The bond between humans and dogs is as old as time itself. With their unfaltering loyalty and endearing companionship, dogs have earned a special place in the hearts of many. But have you ever wondered what makes these magnificent creatures tick? The answer lies in understanding the intricate design of a dog's anatomy, starting with their skeleton. A dog's skeleton is a remarkable structure that provides support, protection, and mobility, enabling them to perform a myriad of activities from fetching a ball to running at incredible speeds.
The skeletal system of a dog is an engineering marvel, consisting of over 300 bones that come together to form a robust yet flexible framework. This system is not only vital for movement but also plays a crucial role in protecting vital organs such as the heart and lungs. The skeleton's design reflects the evolutionary adaptations that have allowed dogs to thrive in various environments, showcasing the diversity and versatility of the canine family.
Understanding the skeleton of a dog offers valuable insights into their health and well-being. As dog owners, having knowledge of canine anatomy can help in identifying potential health issues and ensuring proper care for our furry friends. Whether you're a veterinarian, a pet owner, or simply a dog enthusiast, exploring the wonders of a dog's skeleton can deepen your appreciation for these incredible animals and their complex physiology.
Read also:Mastering T9 To Text The Future Of Mobile Communication
Table of Contents
- What is the biomechanics of a dog's skeleton?
- Key components of a canine skeleton
- How do human and dog skeletons compare?
- Skeletal development in puppies
- What role does the skeleton play in a dog's health?
- Diet and its impact on bone health in dogs
- Common skeletal disorders in dogs
- Diagnosis and treatment of bone issues
- Exercise and skeletal fitness in dogs
- Skeletal care tips for dog owners
- Fascinating facts about dog skeletons
- How does the skeletal system interact with musculature?
- What evolutionary insights can we gain from the skeleton?
- The importance of skeletal health check-ups
- FAQs about skeleton and dog
- Conclusion
What is the biomechanics of a dog's skeleton?
Dogs have a highly specialized skeletal structure that is designed to support their speed, agility, and endurance. The biomechanics of a dog's skeleton allow it to perform a variety of movements with precision and efficiency. The skeletal system provides the framework for muscular attachment, facilitating movement through joint articulations.
One of the defining features of a dog's skeleton is its flexibility, which is crucial for running, jumping, and other dynamic activities. The spine, in particular, plays a significant role in enabling these movements. With its series of vertebrae, the spine allows for flexibility and shock absorption, protecting the dog from injury during high-impact activities.
The limbs of a dog are designed for both speed and strength. The forelimbs are connected to the body via muscles and ligaments, allowing for a wide range of motion. The hind limbs, equipped with strong muscles and tendons, provide the power needed for acceleration and propulsion. Understanding these biomechanics is essential for appreciating the remarkable abilities of our canine companions.
Key components of a canine skeleton
A dog's skeleton is made up of several key components, each serving a specific purpose. These include:
- Skull: Protects the brain and forms the structure of the face.
- Vertebral Column: Supports the body and houses the spinal cord.
- Rib Cage: Protects vital organs like the heart and lungs.
- Forelimbs: Include the scapula, humerus, radius, and ulna, which provide mobility and support.
- Hind Limbs: Consist of the pelvis, femur, tibia, and fibula, which are crucial for movement and stability.
Each of these components is interconnected, working together to provide the necessary support and function for a dog's active lifestyle. The intricate design of the canine skeleton is a testament to the evolutionary adaptations that have allowed dogs to thrive in diverse environments.
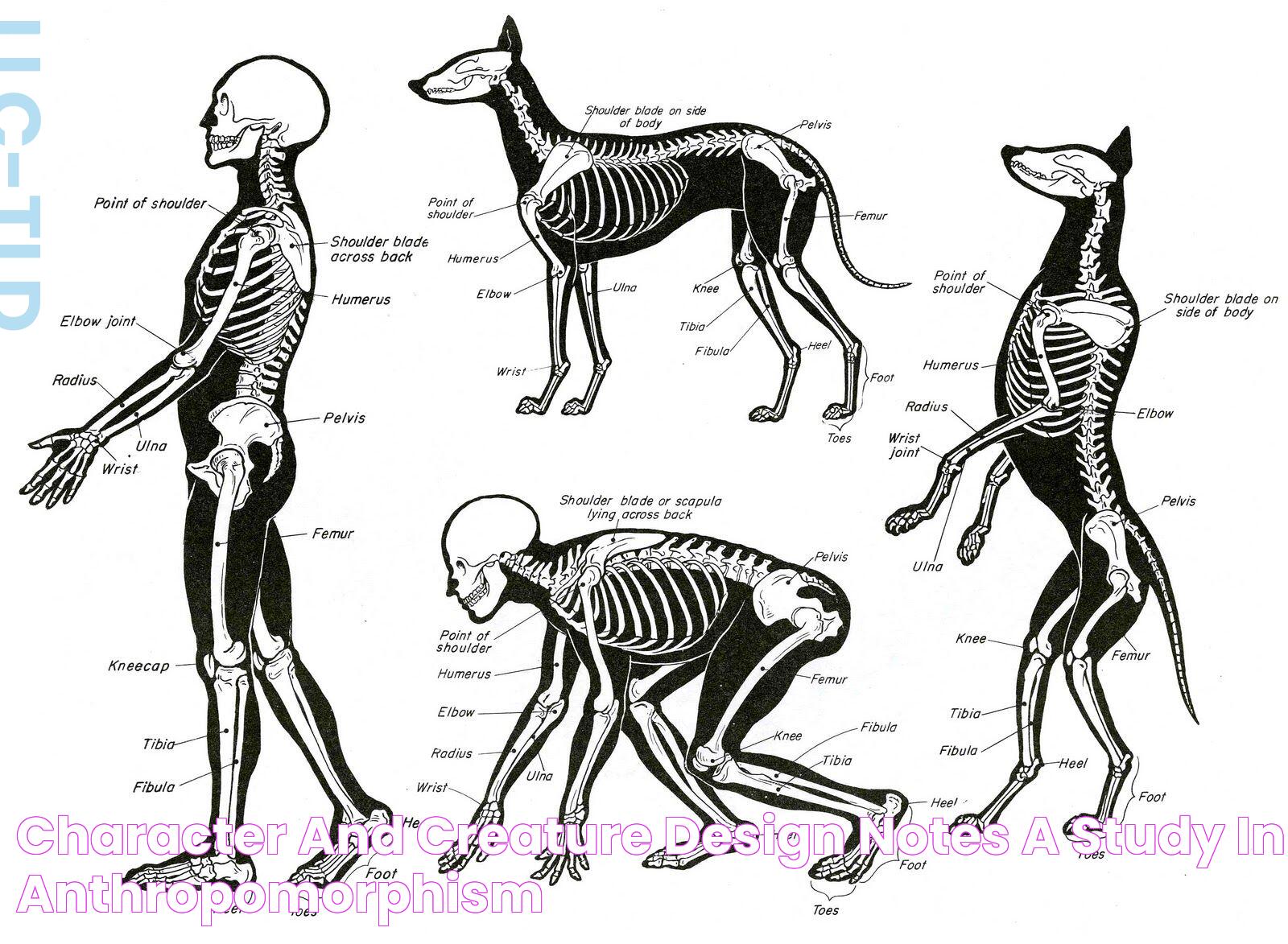
How do human and dog skeletons compare?
While human and dog skeletons share some similarities, such as basic bone structure and joint types, there are notable differences that reflect the distinct evolutionary paths of each species. For instance, humans have a more upright posture, which is supported by a thicker, more robust pelvis and a longer spine. In contrast, dogs have a horizontal body alignment, which is optimized for speed and agility.
Read also:Bohemian Grove Members Secrets Of The Elite Retreat
Another significant difference lies in the limb structure. Humans possess hands and feet with opposable thumbs and toes, allowing for a wide range of manipulative abilities. Dogs, however, have paws designed for running and digging, with adaptations such as cushioned pads and curved claws for traction and grip.
Despite these differences, both human and dog skeletons are marvels of natural engineering, demonstrating the remarkable adaptability of vertebrate anatomy.
Skeletal development in puppies
The skeletal development of puppies is a critical phase that sets the foundation for their future health and mobility. During this period, the bones undergo rapid growth and mineralization, transforming from soft cartilage into strong, robust structures.
Puppies are born with a high proportion of cartilage, which gradually ossifies into bone as they mature. This process is influenced by several factors, including genetics, nutrition, and exercise. Providing a balanced diet rich in calcium and phosphorus is essential for healthy bone development, while regular, moderate exercise helps strengthen the bones and joints.
Monitoring a puppy's growth and development is crucial for identifying potential skeletal issues early on. Regular veterinary check-ups and appropriate care can help ensure a puppy's skeleton develops properly, laying the groundwork for a healthy, active life.
What role does the skeleton play in a dog's health?
The skeleton of a dog plays a vital role in its overall health and well-being. It provides the structural support necessary for movement and activity, while also protecting vital organs from injury. Additionally, the skeleton serves as a reservoir for essential minerals such as calcium and phosphorus, which are crucial for maintaining bone density and strength.
A healthy skeletal system is essential for a dog's quality of life. It enables them to perform a wide range of activities, from running and jumping to playing and exploring. Conversely, skeletal issues can lead to pain, discomfort, and reduced mobility, impacting a dog's ability to enjoy life to the fullest.
Ensuring the health of a dog's skeleton involves providing proper nutrition, regular exercise, and routine veterinary check-ups. By taking proactive steps to support skeletal health, pet owners can help their dogs live long, active, and fulfilling lives.
Diet and its impact on bone health in dogs
Diet plays a crucial role in maintaining the health and strength of a dog's skeleton. Providing a balanced diet that includes adequate amounts of calcium, phosphorus, and other essential nutrients is vital for supporting bone growth and repair.
Calcium and phosphorus are the primary minerals that contribute to bone density and strength. These minerals are often found in high-quality commercial dog foods, but supplementation may be necessary for certain dogs, especially those with specific health needs or dietary restrictions.
In addition to minerals, vitamins such as vitamin D and vitamin K are important for bone health. Vitamin D aids in the absorption of calcium, while vitamin K is involved in bone metabolism and repair. Ensuring a diet that includes these vitamins, either through food or supplements, can help maintain optimal bone health.
It's important for dog owners to consult with a veterinarian when considering dietary changes or supplements, as individual needs can vary based on factors such as age, breed, and activity level.
Common skeletal disorders in dogs
Dogs can suffer from a variety of skeletal disorders that affect their health and mobility. Some of the most common skeletal issues in dogs include:
- Hip Dysplasia: A genetic condition where the hip joint is malformed, leading to arthritis and pain.
- Osteoarthritis: A degenerative joint disease that causes pain and stiffness in the joints.
- Luxating Patella: A condition where the kneecap dislocates from its normal position.
- Fractures: Broken bones resulting from trauma or injury.
- Intervertebral Disc Disease (IVDD): A condition affecting the spinal discs, leading to pain and neurological issues.
Early detection and treatment of these disorders are crucial for managing symptoms and improving a dog's quality of life. Regular veterinary check-ups and monitoring for signs of discomfort or mobility issues can help catch these problems early, allowing for more effective intervention.
Diagnosis and treatment of bone issues
Diagnosing skeletal disorders in dogs often involves a combination of physical examinations, imaging tests (such as X-rays or MRIs), and laboratory tests. These diagnostic tools help veterinarians identify the specific issue and determine the most appropriate course of treatment.
Treatment for skeletal issues can vary depending on the severity and nature of the condition. Common treatment options include:
- Medications: Pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs to manage symptoms.
- Physical Therapy: Exercises and rehabilitation to improve mobility and strength.
- Surgery: Corrective procedures to repair or stabilize affected bones and joints.
- Dietary Supplements: Nutritional support to promote bone health and recovery.
In many cases, a combination of treatments may be necessary to achieve the best outcomes. Working closely with a veterinarian can help ensure a tailored approach that addresses the specific needs of the dog and promotes optimal recovery and well-being.
Exercise and skeletal fitness in dogs
Regular exercise is essential for maintaining the health and fitness of a dog's skeleton. Physical activity helps strengthen bones and muscles, improve joint flexibility, and support overall well-being. However, it's important to tailor exercise routines to the individual needs of the dog, taking into account factors such as age, breed, and health status.
For puppies, moderate, low-impact activities such as walking and playing are ideal for supporting skeletal development without putting undue stress on growing bones. As dogs mature, activities like running, fetch, and agility training can provide excellent cardiovascular and muscular benefits.
Senior dogs may require adjusted exercise routines to accommodate age-related changes in mobility and endurance. Gentle walks, swimming, and low-impact games can help keep older dogs active and engaged while minimizing the risk of injury.
By incorporating regular exercise into a dog's routine, pet owners can help maintain skeletal health and enhance their furry friend's quality of life.
Skeletal care tips for dog owners
Ensuring the health of your dog's skeleton involves a combination of proper care, nutrition, and regular veterinary check-ups. Here are some tips for maintaining optimal skeletal health in dogs:
- Provide a Balanced Diet: Ensure your dog's diet includes essential nutrients such as calcium, phosphorus, and vitamins D and K.
- Encourage Regular Exercise: Tailor exercise routines to your dog's age, breed, and health status to maintain bone and joint health.
- Monitor Weight: Maintain a healthy weight to reduce stress on bones and joints, minimizing the risk of skeletal issues.
- Schedule Regular Veterinary Check-Ups: Routine examinations can help detect and address potential skeletal problems early.
- Provide Supportive Surfaces: Use orthopedic beds and non-slip mats to protect joints and enhance comfort.
By following these tips, dog owners can help promote the well-being of their furry companions and ensure they enjoy a long, active, and healthy life.
Fascinating facts about dog skeletons
Dog skeletons are full of intriguing features and adaptations that reflect their evolutionary history and diverse capabilities. Here are some fascinating facts about the canine skeleton:
- Bone Count: Dogs have more bones than humans, with an average of 319 bones compared to the 206 in the human body.
- Skull Variability: The shape and size of dog skulls vary widely among breeds, contributing to their distinctive appearances and abilities.
- Flexible Spine: A dog's spine is highly flexible, allowing for a wide range of motion and enabling them to perform impressive feats of agility and speed.
- Powerful Jaw: Certain breeds, such as the Bulldog and Mastiff, have incredibly strong jaws capable of exerting significant pressure.
- Unique Adaptations: Breeds like the Greyhound have long, slender limbs and streamlined bodies designed for high-speed pursuits.
These features highlight the incredible diversity and adaptability of the canine family, showcasing the evolutionary innovations that have allowed dogs to thrive in a variety of environments.
How does the skeletal system interact with musculature?
The interaction between the skeletal system and musculature is a key factor in a dog's ability to move, perform tasks, and maintain posture. Muscles attach to bones via tendons, creating a system of levers that enable movement when muscles contract.
This interaction is essential for generating the force needed for activities such as walking, running, and jumping. The bones provide a sturdy structure for muscle attachment, while the joints allow for flexibility and range of motion.
Maintaining the health of both the skeletal and muscular systems is crucial for a dog's overall well-being. A balanced diet, regular exercise, and routine veterinary care can help support this interaction and ensure optimal function and mobility.
What evolutionary insights can we gain from the skeleton?
The skeleton of a dog provides valuable insights into their evolutionary history and the adaptations that have allowed them to thrive in various environments. By studying the skeletal structure, researchers can trace the development of specific traits and understand how dogs have evolved over time.
For example, the diversity in skull shapes and sizes among different breeds reflects their specialized roles and functions, from hunting and herding to companionship. Similarly, the variation in limb structure and body proportions highlights the different environments and lifestyles that have influenced the evolution of the canine family.
These evolutionary insights not only enhance our understanding of dogs as a species but also inform breeding practices and conservation efforts, helping to preserve the unique characteristics and capabilities of different breeds.
The importance of skeletal health check-ups
Regular skeletal health check-ups are essential for maintaining the well-being of dogs and ensuring early detection and management of potential issues. These check-ups typically involve a thorough physical examination, imaging tests, and laboratory assessments to evaluate the condition of the bones and joints.
Skeletal health check-ups can help identify conditions such as arthritis, fractures, and developmental disorders, allowing for timely intervention and treatment. By addressing these issues early, pet owners can help prevent further complications and improve their dog's quality of life.
Veterinarians play a crucial role in guiding pet owners through the process of maintaining skeletal health, providing recommendations for nutrition, exercise, and preventive care. By prioritizing regular check-ups, dog owners can ensure their beloved companions enjoy a long, healthy, and active life.
FAQs about skeleton and dog
- How many bones does a dog have?
Dogs have an average of 319 bones in their skeleton, which varies slightly among breeds.
- Can diet affect a dog's skeletal health?
Yes, diet plays a crucial role in maintaining bone health. A balanced diet with adequate calcium, phosphorus, and vitamins is essential.
- What are common signs of skeletal issues in dogs?
Common signs include limping, stiffness, difficulty moving, and reluctance to engage in physical activities.
- How can I help prevent skeletal disorders in my dog?
Providing a balanced diet, regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, and scheduling routine vet check-ups can help prevent skeletal disorders.
- Are some breeds more prone to skeletal issues?
Yes, certain breeds are more susceptible to conditions like hip dysplasia and arthritis due to genetic factors and body structure.
- What should I do if I suspect my dog has a skeletal problem?
If you suspect a skeletal issue, consult a veterinarian for a thorough examination and appropriate diagnostic tests.
Conclusion
The skeleton of a dog is a complex and fascinating structure that plays a crucial role in their health, mobility, and overall well-being. By understanding the intricacies of canine anatomy and taking proactive steps to support skeletal health, pet owners can help their furry companions lead long, active, and fulfilling lives. Regular veterinary care, a balanced diet, and appropriate exercise are essential components of maintaining optimal skeletal health, ensuring that dogs continue to be our loyal, energetic, and beloved companions for years to come.
For more in-depth information on canine skeletal health and care, consider visiting reputable veterinary websites and resources, such as the American Veterinary Medical Association (AVMA).