exploration and production. The state's size also influenced its cultural identity, with the cowboy and ranching culture becoming synonymous with Texas lifestyle and history.
Moreover, the state's large land area has allowed for significant population growth, with major cities like Houston, San Antonio, and Dallas emerging as cultural and economic centers. The historical trajectory of Texas is intertwined with its geography, shaping its present and future.
Texas Ecosystems: A Diverse Landscape
Texas's vast square miles encompass a wide variety of ecosystems, each with its own unique flora and fauna. The state is home to 10 ecological regions, including the Piney Woods, Gulf Coast Prairies, South Texas Plains, and the Trans-Pecos Desert, to name a few. Each region supports distinct plant and animal life, contributing to the state's rich biodiversity.
The Piney Woods in East Texas are characterized by dense forests of pine and hardwoods, providing habitat for species such as white-tailed deer, squirrels, and numerous bird species. In contrast, the Trans-Pecos region in West Texas is a desert landscape, home to unique species like the Texas horned lizard and the desert bighorn sheep.
Read also:Efficiently Finding Products Look Up Item By Upc At Walmart
The Gulf Coast region features coastal marshes and estuaries, supporting a diverse range of aquatic life, including fish, crabs, and migratory birds. The diverse ecosystems of Texas not only offer opportunities for wildlife observation and conservation but also play a crucial role in maintaining ecological balance and supporting local economies through activities like fishing and tourism.
How Does Texas's Size Impact Its Economy?
Texas's large land area has a profound impact on its economy, providing vast resources and opportunities for various industries. Agriculture remains a significant sector, with Texas leading the nation in cattle production. The state's diverse climates and soils support a wide range of crops, including cotton, corn, and wheat.
Additionally, Texas is a major player in the energy sector, with its extensive oil and natural gas reserves. The Permian Basin, located in West Texas, is one of the largest oil-producing regions in the world. The state's size allows for large-scale energy production, contributing to its status as a global energy leader.
Texas's economy also benefits from its strategic location, serving as a gateway for trade with Mexico and other international markets. The state's transportation infrastructure, including ports, highways, and railways, supports robust trade activities, further bolstering its economic strength. The combination of natural resources, strategic location, and diverse industries makes Texas a vital economic engine for the United States.
Cultural Diversity within Texas's Square Miles
Texas's vast size and diverse geography contribute to a rich tapestry of cultural diversity. The state is home to a wide range of ethnic and cultural groups, each with its own traditions and contributions to the state's identity. From the vibrant Hispanic culture in South Texas to the German and Czech influences in the Hill Country, Texas celebrates a variety of cultural heritages.
The state's large cities, such as Houston and Dallas, are melting pots of cultures, attracting immigrants from around the world. This diversity is reflected in the state's cuisine, music, and festivals, offering a unique blend of traditions and experiences. Texas's cultural diversity is also evident in its languages, with English, Spanish, and various indigenous languages spoken across the state.
The celebration of cultural diversity is an integral part of Texas's identity, fostering a sense of community and inclusivity. The state's cultural heritage is preserved and promoted through various institutions, such as museums, cultural centers, and educational programs, ensuring that future generations continue to appreciate and embrace the rich cultural mosaic of Texas.
Urban vs. Rural: How Does Texas's Size Influence Settlement Patterns?
Texas's large land area has led to varied settlement patterns, with significant differences between urban and rural areas. Major cities like Houston, San Antonio, Dallas, and Austin are urban hubs, characterized by dense populations, diverse industries, and vibrant cultural scenes. These cities attract people from across the state and beyond, offering numerous job opportunities and amenities.
In contrast, rural areas in Texas are often sparsely populated, with economies primarily based on agriculture, ranching, and natural resource extraction. The vast open spaces of rural Texas offer a different lifestyle, with a focus on community and self-sufficiency. The state's size allows for a balance between urban and rural living, providing residents with a range of options depending on their preferences and needs.
The differences between urban and rural areas in Texas also influence political, social, and economic dynamics. Urban areas tend to be more diverse and progressive, while rural areas often emphasize traditional values and community-oriented living. Understanding these settlement patterns is essential for policymakers and planners as they address the needs and challenges of both urban and rural populations.
Climatic Variations Across Texas Square Miles
Texas is a state of climatic extremes, with weather conditions varying significantly across its vast land area. The state's size means it encompasses several climate zones, from arid deserts in the west to humid subtropical regions in the east. This climatic diversity influences the state's agriculture, wildlife, and lifestyle.
In West Texas, the climate is characterized by hot summers and mild winters, with low precipitation levels. The desert regions experience significant temperature fluctuations between day and night. In contrast, the eastern part of the state enjoys a more moderate climate, with higher humidity levels and more frequent rainfall.
The Gulf Coast region is particularly prone to hurricanes and tropical storms, impacting the environment and local communities. Understanding the climatic variations across Texas is crucial for managing natural resources, planning infrastructure, and addressing environmental challenges. It also highlights the importance of adaptability and resilience in the face of changing weather patterns.
Wildlife and Biodiversity in Texas
Texas's vast square miles are home to a rich array of wildlife and biodiversity. The state's diverse ecosystems support a wide range of plant and animal species, making it a haven for nature enthusiasts and conservationists. From the rolling hills of the Hill Country to the arid deserts of West Texas, each region offers unique habitats for wildlife.
Texas is home to iconic species such as the Texas longhorn, the nine-banded armadillo, and the javelina. Birdwatchers can spot a variety of species, including the endangered whooping crane and the colorful painted bunting. The state's rivers, lakes, and coastal areas provide crucial habitats for aquatic life, including fish, turtles, and alligators.
Conservation efforts in Texas focus on preserving these natural habitats and protecting endangered species. State parks, wildlife refuges, and nature reserves play a vital role in maintaining biodiversity and promoting environmental education. The state's commitment to conservation ensures that future generations can continue to enjoy and appreciate Texas's natural wonders.
What are the Transportation Challenges in Texas?
Texas's large land area presents significant transportation challenges, impacting both urban and rural communities. The state's vastness requires an extensive transportation network to connect its cities, towns, and rural areas. Highways, railways, and airports play a crucial role in facilitating the movement of people and goods across the state.
In urban areas, traffic congestion is a major concern, with growing populations placing increasing demands on road infrastructure. Cities like Houston and Dallas are investing in public transportation systems and infrastructure improvements to address these challenges and promote sustainable mobility.
In rural areas, transportation challenges often involve maintaining and upgrading road networks to ensure accessibility and connectivity. The vast distances between communities can make it difficult for residents to access essential services and opportunities. Addressing these transportation challenges requires a coordinated effort from state and local governments, as well as investments in innovative solutions like advanced transportation technologies and infrastructure expansion.
Tourism Attractions Across Texas
Texas's vast square miles offer a wealth of tourism attractions, drawing visitors from around the world. The state's diverse landscapes, rich history, and vibrant culture provide endless opportunities for exploration and adventure. From natural wonders to cultural landmarks, Texas has something to offer every traveler.
Nature enthusiasts can explore the rugged beauty of Big Bend National Park, hike the trails of the Guadalupe Mountains, or relax on the sandy beaches of the Gulf Coast. History buffs can visit the Alamo in San Antonio, explore the historic districts of Galveston, or learn about Texas's cowboy heritage at the Fort Worth Stockyards.
Texas's cities also offer a range of attractions, from the Space Center Houston to the vibrant arts and music scenes in Austin. The state's culinary scene is a highlight, with diverse cuisine reflecting its multicultural heritage. Whether you're seeking outdoor adventures, cultural experiences, or culinary delights, Texas's tourism attractions provide a rich and rewarding experience for visitors.
Natural Resources and Their Management
Texas is endowed with a wealth of natural resources, contributing to its economic prosperity and environmental health. The state's vast land area encompasses abundant reserves of oil, natural gas, and minerals, driving its energy sector and supporting industries such as manufacturing and transportation.
Water resources are also a critical aspect of Texas's natural wealth, with major rivers like the Rio Grande, Colorado, and Trinity providing water for agriculture, industry, and urban areas. The state's diverse ecosystems support a variety of plant and animal species, offering opportunities for conservation and sustainable use.
Effective management of Texas's natural resources is essential for ensuring their long-term sustainability and economic viability. State agencies, environmental organizations, and local communities work together to develop strategies for resource conservation, pollution control, and habitat preservation. Responsible resource management is key to balancing economic growth with environmental protection, ensuring that Texas's natural heritage is preserved for future generations.
Education and Research Opportunities in Texas
Texas's vast land area and diverse population provide a wealth of education and research opportunities. The state is home to several prestigious universities, including the University of Texas at Austin, Texas A&M University, and Rice University, which offer a wide range of academic programs and research initiatives.
These institutions attract students and researchers from around the world, contributing to Texas's reputation as a hub of innovation and knowledge. Research in Texas spans various fields, from energy and agriculture to technology and healthcare, driving advancements that benefit the state and beyond.
In addition to higher education institutions, Texas's education system includes numerous public and private schools, providing quality education to students across the state. Educational programs and initiatives focus on promoting STEM education, career readiness, and cultural awareness, preparing students for success in a rapidly changing world.
Future Prospects: What Lies Ahead for Texas?
The future prospects for Texas are shaped by its vast land area, diverse population, and dynamic economy. As the state continues to grow and evolve, it faces both opportunities and challenges that will influence its trajectory in the coming years.
Texas's economy is expected to remain strong, driven by its energy sector, agriculture, technology, and trade. The state's strategic location and natural resources provide a competitive advantage, attracting businesses and investments. However, addressing issues such as infrastructure development, environmental sustainability, and social equity will be crucial for ensuring long-term prosperity.
The state's cultural diversity and vibrant communities will continue to be a source of strength, fostering innovation and collaboration. Embracing inclusivity and promoting cultural awareness will be essential for building a cohesive and resilient society. As Texas looks to the future, it has the potential to lead the nation in economic development, environmental stewardship, and social progress.
Frequently Asked Questions
How big is Texas in square miles?
Texas covers an area of 268,596 square miles, making it the second-largest state in the United States.
What are the major cities in Texas?
Major cities in Texas include Houston, San Antonio, Dallas, Austin, and Fort Worth.
What is the climate like in Texas?
Texas has a diverse climate, ranging from arid deserts in the west to humid subtropical regions in the east, with significant variations in temperature and precipitation across the state.
What are some popular tourist attractions in Texas?
Popular tourist attractions in Texas include Big Bend National Park, the Alamo, Space Center Houston, and the Fort Worth Stockyards.
What industries drive Texas's economy?
Key industries in Texas's economy include energy (oil and natural gas), agriculture, technology, and trade.
How does Texas manage its natural resources?
Texas manages its natural resources through a combination of state agencies, environmental organizations, and local communities, focusing on conservation, sustainable use, and pollution control.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Texas's vast square miles offer a wealth of opportunities and challenges, shaping the state's identity and future prospects. Its diverse geography, rich history, and vibrant culture make it a unique and dynamic state, attracting people from around the world. Understanding the significance of Texas's size provides valuable insights into its economic, social, and environmental landscape. As Texas continues to grow and evolve, it remains a land of opportunity, innovation, and adventure.