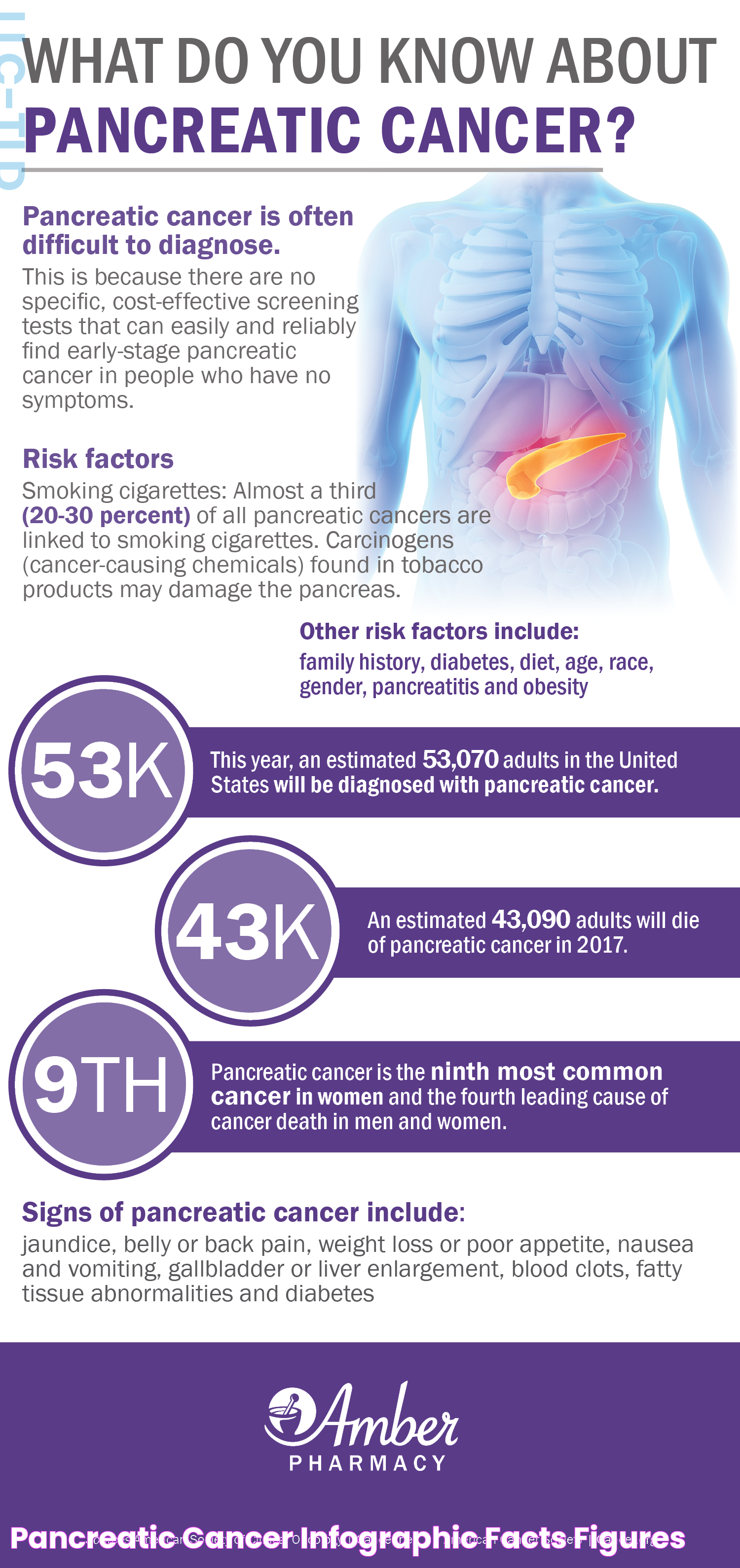
Pancreatic cancer, a formidable adversary in the realm of oncology, poses a significant challenge with its insidious progression and complex treatment landscape. As patients approach the last stage of this disease, understanding the side effects becomes paramount for both patients and caregivers. The journey through the final stage of pancreatic cancer is often fraught with physical, emotional, and psychological hurdles. However, awareness and proactive management of side effects can lead to enhanced quality of life and dignity during this critical time.
The last stage of pancreatic cancer, often referred to as stage IV, is characterized by the spread of cancer cells to distant organs such as the liver, lungs, or peritoneum. This metastasis introduces a unique set of challenges and symptoms that require specialized care and attention. While the prognosis at this stage can be daunting, it is essential to focus on palliative care, which aims to alleviate symptoms and provide emotional support. By addressing the side effects head-on, there is potential to improve comfort and well-being for those navigating this intricate phase of their cancer journey.
Medically managing the side effects of pancreatic cancer in its last stage involves a multidisciplinary approach, including oncologists, palliative care specialists, nutritionists, and mental health professionals. Common side effects such as pain, fatigue, digestive issues, and emotional discomfort necessitate tailored interventions. Through collaborative efforts, healthcare providers strive to ensure that patients receive comprehensive care that addresses both physical symptoms and emotional needs. While the path may be challenging, a focus on holistic care and support can offer solace and hope to patients and their families.
Read also:Enhancing Meals With Medium Eggs Nutritional Benefits And Culinary Uses
Table of Contents
- What is Pancreatic Cancer?
- How Does Pancreatic Cancer Progress?
- Signs and Symptoms of Last Stage Pancreatic Cancer
- What Are the Side Effects of Pancreatic Cancer Last Stage?
- Managing Pain and Discomfort
- Addressing Fatigue and Weakness
- Coping with Digestive Issues
- Emotional and Psychological Support
- Role of Palliative Care
- Nutrition and Hydration
- Caregiver Support and Resources
- What Questions Should I Ask My Healthcare Provider?
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
What is Pancreatic Cancer?
Pancreatic cancer is a malignant neoplasm originating in the tissues of the pancreas, an organ located behind the stomach that plays a crucial role in digestion and blood sugar regulation. The pancreas contains two main types of cells: exocrine cells, which produce digestive enzymes, and endocrine cells, which produce hormones like insulin. The majority of pancreatic cancers arise from the exocrine cells and are known as pancreatic adenocarcinomas.
Pancreatic cancer is notorious for its aggressive nature and its tendency to be diagnosed at an advanced stage. This is partly due to the pancreas's deep location in the abdomen, which makes early tumors difficult to detect. Additionally, early-stage pancreatic cancer often presents with nonspecific symptoms or no symptoms at all, leading to delayed diagnosis.
The exact cause of pancreatic cancer remains elusive, but several risk factors have been identified, including smoking, obesity, a family history of pancreatic cancer, chronic pancreatitis, and certain genetic syndromes. Understanding these risk factors can aid in early detection strategies and potentially reduce the incidence of the disease.
How Does Pancreatic Cancer Progress?
The progression of pancreatic cancer is generally classified into four stages, with the last stage representing the most advanced form of the disease. Here's a brief overview of each stage:
- Stage I: The cancer is confined to the pancreas and has not spread to nearby lymph nodes or distant sites. Surgical resection is often possible at this stage, offering the best chance for a cure.
- Stage II: The cancer has grown into nearby tissues or organs and may have spread to nearby lymph nodes. Surgical resection may still be possible, but the prognosis becomes more guarded.
- Stage III: The cancer has spread to major blood vessels near the pancreas and is generally considered unresectable. Treatment focuses on controlling the disease and alleviating symptoms.
- Stage IV: The cancer has metastasized to distant organs such as the liver, lungs, or peritoneum. Treatment is primarily palliative, aimed at improving quality of life and managing symptoms.
Understanding the progression of pancreatic cancer is crucial for determining the most appropriate treatment strategy. While early-stage disease may be treated with surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation, advanced stages often require a focus on symptom management and palliative care.
Signs and Symptoms of Last Stage Pancreatic Cancer
The signs and symptoms of pancreatic cancer in its last stage can vary depending on the extent of the disease and the organs affected by metastasis. Common symptoms include:
Read also:Mastering The Art Of Alto Saxophone Music A Harmonious Guide
- Pain: Abdominal or back pain is a common symptom due to the tumor pressing on surrounding organs and nerves.
- Jaundice: Yellowing of the skin and eyes occurs when the bile duct is blocked by the tumor, leading to a buildup of bilirubin in the blood.
- Weight Loss: Unintentional weight loss is common as the body's ability to absorb nutrients is compromised.
- Nausea and Vomiting: These symptoms may result from the tumor pressing on the stomach or intestines, causing obstruction.
- Fatigue: Persistent tiredness and lethargy are common as the body expends energy fighting the disease.
- Changes in Bowel Habits: Diarrhea or constipation can occur due to changes in digestion and absorption.
It is essential to recognize these symptoms early and communicate them to healthcare providers to ensure timely intervention and management.
What Are the Side Effects of Pancreatic Cancer Last Stage?
The side effects experienced during the last stage of pancreatic cancer are often a result of both the disease itself and the treatments administered to manage it. Common side effects include:
- Pain: Pain is a prevalent side effect, often requiring strong analgesics or nerve blocks for relief.
- Fatigue: Patients may experience profound fatigue due to the cancer's metabolic demands and treatment side effects.
- Digestive Issues: Nausea, vomiting, and loss of appetite can significantly impact nutrition and hydration.
- Emotional Distress: Anxiety, depression, and fear are common as patients and families cope with the disease's progression.
- Skin Changes: Jaundice, dry skin, and itching can occur due to liver involvement or bile duct obstruction.
- Respiratory Issues: Shortness of breath may result from lung metastasis or fluid accumulation in the chest.
Addressing these side effects through a multidisciplinary approach is essential for enhancing the quality of life and providing comfort to patients in the last stage of pancreatic cancer.
Managing Pain and Discomfort
Pain management is a critical component of care for patients with advanced pancreatic cancer. Effective pain control can significantly improve a patient's quality of life and overall well-being. Here are some strategies for managing pain and discomfort:
- Medications: Analgesics, including opioids and non-opioids, are commonly used to alleviate pain. The choice of medication depends on the severity of the pain and the patient's response to treatment.
- Nerve Blocks: In some cases, nerve blocks can be used to provide relief from severe pain by interrupting pain signals to the brain.
- Palliative Radiation: Radiation therapy can help shrink tumors and relieve pain caused by tumor growth pressing on organs or nerves.
- Complementary Therapies: Techniques such as acupuncture, massage, and relaxation exercises can provide additional relief and improve comfort.
Collaborating with pain specialists and palliative care teams can ensure a comprehensive approach to pain management, allowing patients to focus on their emotional and spiritual needs.
Addressing Fatigue and Weakness
Fatigue and weakness are common and debilitating symptoms experienced by patients with advanced pancreatic cancer. Addressing these symptoms requires a multifaceted approach that includes:
- Energy Conservation: Encouraging patients to prioritize activities and take frequent rest breaks can help manage energy levels.
- Nutrition and Hydration: Adequate nutrition and hydration are essential to combat fatigue. Working with a nutritionist can help develop a personalized eating plan that meets the patient's needs.
- Physical Activity: Gentle exercises, such as walking or stretching, can help maintain muscle strength and reduce fatigue.
- Psychosocial Support: Addressing emotional and psychological factors contributing to fatigue, such as depression or anxiety, can improve overall energy levels.
By implementing these strategies, patients can better manage fatigue and enhance their ability to engage in meaningful activities.
Coping with Digestive Issues
Digestive issues, including nausea, vomiting, and changes in appetite, are common side effects of pancreatic cancer and its treatment. To cope with these challenges, consider the following approaches:
- Dietary Modifications: Eating smaller, more frequent meals can help manage nausea and maintain nutritional intake.
- Anti-Nausea Medications: Medications such as antiemetics can be prescribed to alleviate nausea and improve appetite.
- Hydration: Ensuring adequate fluid intake is essential to prevent dehydration and support overall health.
- Consulting a Nutritionist: A nutritionist can provide guidance on dietary changes and suggest supplements to meet the patient's nutritional needs.
Addressing digestive issues requires a personalized approach that considers the patient's preferences and the underlying causes of their symptoms.
Emotional and Psychological Support
The emotional and psychological impact of advanced pancreatic cancer can be profound, affecting both patients and their families. Providing support and addressing emotional needs is a crucial aspect of comprehensive care. Consider the following strategies:
- Counseling and Therapy: Individual or family counseling can help patients and loved ones process their emotions and cope with the challenges of the disease.
- Support Groups: Joining a support group allows patients and families to connect with others facing similar challenges, providing a sense of community and understanding.
- Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques: Practices such as meditation, yoga, and deep breathing exercises can help reduce stress and promote emotional well-being.
- Spiritual Support: For some patients, spiritual or religious support can provide comfort and a sense of peace during difficult times.
By addressing emotional and psychological needs, patients and families can find strength and resilience as they navigate the complexities of advanced pancreatic cancer.
Role of Palliative Care
Palliative care plays a pivotal role in the management of advanced pancreatic cancer, focusing on improving quality of life by addressing physical, emotional, and spiritual needs. The goals of palliative care include:
- Symptom Management: Palliative care teams work to relieve symptoms such as pain, nausea, and fatigue, enhancing patient comfort.
- Emotional and Psychological Support: Providing counseling and support to patients and families helps address the emotional impact of the disease.
- Care Coordination: Palliative care specialists collaborate with other healthcare providers to ensure seamless and comprehensive care.
- Advance Care Planning: Helping patients and families make informed decisions about treatment options and end-of-life care preferences.
Engaging with palliative care services early in the disease trajectory can provide significant benefits and support for both patients and caregivers.
Nutrition and Hydration
Maintaining adequate nutrition and hydration is essential for patients with advanced pancreatic cancer, as these factors play a crucial role in overall health and well-being. Consider the following tips for optimizing nutrition and hydration:
- Balanced Diet: Encourage a balanced diet rich in nutrients, focusing on high-calorie and high-protein foods to meet energy needs.
- Small, Frequent Meals: Eating smaller, more frequent meals can help manage digestive issues and improve appetite.
- Hydration: Ensure adequate fluid intake through water, soups, and other hydrating beverages to prevent dehydration.
- Nutritional Supplements: Consider incorporating nutritional supplements or meal replacement shakes to enhance caloric intake.
- Consulting a Nutritionist: A nutritionist can provide personalized dietary recommendations and assist in meal planning.
By prioritizing nutrition and hydration, patients can support their body's ability to cope with the demands of the disease and treatment.
Caregiver Support and Resources
Caregivers play a vital role in the support and care of patients with advanced pancreatic cancer. Providing resources and support for caregivers is essential to ensure they can effectively fulfill their responsibilities while maintaining their own well-being. Consider the following strategies:
- Education and Training: Providing caregivers with information and training on managing symptoms and providing care can enhance their confidence and competence.
- Respite Care: Offering respite care allows caregivers to take breaks and recharge, reducing the risk of burnout.
- Support Groups: Caregiver support groups provide a platform for sharing experiences, advice, and emotional support with others in similar situations.
- Access to Resources: Connecting caregivers with resources such as financial assistance, counseling services, and community programs can alleviate stress and burden.
By supporting caregivers, healthcare providers can ensure that both patients and their families receive comprehensive and compassionate care.
What Questions Should I Ask My Healthcare Provider?
Engaging in open and honest communication with healthcare providers is essential for patients and families navigating advanced pancreatic cancer. Consider asking the following questions to gain a better understanding of the disease and treatment options:
- What are the available treatment options for managing symptoms and improving quality of life?
- How can we effectively manage pain and other side effects of the disease and treatment?
- What support services are available for patients and caregivers, including palliative care and counseling?
- What can we expect in terms of disease progression and potential complications?
- Are there clinical trials or experimental treatments that may be suitable for the patient?
- What resources are available for advance care planning and end-of-life decision-making?
By asking these questions, patients and families can make informed decisions and actively participate in their care.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are the common symptoms of last stage pancreatic cancer?
Common symptoms include pain, jaundice, weight loss, nausea, vomiting, fatigue, and changes in bowel habits.
2. How is pain managed in advanced pancreatic cancer?
Pain management strategies include medications, nerve blocks, palliative radiation, and complementary therapies.
3. What role does palliative care play in managing pancreatic cancer?
Palliative care focuses on symptom management, emotional support, care coordination, and advance care planning.
4. How can caregivers support patients with advanced pancreatic cancer?
Caregivers can provide emotional support, assist with daily activities, and ensure the patient receives appropriate medical care.
5. What dietary changes can help manage digestive issues in pancreatic cancer?
Dietary changes include eating small, frequent meals, using anti-nausea medications, and consulting a nutritionist for personalized advice.
6. What resources are available for caregiver support?
Resources include education and training, respite care, support groups, and access to financial assistance and counseling services.
Conclusion
Navigating the challenges of pancreatic cancer side effects last stag requires a comprehensive and compassionate approach that addresses both physical and emotional needs. By understanding the side effects and implementing strategies for symptom management, patients and caregivers can find hope and solace during this difficult time. Empowered with knowledge and support, individuals can focus on enhancing quality of life and making meaningful connections with loved ones. As we continue to advance in our understanding of pancreatic cancer, the importance of holistic and patient-centered care remains at the forefront, providing strength and resilience to those affected by this formidable disease.
For more information and support, consider visiting reputable sources such as the American Cancer Society or the Pancreatic Cancer Action Network.