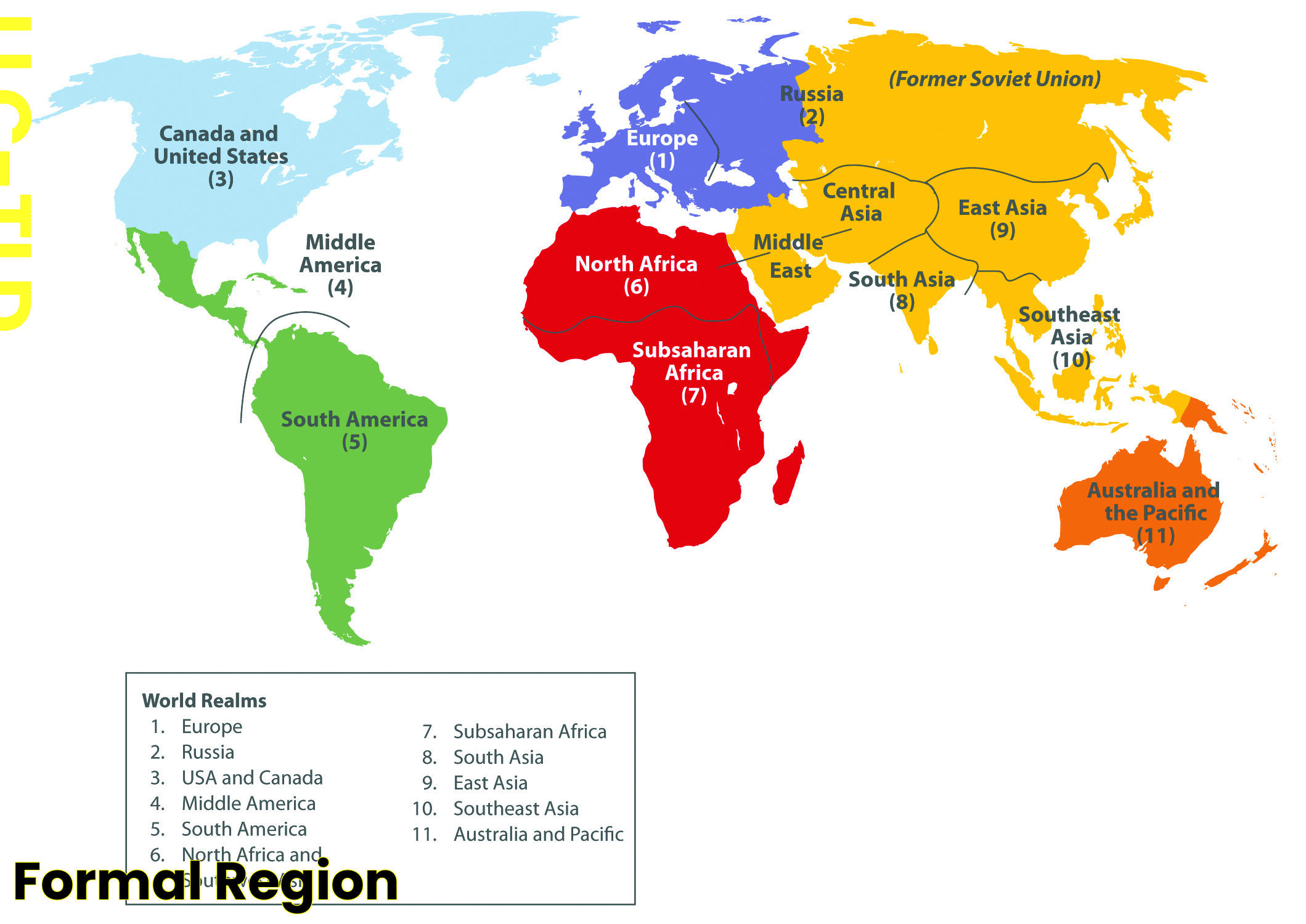
Formal regions are a fundamental concept in geography and sociology, serving as a means to categorize areas based on shared characteristics. These regions are defined by governmental, cultural, or physical attributes that are uniform throughout the area. Recognizing and understanding formal regions allows for clearer communication and analysis of geographical data, as well as providing insights into the socio-economic dynamics of a particular area.
In the context of geography, a formal region is often characterized by a legal or administrative boundary, such as a country, state, or city. These boundaries are established through political agreements or laws and are recognized by governing bodies. Formal regions can also be identified by uniform physical features, such as climate zones or vegetation types. The clear definition of these regions allows geographers to study patterns and relationships within and between areas, leading to more informed decision-making processes.
Furthermore, formal regions are not limited to physical geography but extend into cultural and economic realms. Cultural formal regions may include areas where a specific language is spoken or where a particular religion dominates. Economically, formal regions can be identified by shared economic activities, such as industrial regions or agricultural zones. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of formal regions, exploring their various types, applications, and significance in understanding the world around us.
Read also:Mastering The Art Of Maintaining Wood Stove Glass
Table of Contents
- What is a Formal Region?
- Characteristics of Formal Regions
- Types of Formal Regions
- How Are Formal Regions Defined?
- Examples of Formal Regions
- Importance of Formal Regions
- Formal Regions vs. Functional Regions
- Applications of Formal Regions in Society
- Geopolitical Aspects of Formal Regions
- Advantages of Using Formal Regions
- Challenges in Defining Formal Regions
- How Do Formal Regions Impact Policy?
- Can Formal Regions Change Over Time?
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
What is a Formal Region?
A formal region, also known as a uniform or homogeneous region, is an area defined by a high level of consistency in a specific attribute. This attribute could be political, cultural, or physical. The boundaries that define a formal region are clearly marked and widely recognized, often established by legal or political means. These regions are crucial in facilitating the administration of large areas, as well as in conducting regional planning and development.
Defining Attributes
Formal regions are characterized by a uniformity that can be measured or observed. Some of the defining attributes may include:
- Political boundaries such as countries, states, or provinces.
- Physical features like mountain ranges, climate zones, or river basins.
- Cultural elements such as language, religion, or ethnicity.
- Economic activities including agriculture, industry, or tourism.
Role in Geography
In the study of geography, formal regions play a pivotal role in analyzing spatial patterns and relationships. Geographers use formal regions to categorize areas for easier data collection, comparison, and analysis. This facilitates the study of human-environment interactions, economic trends, and cultural diffusion. By providing a structured framework, formal regions help geographers to understand and explain complex geographical phenomena.
Characteristics of Formal Regions
Formal regions exhibit several characteristics that set them apart from other types of regions. These characteristics help in the identification and classification of formal regions across the globe.
Uniformity
The most prominent feature of a formal region is its uniformity in one or more aspects. This uniformity can be seen in the consistent application of laws, the prevalence of a single language, or the dominance of a particular climate type. The uniformity aspect makes formal regions easily recognizable and distinguishable from surrounding areas.
Defined Boundaries
Formal regions have clearly defined boundaries that are recognized by governing bodies and organizations. These boundaries are often established through political agreements or natural features, providing a clear demarcation between different regions. The defined boundaries allow for efficient governance, resource allocation, and planning.
Read also:Inter Miami Jersey A Symbol Of Passion And Style
Stability
Formal regions tend to exhibit a level of stability over time. The defined boundaries and uniform attributes provide consistency, making these regions relatively stable compared to other types of regions. However, changes can occur due to political, economic, or environmental factors.
Types of Formal Regions
Formal regions can be categorized into several types based on the defining attribute. Understanding these types allows for a deeper insight into the diversity and complexity of formal regions.
Political Regions
Political regions are defined by governmental boundaries such as countries, states, or municipalities. These regions are established through legal or political agreements and are recognized by national or international bodies. Political regions play a crucial role in governance, diplomacy, and international relations.
Physical Regions
Physical regions are characterized by natural features such as mountains, deserts, or climate zones. These regions are defined by consistent physical attributes that influence the environment and human activities. Physical regions are often used in environmental studies, conservation efforts, and disaster management.
Cultural Regions
Cultural regions are defined by shared cultural characteristics such as language, religion, or ethnicity. These regions reflect the cultural diversity and heritage of an area, influencing social interactions, traditions, and identity. Cultural regions are often studied in anthropology, sociology, and cultural geography.
Economic Regions
Economic regions are defined by dominant economic activities such as agriculture, industry, or tourism. These regions are identified based on the prevalent economic practices that drive the local economy. Economic regions are essential in economic planning, development, and trade analysis.
How Are Formal Regions Defined?
Defining formal regions involves a combination of legal, political, and geographical factors. The process of defining these regions varies depending on the attribute being considered, but generally follows a systematic approach.
Legal and Political Agreements
For political regions, formal definitions are often established through legal or political agreements. These agreements are made at various levels of governance, from local to international, and are recognized by relevant authorities. The legal framework provides clarity and legitimacy to the defined boundaries.
Geographical Features
Physical regions are defined based on consistent geographical features such as topography, climate, or vegetation. These features are identified through scientific research and mapping, providing a clear basis for defining the boundaries of a physical region.
Cultural and Economic Indicators
Cultural and economic regions are defined by analyzing cultural practices and economic activities. Data on language distribution, religious practices, or industrial output is collected and analyzed to identify patterns and define the boundaries of these regions. The use of statistical and spatial analysis tools aids in accurately defining cultural and economic regions.
Examples of Formal Regions
Formal regions can be found worldwide, each with unique characteristics and significance. Here are some examples of formal regions that highlight the diversity and complexity of these areas.
Countries and States
One of the most recognizable examples of formal regions are countries and states. These political regions are defined by governmental boundaries and are recognized by international organizations such as the United Nations. Countries and states have distinct legal systems, cultures, and economies, making them key players on the global stage.
Climate Zones
Climate zones are physical regions defined by consistent climatic conditions such as temperature, precipitation, and humidity. Examples of climate zones include tropical, temperate, and polar regions. These zones influence the natural environment, biodiversity, and human activities, making them crucial in environmental studies and planning.
Language Areas
Language areas are cultural regions defined by the prevalence of a specific language or dialect. Regions where a single language dominates, such as the French-speaking areas of Quebec or the Spanish-speaking regions of Latin America, are examples of language areas. These regions reflect cultural identity and influence communication, education, and media.
Economic Hubs
Economic hubs are regions characterized by a concentration of economic activities such as finance, manufacturing, or technology. Examples include Silicon Valley in the United States, known for its tech industry, or the Ruhr Valley in Germany, known for its industrial output. These hubs drive economic growth and innovation, impacting local and global economies.
Importance of Formal Regions
Formal regions play a vital role in understanding and managing the complexities of the world. Their importance spans across various fields such as geography, economics, politics, and sociology.
Facilitating Governance
Formal regions provide a structured framework for governance, enabling efficient administration and resource allocation. Political regions such as countries and states have defined legal systems, allowing for the implementation of laws and policies. This structure is essential in maintaining order and stability within a region.
Enhancing Regional Planning
Regional planning and development benefit from the clear definition of formal regions. These regions provide a basis for analyzing spatial patterns and trends, facilitating informed decision-making. Planners and policymakers use formal regions to identify opportunities and challenges, guiding sustainable development initiatives.
Promoting Cultural Understanding
Cultural regions help in recognizing and appreciating the diversity and richness of human cultures. By understanding cultural regions, individuals and organizations can foster cross-cultural communication, collaboration, and respect. This understanding is crucial in promoting social cohesion and harmony in a globalized world.
Driving Economic Growth
Economic regions play a significant role in driving economic growth and development. By identifying dominant economic activities, regions can focus on strengthening their industries, attracting investment, and creating jobs. Economic regions also facilitate trade and cooperation, contributing to regional and global prosperity.
Formal Regions vs. Functional Regions
While formal regions are defined by uniform characteristics, functional regions are characterized by a central focal point and the interactions that occur within the region. Understanding the differences between formal and functional regions is essential in geography and regional planning.
Defining Attributes
Formal regions are defined by consistent attributes such as political boundaries or physical features. In contrast, functional regions are defined by a central node and the activities that connect the surrounding areas to this node. Examples of functional regions include metropolitan areas, where a city serves as the central hub for economic, social, and cultural activities.
Boundaries
The boundaries of formal regions are clearly defined and recognized, whereas the boundaries of functional regions are often more fluid and dynamic. Functional regions can change over time as the interactions and activities within the region evolve. This makes functional regions more adaptable to changes in social, economic, or technological conditions.
Applications
Formal regions are used in governance, regional planning, and cultural studies, while functional regions are often used in transportation planning, economic development, and urban studies. Understanding both types of regions allows for a comprehensive analysis of spatial patterns and interactions, leading to more effective planning and decision-making.
Applications of Formal Regions in Society
Formal regions have numerous applications in various fields, contributing to the efficient management and understanding of societal dynamics.
Geographical Research
Geographers use formal regions to study spatial patterns, relationships, and processes. By categorizing areas into formal regions, researchers can analyze data systematically, leading to more accurate and meaningful insights. This research is essential in understanding human-environment interactions, cultural diffusion, and economic trends.
Education and Curriculum Development
Formal regions are used in education to teach students about geography, history, and culture. By understanding the concept of formal regions, students can better grasp the complexities of the world around them, fostering critical thinking and global awareness. Curriculum development often incorporates formal regions to provide a structured framework for learning.
Policy and Governance
Policymakers use formal regions to design and implement policies that address regional needs and challenges. By understanding the unique characteristics of a formal region, governments can tailor policies to promote economic growth, social welfare, and environmental sustainability. This targeted approach enhances the effectiveness of governance and resource allocation.
Business and Economic Planning
Businesses and economic planners use formal regions to identify market opportunities, assess risks, and develop strategies. By analyzing formal regions, companies can gain insights into consumer behavior, industry trends, and competitive dynamics. This information is crucial in making informed business decisions and driving economic growth.
Geopolitical Aspects of Formal Regions
Formal regions have significant geopolitical implications, influencing international relations, diplomacy, and conflict resolution.
International Relations
Formal regions such as countries and states play a critical role in international relations. These regions are recognized as sovereign entities, engaging in diplomacy, trade, and cooperation with other regions. Understanding the geopolitical dynamics of formal regions is essential in promoting peace, stability, and collaboration on a global scale.
Border Disputes
Defined boundaries of formal regions can sometimes lead to border disputes and conflicts. These disputes arise when neighboring regions have competing claims over a particular area, often due to historical, cultural, or economic reasons. Resolving border disputes requires diplomatic negotiations, legal agreements, and sometimes international intervention.
Global Governance
Global governance relies on the recognition and cooperation of formal regions. International organizations such as the United Nations and the World Trade Organization work with formal regions to address global challenges such as climate change, poverty, and security. The cooperation of formal regions is crucial in achieving global goals and ensuring a sustainable future.
Advantages of Using Formal Regions
Formal regions offer several advantages that make them valuable tools in geography, planning, and governance.
Clarity and Precision
The clearly defined boundaries and uniform characteristics of formal regions provide clarity and precision in analysis and decision-making. This structured framework allows for systematic data collection, comparison, and interpretation, leading to more accurate and reliable insights.
Efficiency in Administration
Formal regions facilitate efficient administration and governance by providing a clear basis for resource allocation, policy implementation, and service delivery. The defined boundaries allow for the establishment of legal and administrative systems, ensuring order and stability within the region.
Facilitating Communication
Formal regions enhance communication and understanding by providing a common reference point for discussing geographical, cultural, and economic issues. This shared framework allows for effective collaboration and cooperation among individuals, organizations, and governments.
Supporting Research and Analysis
The use of formal regions supports research and analysis by providing a structured framework for studying spatial patterns and relationships. Researchers can focus on specific attributes within a formal region, leading to more in-depth and meaningful insights. This research is crucial in advancing knowledge and informing decision-making.
Challenges in Defining Formal Regions
While formal regions offer numerous benefits, there are also challenges associated with defining and managing these regions.
Dynamic Nature of Regions
The dynamic nature of regions can pose challenges in defining formal regions. Changes in political, economic, or environmental conditions can alter the characteristics of a region, making it difficult to maintain consistent boundaries. This requires ongoing monitoring and adaptation to ensure the relevance and accuracy of formal regions.
Conflicting Interests
Conflicting interests among stakeholders can complicate the process of defining formal regions. Different groups may have competing claims or priorities, leading to disagreements over the boundaries and attributes of a region. Resolving these conflicts requires negotiation, compromise, and sometimes legal intervention.
Complexity of Attributes
The complexity of attributes within a region can make it challenging to define formal regions accurately. Multiple factors such as culture, economy, and environment may interact in complex ways, making it difficult to identify clear and consistent patterns. This requires careful analysis and consideration of multiple perspectives.
Data Availability and Accuracy
The availability and accuracy of data can impact the definition of formal regions. Inaccurate or incomplete data can lead to misinterpretations and incorrect conclusions, affecting the reliability and validity of formal regions. Ensuring access to high-quality data is essential in defining and managing formal regions effectively.
How Do Formal Regions Impact Policy?
Formal regions have a significant impact on policy formulation and implementation, influencing various aspects of governance and development.
Resource Allocation
Formal regions provide a basis for resource allocation, ensuring that resources are distributed equitably and efficiently. Policymakers use formal regions to identify areas of need and prioritize investments in infrastructure, social services, and economic development.
Policy Targeting
By understanding the unique characteristics of formal regions, policymakers can design targeted policies that address specific regional challenges and opportunities. This targeted approach enhances the effectiveness and efficiency of policies, leading to better outcomes for individuals and communities.
Monitoring and Evaluation
Formal regions provide a framework for monitoring and evaluating policy outcomes. By analyzing data within and between formal regions, policymakers can assess the impact of policies, identify areas for improvement, and make informed decisions.
Collaboration and Coordination
Formal regions facilitate collaboration and coordination among governments, organizations, and stakeholders. By providing a common reference point, formal regions enable effective communication, cooperation, and partnership in addressing regional and global challenges.
Can Formal Regions Change Over Time?
While formal regions are characterized by stability, they are not immune to change. Various factors can lead to changes in the boundaries or characteristics of formal regions over time.
Political and Legal Changes
Political and legal changes can alter the boundaries of formal regions. Changes in government, legislation, or international agreements can lead to the redefinition of political regions, impacting governance and administration.
Economic and Social Dynamics
Economic and social dynamics can influence the characteristics of formal regions. Shifts in population, industry, or cultural practices can alter the uniformity of a region, leading to changes in its classification.
Environmental Factors
Environmental factors such as climate change, natural disasters, or resource depletion can impact the characteristics of physical regions. These changes can alter the natural environment, leading to shifts in the boundaries or attributes of a region.
Technological Advancements
Technological advancements can impact the definition and management of formal regions. Improved data collection, analysis, and communication tools can enhance the accuracy and relevance of formal regions, leading to more informed decisions and actions.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What distinguishes a formal region from other types of regions?
A formal region is distinguished by its uniform characteristics and clearly defined boundaries. Unlike functional regions, which are based on interactions around a central point, formal regions maintain consistent attributes throughout the area, such as political boundaries or cultural practices.
2. Can formal regions overlap with other types of regions?
Yes, formal regions can overlap with other types of regions, such as functional or perceptual regions. For example, a political region may also serve as a functional region if it includes a metropolitan area with economic activities centered around a city.
3. How are formal regions used in education?
In education, formal regions are used to teach students about geography, history, and cultural diversity. They provide a structured framework for understanding spatial patterns and relationships, fostering critical thinking and global awareness among students.
4. What role do formal regions play in economic planning?
Formal regions are essential in economic planning by identifying dominant economic activities and market opportunities. Businesses and economic planners use formal regions to assess risks, develop strategies, and drive economic growth and development.
5. How do formal regions contribute to international relations?
Formal regions, such as countries and states, play a critical role in international relations by engaging in diplomacy, trade, and cooperation with other regions. They influence geopolitical dynamics, promoting peace, stability, and collaboration on a global scale.
6. What challenges are associated with defining formal regions?
Challenges in defining formal regions include the dynamic nature of regions, conflicting interests, and the complexity of attributes. Ensuring accurate and reliable data is also crucial in maintaining the relevance and accuracy of formal regions.
Conclusion
Formal regions are a fundamental concept in geography and sociology, characterized by uniform attributes and clearly defined boundaries. They play a crucial role in facilitating governance, regional planning, cultural understanding, and economic growth. By providing a structured framework, formal regions enhance communication, research, and analysis, contributing to a more informed and connected world. While challenges exist in defining and managing formal regions, their importance and applications across various fields make them indispensable tools in understanding and addressing the complexities of the world. As we continue to explore and adapt to changes in our environment, the study and application of formal regions will remain a vital aspect of our collective efforts to build a sustainable and prosperous future.